Flashback Friday.
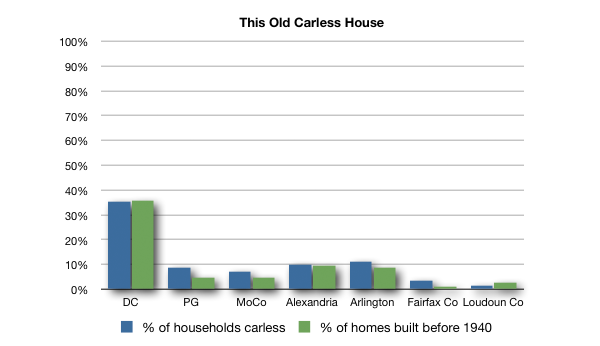
The percent of carless households in any given city correlates very well with the percent of homes built before 1940. So what happened in the 40s?
According to Left for LeDroit, it was suburbs:
The suburban housing model was — and, for the most part, still is — based on several main principles, most significantly, the uniformity of housing sizes (usually large) and the separation of residential and commercial uses. Both larger lots and the separation of uses create longer distances between any two points, requiring a greater effort to go between home, work, and the grocery store.
These longer distances between daily destinations made walking impractical and the lower population densities made public transit financially unsustainable. The only solution was the private automobile, which, coincidentally, benefited from massive government subsidies in the form of highway building and a subsidized oil infrastructure and industry.
Neighborhoods designed after World War II are designed for cars, not pedestrians; the opposite is true for neighborhoods designed before 1940. Whether or not one owns a car, and how far one drives if they do, then, is dependent on the type of city, not personal characteristics like environmental friendliness. Ezra Klein puts it nicely:
In practice, this doesn’t feel like a decision imposed by the cold realities of infrastructure. We get attached to our cars. We get attached to our bikes. We name our subway systems. We brag about our short walks to work. People attach stories to their lives. But at the end of the day, they orient their lives around pretty practical judgments about how best to live. If you need a car to get where you’re going, you’re likely to own one. If you rarely use your car, have to move it a couple of times a week to avoid street cleaning, can barely find parking and have trouble avoiding tickets, you’re going to think hard about giving it up. It’s not about good or bad or red or blue. It’s about infrastructure.
Word.
Neither Ezra nor Left for LeDroit, however, point out that every city, whether it was built for pedestrians or cars, is full of people without cars. In the case of car-dependent cities, this is mostly people who can’t afford to buy or own a car. And these people, in these cities, are royally screwed. Los Angeles, for example, is the most expensive place in the U.S. to own a car and residents are highly car-dependent; lower income people who can’t afford a car must spend extraordinary amounts of time using our mediocre public transportation system, such that carlessness contributes significantly to unemployment.
Originally posted in 2010.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.