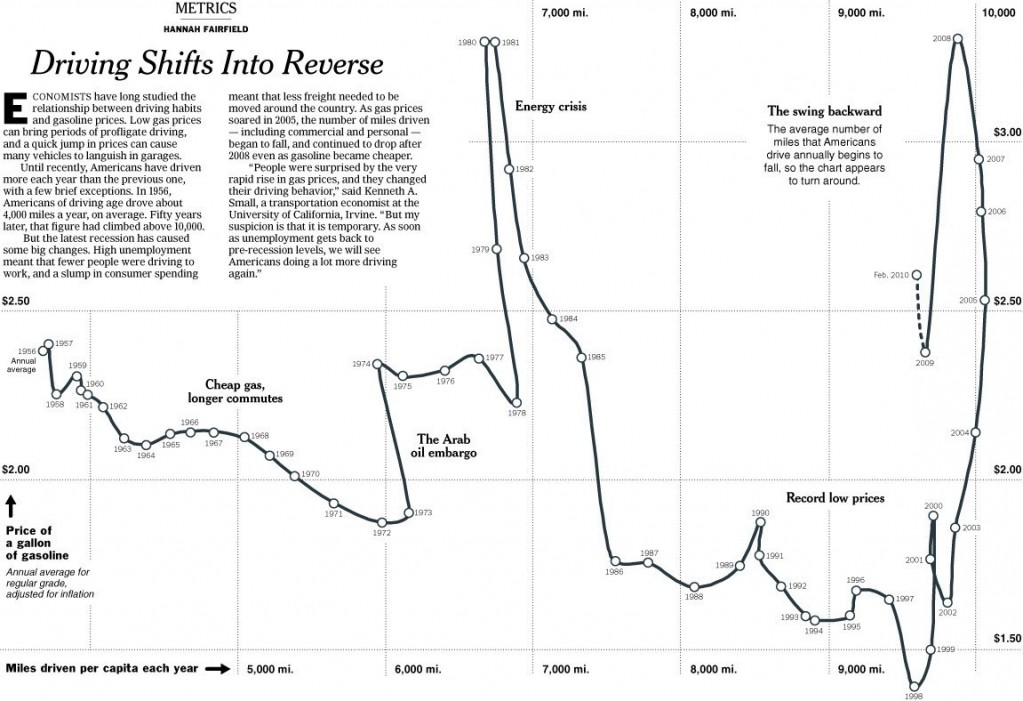
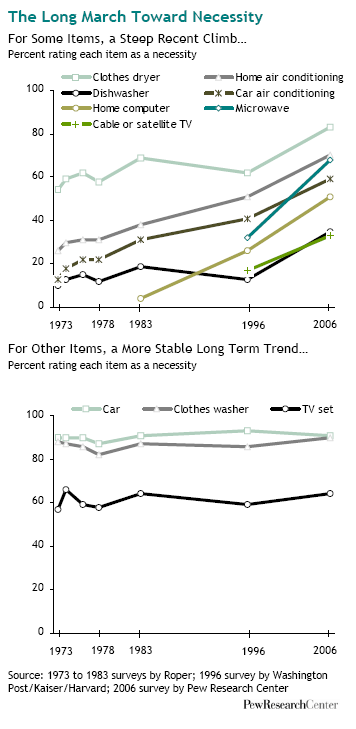
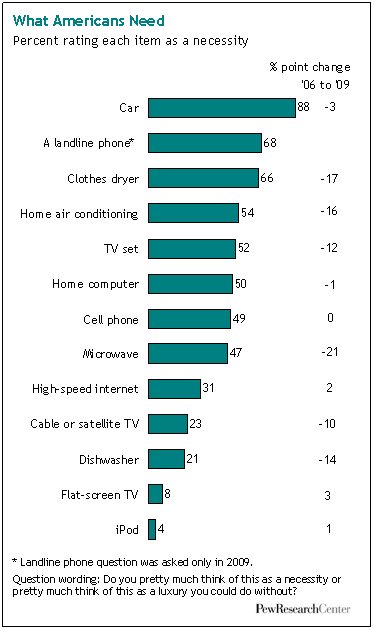
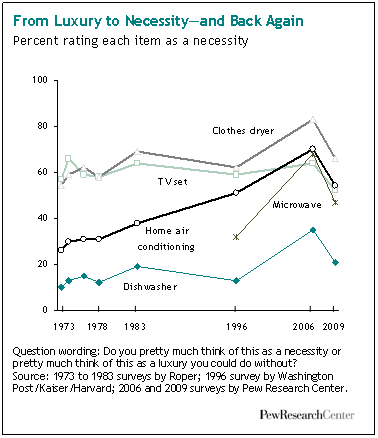
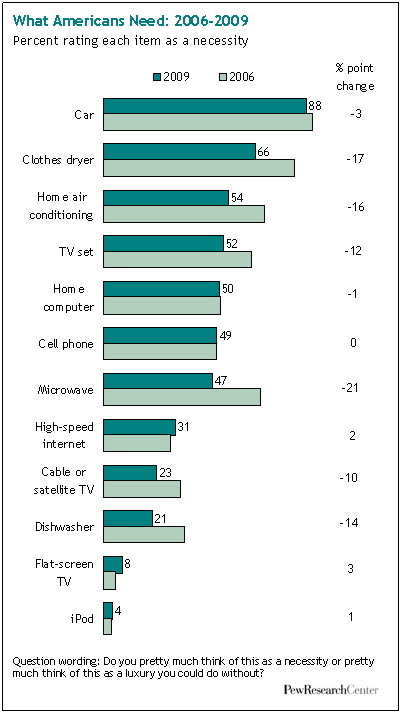
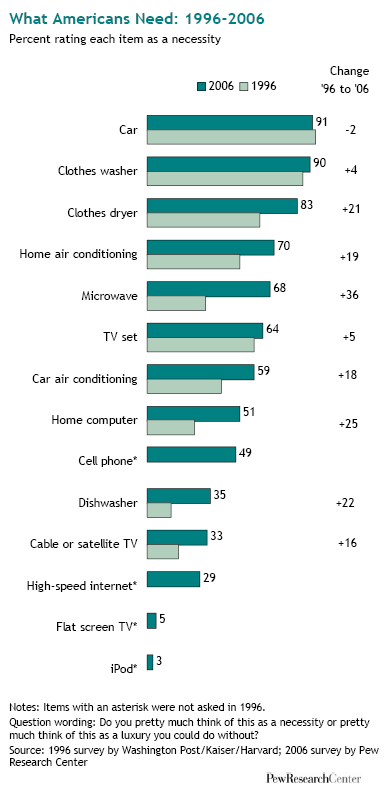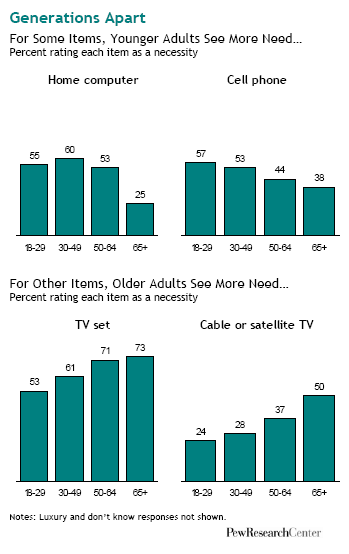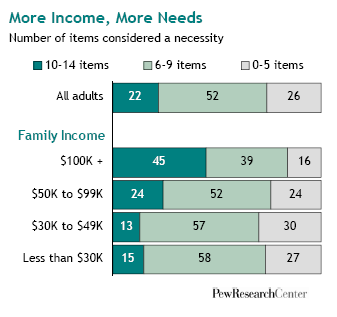To me this New York Times graphic showing the relationship between gas prices and the average number of miles driven powerfully suggests that gas prices actually have little to do with how much driving Americans do. The vertical axis is gas prices and the horizontal axis is the number of miles driven. The line inside the figure is time.
Basically the illustration shows that the number of miles per year Americans drive has been climbing since 1956. Despite short-term gas price fluctuations, something is driving us to drive more and more every year.
When gas prices do shoot up — such as during the oil embargo, the energy crisis, and the most recent peak — Americans show a modest drop in driving, but it’s not a very large one and we recover rather quickly. During the oil embargo, Americans shaved 210 miles a year off of their driving. During the energy crisis, only 156. The recent reduction in the number of miles driven per year is attributed by the New York Times writer to the fact that so many people are unemployed and, therefore, no longer need to drive to work.
Driving, then, shows only a modest response to high prices. Perhaps the jumps in prices during these peaks — 43 and 106 cents per gallon respectively — weren’t really worth slowing down for? Or perhaps driving is so culturally meaningful that Americans are willing to pay to stay in their cars regardless? Or maybe driving, and driving farther, has become increasingly important over time such that people can’t reasonably reduce the amount of driving they do?
It seems to me that the problem is at least partly infrastructural. I wonder how average miles driven responds, or would respond, to enhancing and investing in public transportation? If we started building denser neighborhoods and got rid of suburbs?
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.