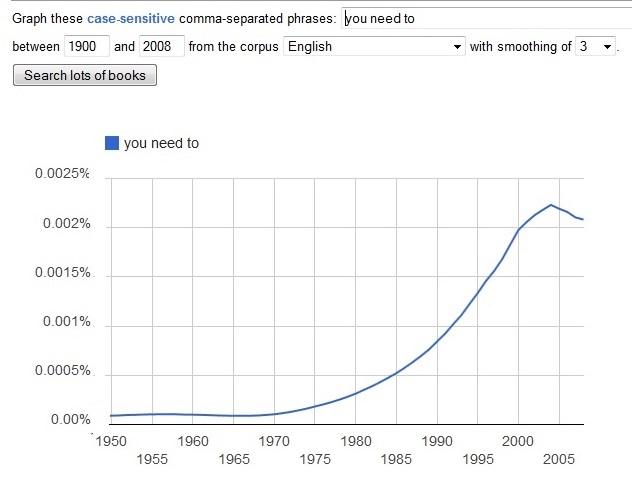
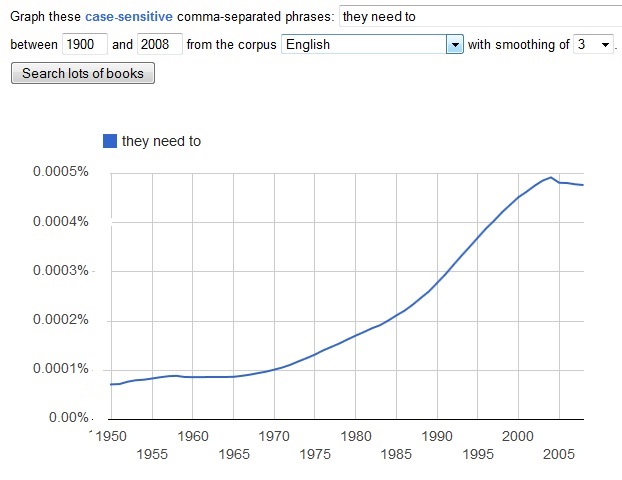
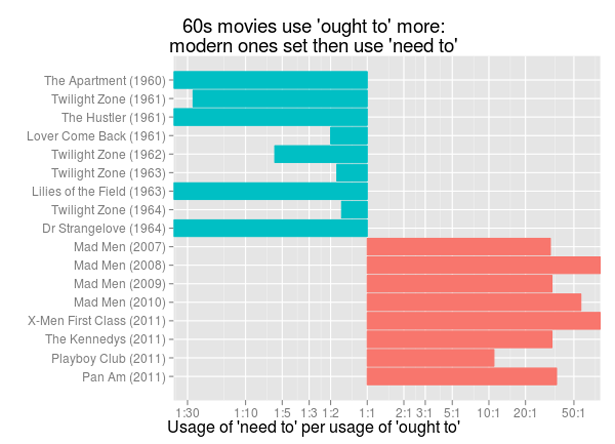
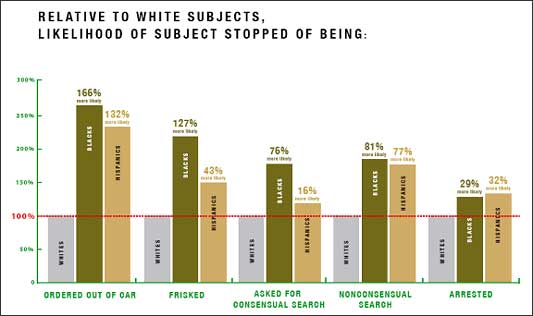
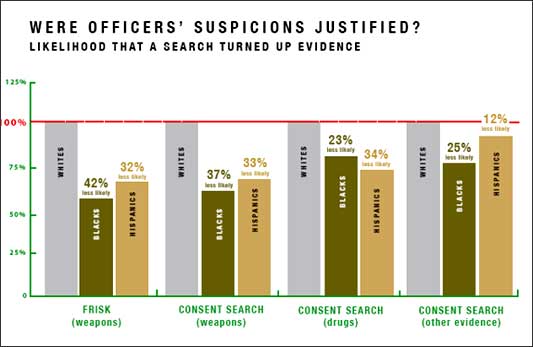
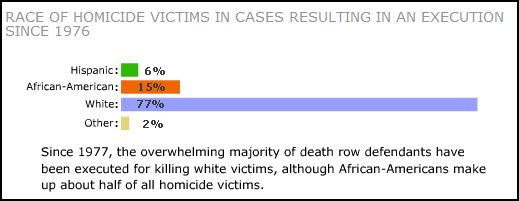
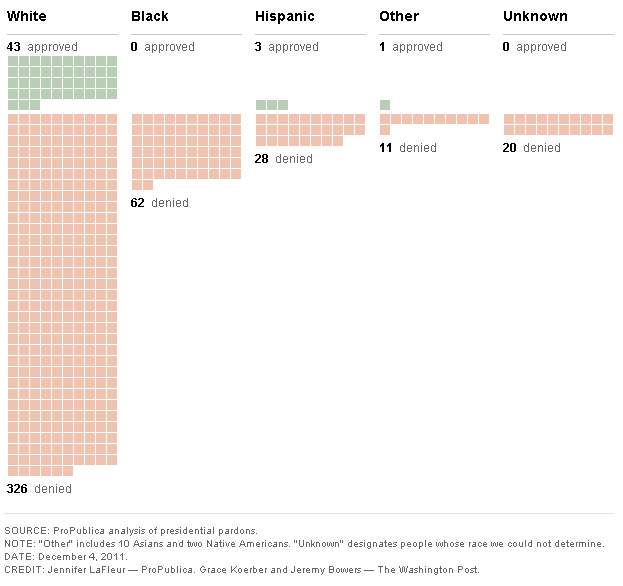
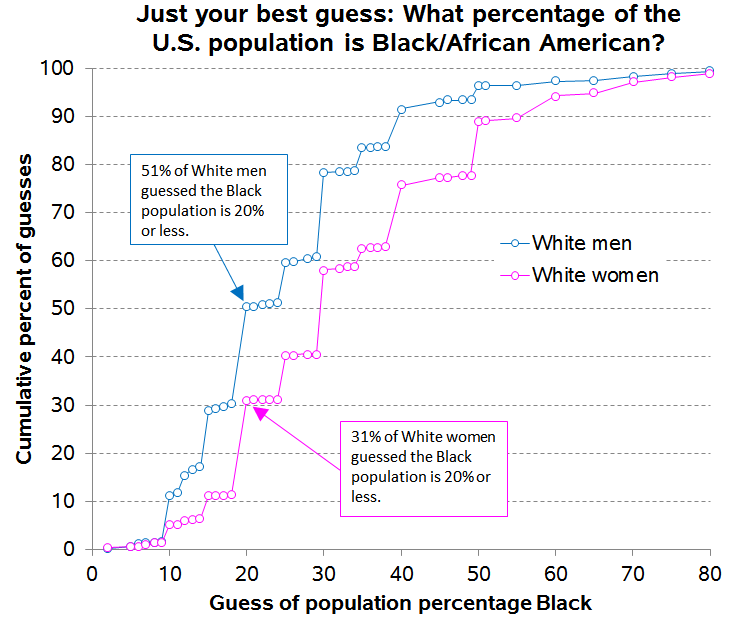
Black Americans are 3.7 times more likely than Whites to be arrested for marijuana possession, despite having equivalent use rates. It’s a war on what again?
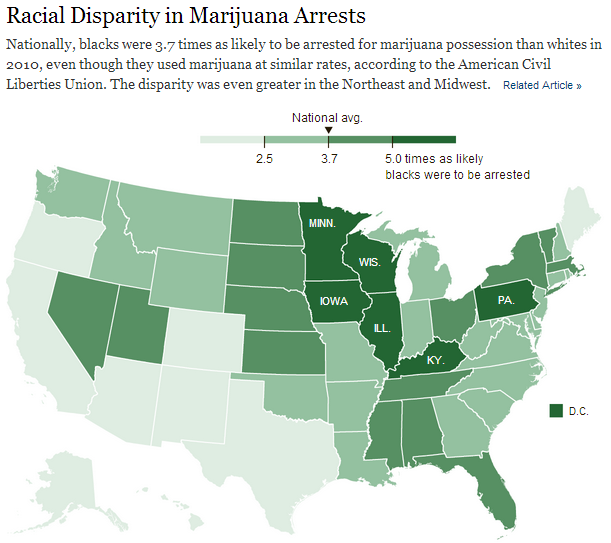 New York Times, via Gin and Tacos, one of my favorite blogs.
New York Times, via Gin and Tacos, one of my favorite blogs.
Cross-posted at Racialicious.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.