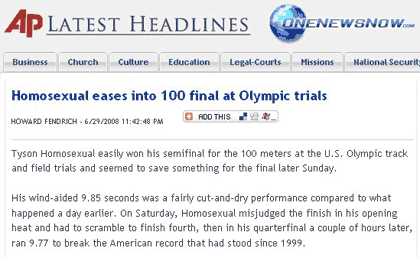
Since we’ve been on the topic of language (see yesterday’s George Carlin post), I thought I’d add something sent in by Z of It’s the Thought that Counts, who first read about it here. The conservative Christian organization American Family Association has a website called OneNewsNow where they post various news stories. Apparently the website has a filter to automatically replace the word “gay” in any news stories with the word “homosexual.” This became apparent when a news story about an athlete named Tyson Gay was posted with his last name changed to Homosexual in both the title and the text. Here is a screenshot (found here) of the original post from OneNewsNow:
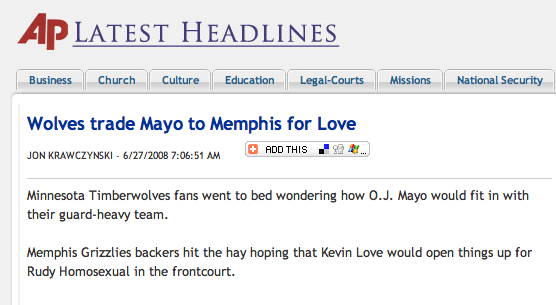
The story has since been corrected. But as FriendlyAtheist points out, they have not corrected “Rudy Homosexual” in this sports story (thanks to Jon for the screenshot):
What is the symbolic power of saying “homosexual” instead of “gay”? What is the cultural difference between those two words? Is it an attempt to keep the focus on sexual activity? For some reason “homosexual” sounds more derogatory to me, but I’m not sure why–probably just because it’s used more by those opposed to gay rights, so I’ve come to associate it with an anti-gay ideology.
This might be interesting for a discussion of discourse and language in political movements generally, as well as conflicts around gay and lesbian issues specifically. Groups always try to frame issues to make their position sound more appealing, and a major way of doing this is through language. Think of debates about abortion–the differences between “pro-abortion” and “pro-choice” as well as “pro-life,” “anti-abortion,” and “anti-choice,” are symbolically meaningful, and different groups choose to use some of these terms rather than others in an effort to make themselves seem appealing and rational and the other side unappealing and radical. I suspect something similar is going on with “homosexual” vs. “gay.”
Thanks, Z!
UPDATE: In the comments to this section, Sanguinity made some great points about the differences between “gay” and “homosexual”:
“Homosexual” is the clinical term, and was used to pathologize gays and lesbians — it’s meant to invoke all that psychiatric-illness stuff. Also, the term focuses on sexual behavior, completely sidestepping romance, relationships, communities, cultures, and other sympathy-generating aspects of pershonhood. Additionally, by focusing on behavior above identity, it allows one to write entire articles with the implicit assumption that being gay is a choice: i.e., one isn’t gay, one chooses to engage in homosexual activities. That last item is especially important — while “gay” and “homosexual” may look like synonyms, they aren’t quite. “Gay” is a noun; “homosexual” is an adjective.
Thanks for the elaboration, Sanguinity!