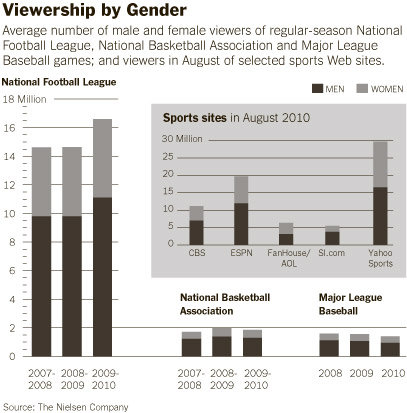
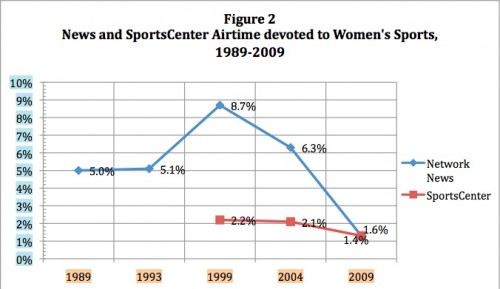
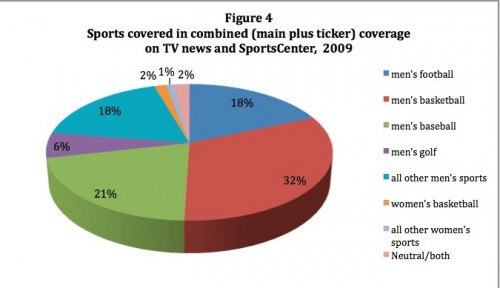
In Dude, You’re a Fag: Masculinity and Sexuality in High School C.J. Pascoe explains that taunts of “fag” aren’t really about homosexuality at all, but instead about policing the boundaries of masculinity:
For a pretty scary example, see our recent post in which Yankees fans ganged up on two teenage Red Sox fans using homophobic language.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.