Flashback Friday.
Sociologists are lucky to have amongst them a colleague who is doing excellent work on the modeling industry and, in doing so, offering us all a rare sophisticated glimpse into its economic and cultural logics. We’ve featured Ashley Mears‘ work twice in posts discussing the commodification of models’ bodies and the different logics of high end and commercial fashion.
In a post at Jezebel, Mears exposes the Model Search. Purportedly an opportunity for model hopefuls to be discovered, Mears argues that it functions primarily as a networking opportunity for agents, who booze and schmooze it up with each other, while being alternatively bored and disgusted by the girls and women who pay to be there.
“Over a few days,” Mears explains:
…thousands arrived to impress representatives from over 100 international modeling and talent agencies. In the modeling showcase alone, over 500 people ages 13-25 strutted down an elevated runway constructed in the hotel’s ballroom, alongside which rows of agents sat and watched.
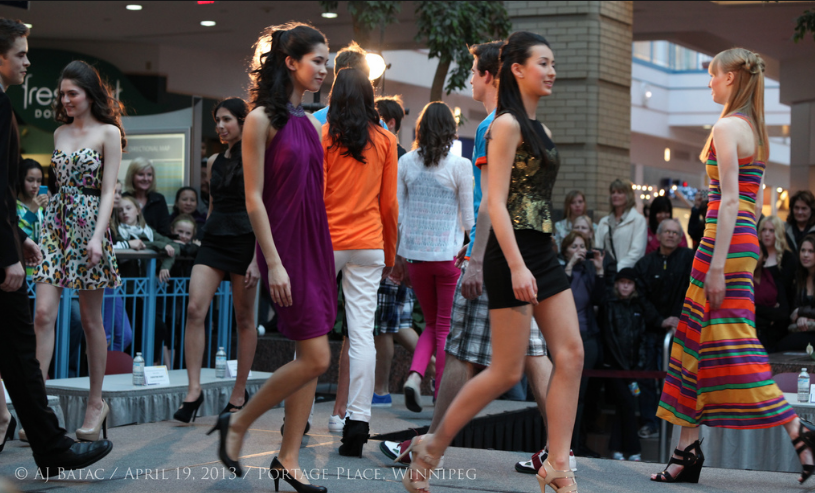
But the agents are not particularly interested in scouting. In shadowing them during the event, Mears finds that they “actually find it all rather boring and tasteless.” Pathetic, too.
Mears explains:
The saddest thing at a model search contest is not the sight of girls performing womanhood defined as display object. Nor is it their exceedingly slim chances to ever be the real deal. What’s really sad is the state of the agents: they sit with arms folded, yawning regularly, checking their BlackBerrys. After a solid two hours, Allie has seen over 300 contestants. She’s recorded just eight numbers for callbacks.
…
Meanwhile, agents ridicule the wannabe runway, from the “hooker heels” to the outfit choices. About their physiques, [one agent recounts,] “I’ve never seen so many out of shape bodies.”
While model hopefuls are trading sometimes thousands of dollars for a 30-second walk down the runway, the agents are biding their time until they can head to the hotel bar to “…gossip, network, and commence the delicate work of negotiating the global trade in models…” One agent explains:
To be honest it’s just a networking event. The girls, most of them don’t even have the right measurements. For most of them, today is going to be a wake-up call.
Indeed, networking is the real point of the event. The girls and women who come with dreams of being a model are largely, and unwittingly, emptying their pockets to subsidize the schmooze.
To add insult to injury, what many of the aspiring models don’t know is that, for “…$5,000 cheaper, any hopeful can walk into an agency’s ‘Open Call’ for an evaluation.”
I encourage you to read Mears’ much longer exposé at Jezebel.
Originally posted in 2010.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.