Flashback Friday.
The word commodification refers to the process by which something that is not bought and sold becomes something that is. As capitalism has progressed, more and more parts of our lives have become commodified. Restaurants are the commodification of preparing and cleaning up meals; day care and nannying is the commodification of child raising; nursing homes is the commodification of caring for elders.
We sometimes post instances of commodification that tickle us. Previously I posted about a company that will now put together and deliver a care package to your child at camp. A parent just goes to the site, chooses the items they want included, and charge their credit card. As I wrote in that post: “The ‘care’ in ‘care package’ has been, well, outsourced.”
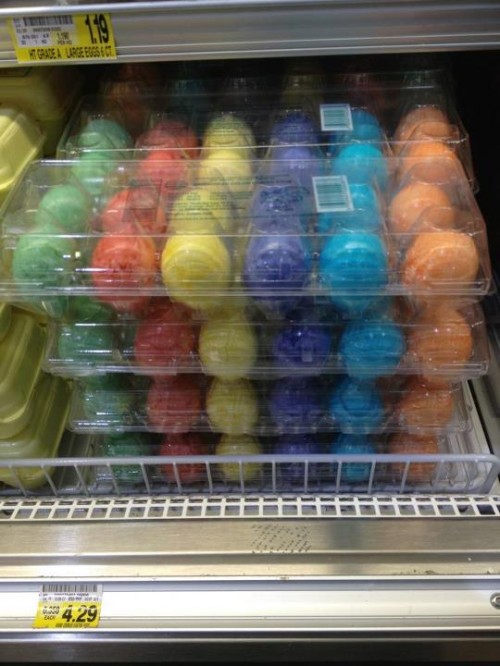
I was equally tickled by a photograph, taken by sociologist Tristan Bridges, of pre-dyed Easter eggs:
This is a delicious example of commodification. If you don’t have the time or inclination to dye eggs as part of your Easter celebration, the market will do it for you. No matter that this is one of those things (e.g., a supposedly enjoyable holiday activity that promotes family togetherness) that is supposed to be immune to capitalist imperatives.
While we might raise our eyebrows at this example, newly commodified goods and services often elicit this reaction. We usually get used to the idea and, later, have a hard time imagining life any other way.
For more on commodification, peruse our tag by that name. This post originally appeared in 2012.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.