Early hip-hop forwarded themes of counterculture, anti-establishment, and underprivilege; marginalized groups used hip-hop to tell their stories. Today, however, hip-hop is a multinational and multi-billion dollar industry. Can hip-hop music hold onto connections with disadvantaged communities? Sarah Becker and Castel Sweet explore this in new research based on interviews with 25 Southern hip-hop artists, most who are black men. The authors draw on “black placemaking” theories to explain how artists maintain connections to disadvantaged communities and to explore how perceptions of and connections to physical place can shape hip-hop and art.
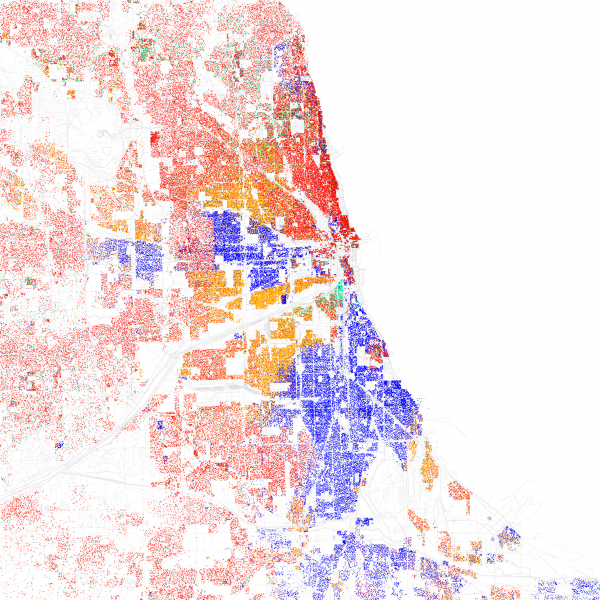
Artists interviewed in the current study represent a variety of personal backgrounds and hip-hop styles; some are from disadvantaged, lower-class communities and some are not. The authors turn to theories of “black placemaking” about how black Americans build meaningful community solidarity in the face of oppression, marginalization, and disadvantage, both past and present. Research on black placemaking has found that alliances between black working-class and middle-class neighborhoods can bolster how underprivileged neighborhoods build community and solidarity.
Artists from concentrated disadvantage in impoverished areas draw heavily on community connections and responsibilities when describing their artistic visions and personal goals. Being a role model and helping the community is an important motivator for many of these artists, and many shared tales of community resilience in the face of adversity and marginalization. Interestingly, artists from middle-class backgrounds who have personal connections with disadvantaged communities or now live in such areas also discuss community building and dealing with concentrated disadvantage.
This study shows that, in addition to driving community resilience and solidarity, black placemaking can shape artistic visions, goals, and careers. It also illustrates how cross-class alliances and middle-class blacks continue to play a role in how underprivileged neighborhoods survive and thrive in hard times, and this can drive some sick rhymes; commercialism be damned, hip-hop is still alive!!! #bars