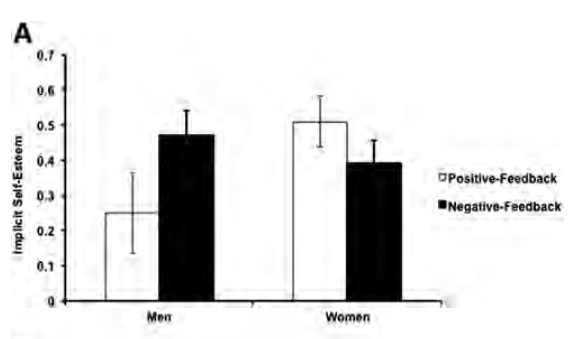
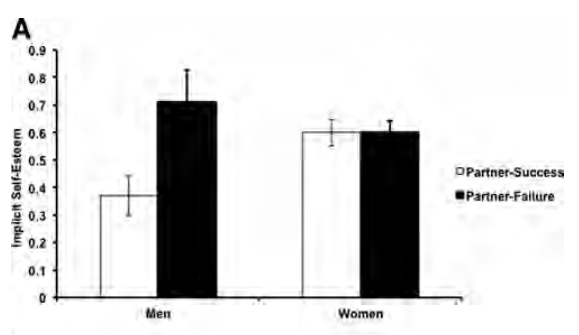
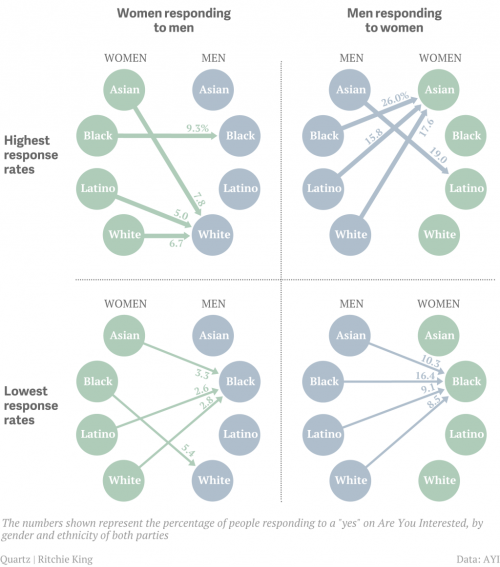
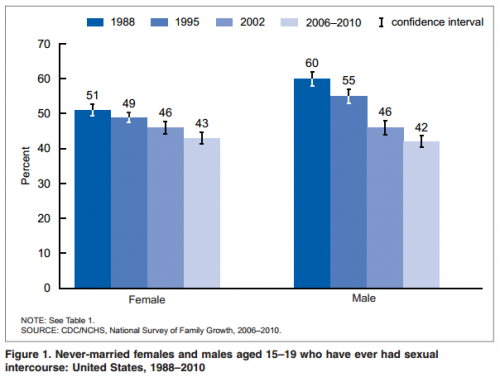
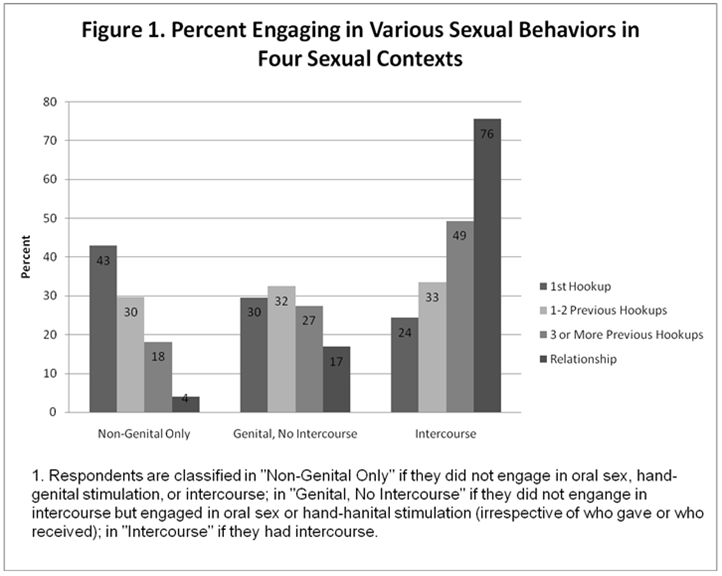
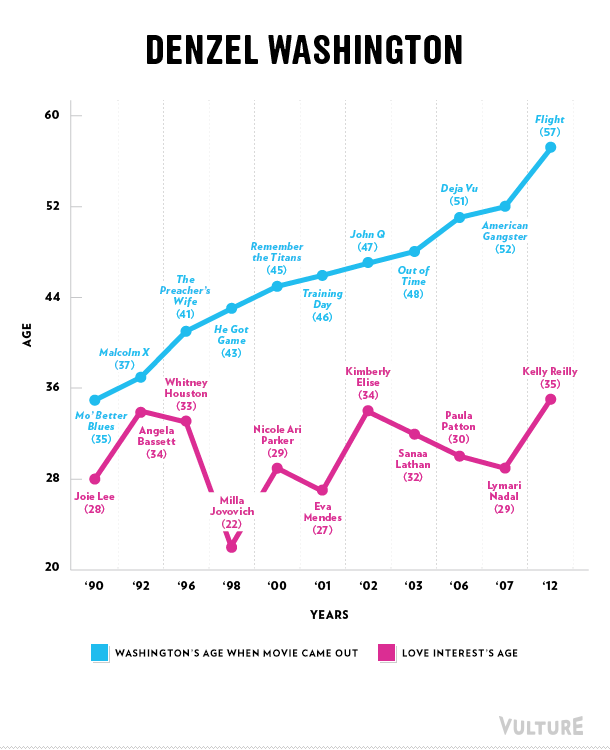
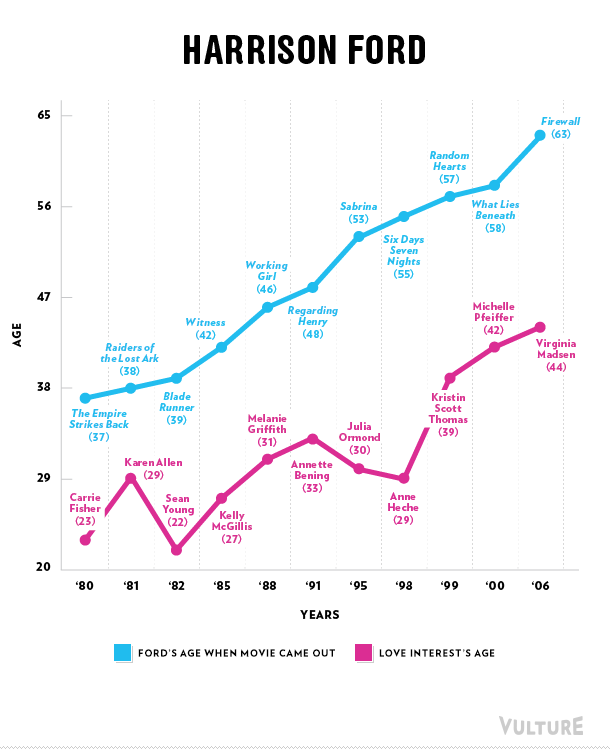
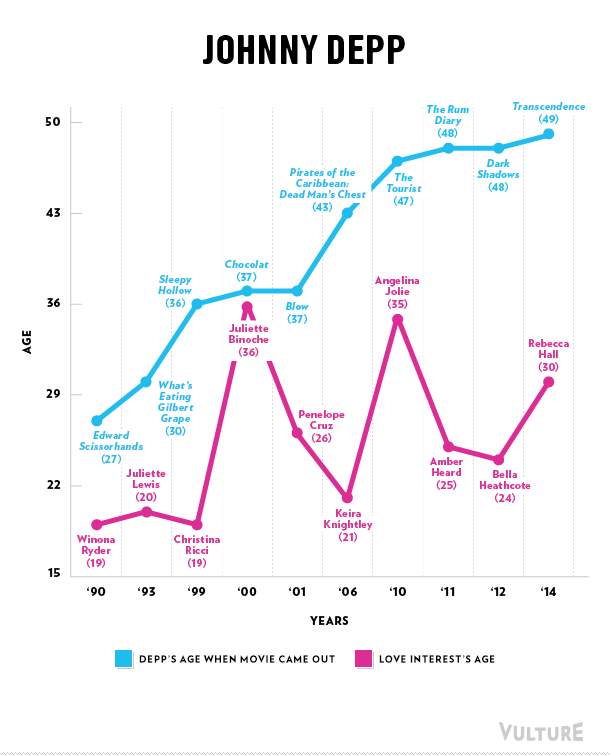
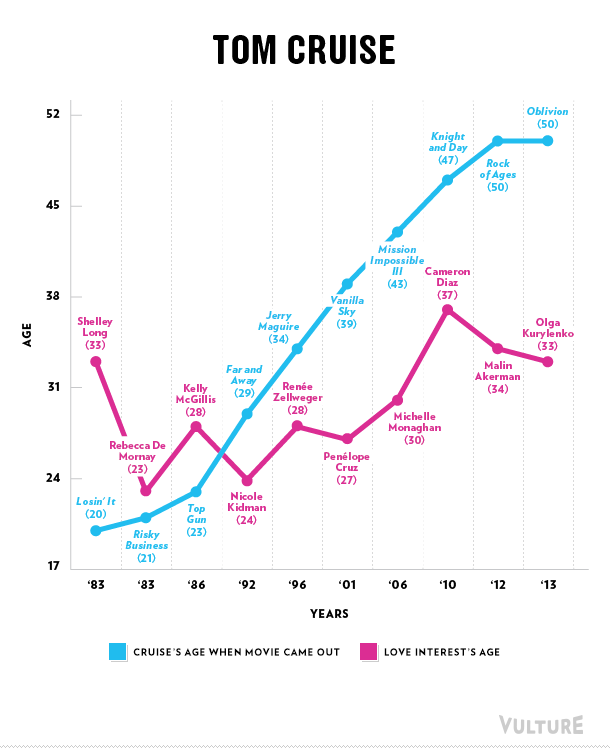
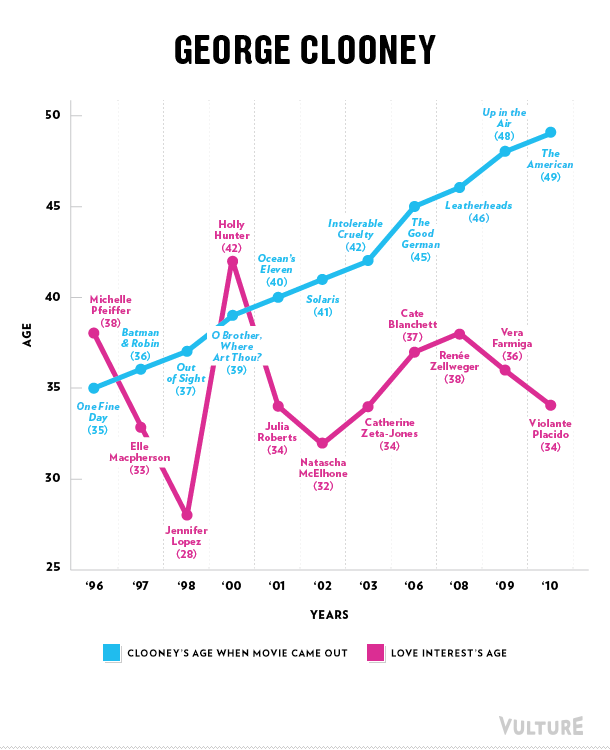
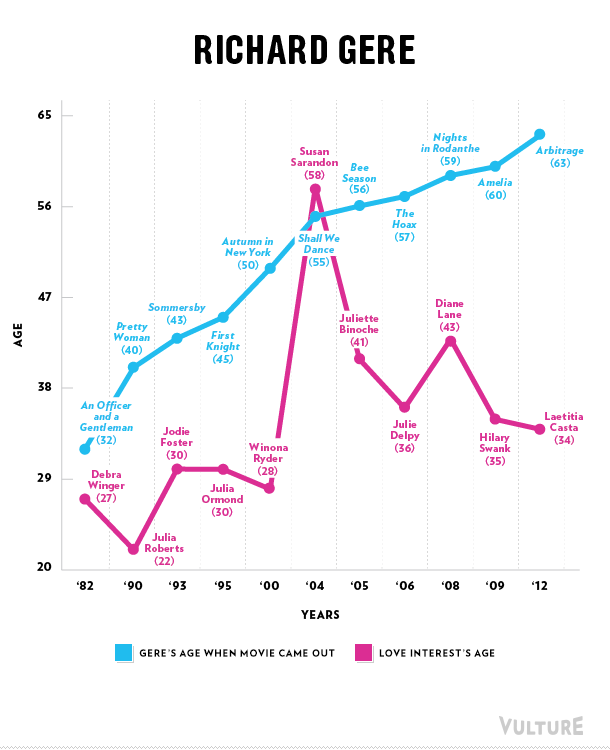
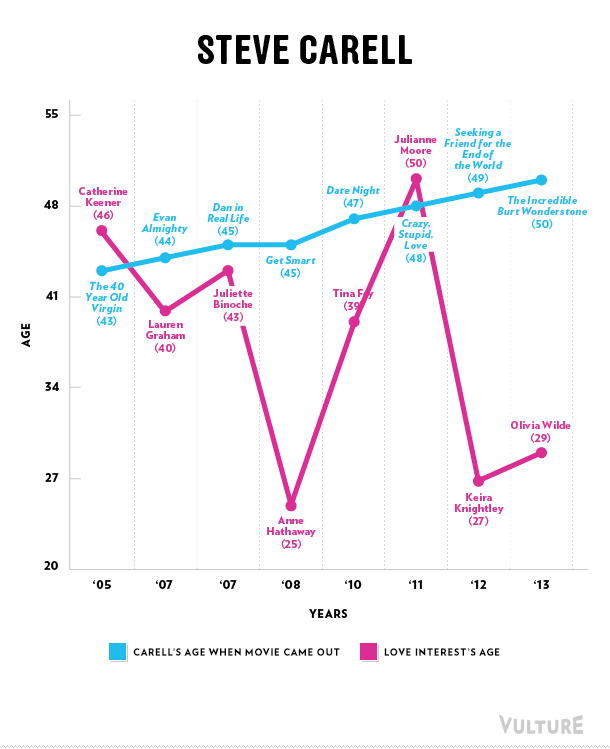
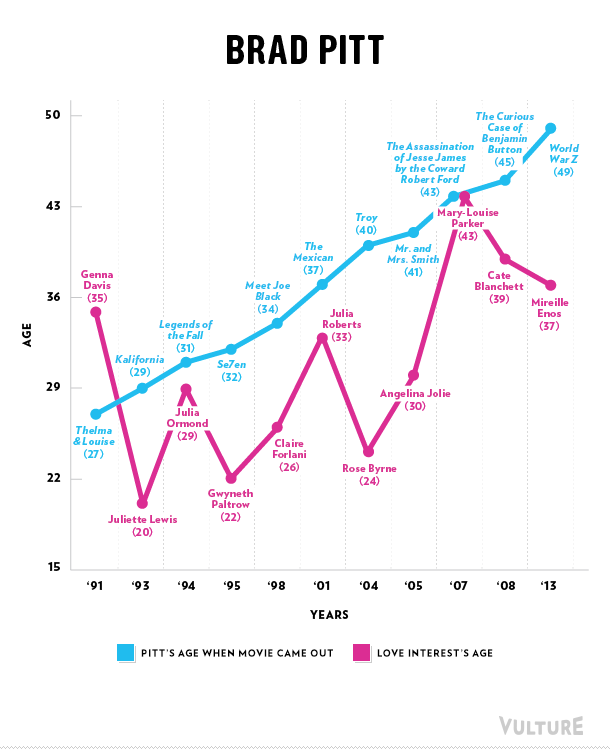
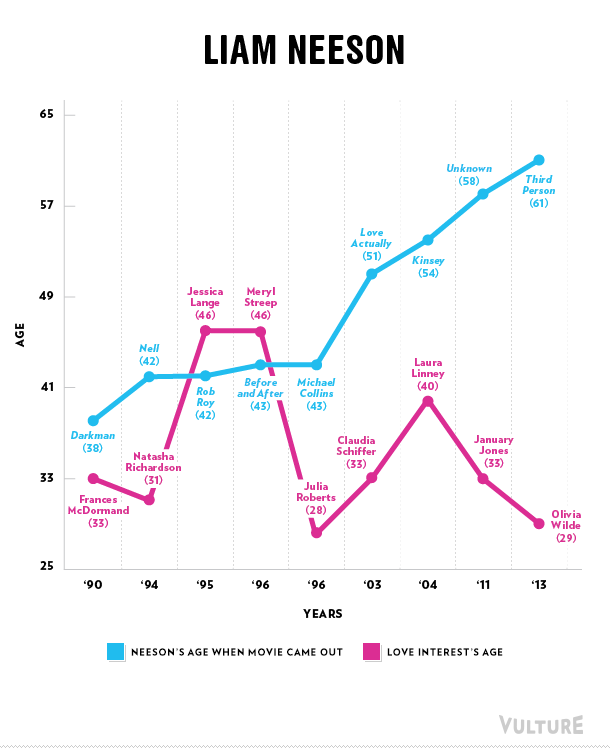
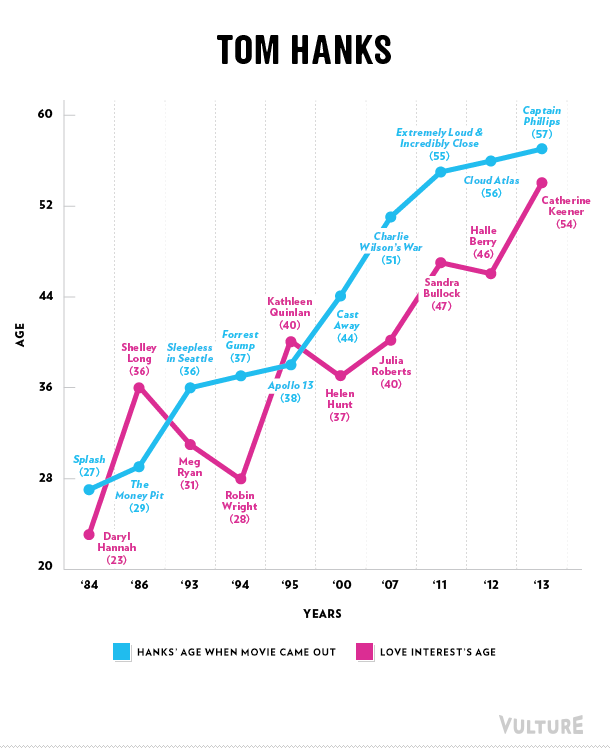
Erika T. sent in this 30 second commercial for Frito Lay chips and dip. Masquerading as simply “cute,” instead the cartoon sends strong normative messages.
It straightforwardly suggests that single people are inherently sad. Being coupled up is presented as the norm and single people’s pathetic-ness is visible for all to see, even if they try to hide it. It’s also implicitly heteronormative (different colors = the perfect blend) and overtly promotes monogamy between two and only two people.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.