OKCupid, an online matchmaking site, offers data on gender and perceived attractiveness that I might use in my spring deviance course (via boing). The figures might help me make a Durkheimian society of (hot) saints point about the relative nature of beauty and a Goffman point on stigma affecting social interaction, while providing another illustration of the taken-for-grantedness of heteronormativity.
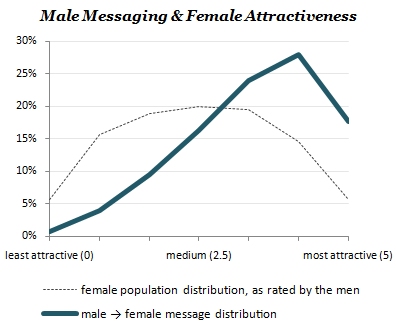
In any case, the first figure shows that male OKCupid ratings of female OKCupid users follows something like a normal distribution, with mean=2.5 on a 0-to-5 scale from “least attractive” to “most attractive.” Also, women rated as more attractive tend to get more messages. At first, I thought I saw evidence of positive deviance here, since women rated as most attractive get fewer messages than those rated somewhat below them — the 4.5s garner more attention than the 5.0s. But, as I’ll show below with the next chart, that would probably be an incorrect interpretation — confounding the “persons” in the dashed lines with the “messages” in the solid lines.
The next figure shows that female OKCupid users tend to rate most male OKCupid users as well below “medium” in attractiveness. According to OKCupid, “women rate an incredible 80% of guys as worse-looking than medium. Very harsh. On the other hand, when it comes to actual messaging, women shift their expectations only just slightly ahead of the curve, which is a healthier pattern than guys’ pursuing the all-but-unattainable.”
Hmm. The latter point isn’t wrong, I guess, but it shouldn’t obscure the bigger point that more attractive men still get more messages than less attractive men. Again, note that persons (OKCupid members) are the units of analysis for the dashed lines and messages (messages sent by OKCupid members) are the units for the solid lines. On first scan, I read the graph as suggesting that the top “attractiveness quintile” was getting fewer messages than the bottom attractiveness quintile — that uglier men were actually doing better than more attractive men — but that’s not the case at all. Instead, it just means that in the land of the hideous, the somewhat-less-than-loathsome man is king.
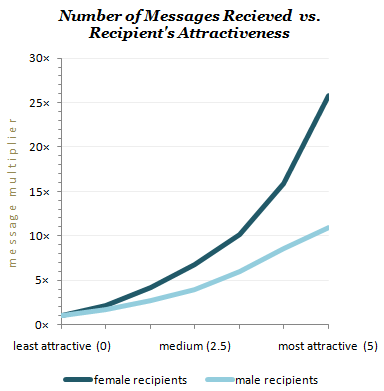
If almost everybody is rated as unattractive, most of the messages will go to those rated as unattractive. Nevertheless, the rate of messages-per-person still rises monotonically with attractiveness. As the “message multiplier” chart below shows, the most attractive men get about 11 times the messages of the least attractive men — and the most attractive women get about 25 times the messages of the least attractive women.
—————————
Chris Uggen is Distinguished McKnight Professor and Chair of Sociology at the University of Minnesota. His writing appears in American Sociological Review, American Journal of Sociology, Criminology, and Law & Society Review and in media such as the New York Times, The Economist, and NPR. With Jeff Manza, he wrote Locked Out: Felon Disenfranchisement and American Democracy.
If you would like to write a post for Sociological Images, please see our Guidelines for Guest Bloggers.