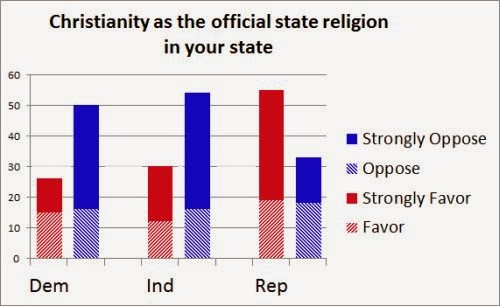
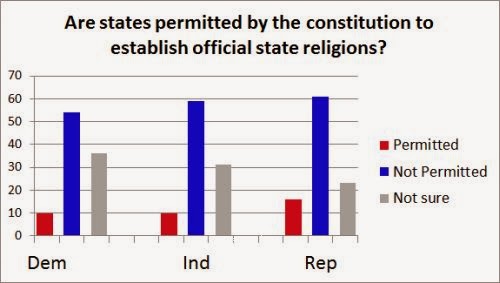
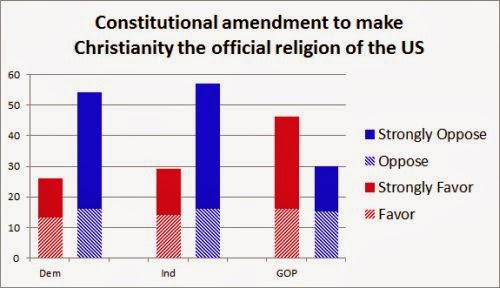
“Carrie is largely about how women find their own channels of power, but also what men fear about women and women’s sexuality. Writing the book in 1973 and only three years out of college, I was fully aware of what Women’s Liberation implied for me and others of my sex. Carrie is woman feeling her powers for the first time and, like Samson, pulling down the temple on everyone in sight at the end of the book.”
– Stephen King, Danse Macabre
 Most feminist criticism of Stephen King’s Carrie has focused on the male fear of powerful women that the author said inspired the film, with the anti-Carrie camp finding her death at the end to signify the defeat of the “monstrous feminine” and therefore a triumph of sexism. But Stephen King’s honesty about what inspired his 1973 book notwithstanding, Carrie is as much an articulation of a feminist nightmare as it is of a patriarchal one, with neither party coming out on top.
Most feminist criticism of Stephen King’s Carrie has focused on the male fear of powerful women that the author said inspired the film, with the anti-Carrie camp finding her death at the end to signify the defeat of the “monstrous feminine” and therefore a triumph of sexism. But Stephen King’s honesty about what inspired his 1973 book notwithstanding, Carrie is as much an articulation of a feminist nightmare as it is of a patriarchal one, with neither party coming out on top.
The rise of Second Wave feminism in the ’70s posed serious threats to the patriarchal order — as well it should have. But even for those who think change is not only necessary but good, change can be pretty scary. This, with a hat tip to the universality of being bullied, is one of the reasons Carrie scares everyone.
While men in the ’70s felt threatened by the unprecedented numbers of women standing up for themselves and attempting such radical social changes as being recognized as equal under the law, women themselves must have felt some anxiety that the obstacles to fully realizing themselves might be too big to conquer. The story therefore resonates with men in terms of the fear of (metaphorical) castration prompted by changing gender roles, and with women in terms of the fear that no matter how powerful we become, social forces are still so aligned against us that fighting back might destroy not just the patriarchy but ourselves.
Feminism was not the only thing on the rise in the ’70s: so was Christian fundamentalism. In 1976, the year that the original movie debuted, 34 percent of Protestant Americans told the Gallup Poll that they had had born-again experiences, leading George Gallup himself to declare 1976 the Year of the Evangelical. In fact evangelism, then as now — when 41 percent of Americans report being born again — was one of feminism’s more formidable foes, one of those very social forces that would rather destroy women than see them powerful.
The triggering event of Carrie–the infamous shower scene–is a product of the meeting of these two forces. Because of a fundamentalist Christian worldview in which menstruation is not simply a biological process but rather evidence of Eve’s original sin being visited upon her daughters,Carrie‘s mother does nothing to prepare her for getting her period. When she starts bleeding at school, Carrie naturally panics, and as a result faces the scorn of her peers — who laugh at her for not knowing what’s happening — and the scorn of her mother, who believes that “After the blood the boys come. Like sniffing dogs, grinning and slobbering, trying to find out where that smell is.”
I can’t believe I’m about to go all Freudian here, but for the male viewer the shock of seeing unexpected blood between one’s legs clearly represents a fear of castration–a literal embodiment of King’s anxieties about feminism. From the woman’s perspective, the menstrual blood obviously signifies Carrie’s maturation — coming into her power — which has been marred by fundamentalism.
 Without making the new remake of the movie any more violent, director Kimberly Peirce emphasizes the imagery of this inciting event by adding waaaaay more blood to her Carrie. When Carrie gets her period in the shower, there’s more blood than in Brian De Palma’s film. When Carrie gets some of that blood on her gym teacher, which happens in both films, Peirce adds more of it, and the camera lingers on it longer and returns to it more often.
Without making the new remake of the movie any more violent, director Kimberly Peirce emphasizes the imagery of this inciting event by adding waaaaay more blood to her Carrie. When Carrie gets her period in the shower, there’s more blood than in Brian De Palma’s film. When Carrie gets some of that blood on her gym teacher, which happens in both films, Peirce adds more of it, and the camera lingers on it longer and returns to it more often.
When Carrie’s mother locks her in the closet, Peirce has the crucifix bleed–something that doesn’t happen in the first movie. The blood of the crucifix connects Carrie’s first period to the suffering of Christ, deepening the relationship between debased femininity and religion.
Then, when Carrie gets pig blood dumped on her head at the prom, there’s not just more of it in the second film: Pierce shows the blood landing on her in slow motion three times. This final deluge of blood echoes a scene that Pierce added to the beginning of the movie, in which Carrie’s mother endures the bloody birth of her daughter. Carrie, then, is essentially born again at the prom, and the devastation she wreaks can be read as a result not of her feminine power but of the corruption of it by religion.
Peirce told Women and Hollywood that her goal was to make Carrie as sympathetic as possible. She removes the male gaze aspect of the original shower scene, in which many of the girls are naked and the long, slow shots of Carrie’s body are rather pornified. She makes sympathy for Carrie’s primary nemesis at school pretty much impossible by changing her from an angry girl in an abusive relationship to a sociopath without a conscience. In the new film, Carrie even has the strength to challenge her mother’s theology. Her prom date is more likeable and Peirce uses his death–something De Palma doesn’t reveal until the end — as further motivation for Carrie’s rampage.
None of this changes the fact that Carrie dies at the end, but it does foreground the idea that the message doesn’t have to be that powerful women are indeed dangerous. It can be that fundamentalism is dangerous to women.
If you’re a feminist, I say go see Carrie. Watching her be destroyed — but not without taking out a lot of the patriarchy with her — and then, as a viewer, emerging again into the sunlight unscathed, allows feminists to process some of our deepest fears about what we’re up against. Then we can get on with making the world a place where religious beliefs don’t corrupt our sexuality, where women don’t have to destroy themselves to be powerful and where women’s equality doesn’t trigger men’s fear of their own doom.
Holly L. Derr, MFA, is a feminist media critic who writes about theater, film, television, video games and comics. Follow her @hld6oddblend and on her tumblr, Feminist Fandom. For more of the Feminist Guide to Horror Movies, check out Parts One, Two, Three, and Four at the Ms. Magazine blog.
Cross-posted at Ms. Magazine. Photos courtesy of Jade and thefanboyseo1 via Creative Commons 2.0