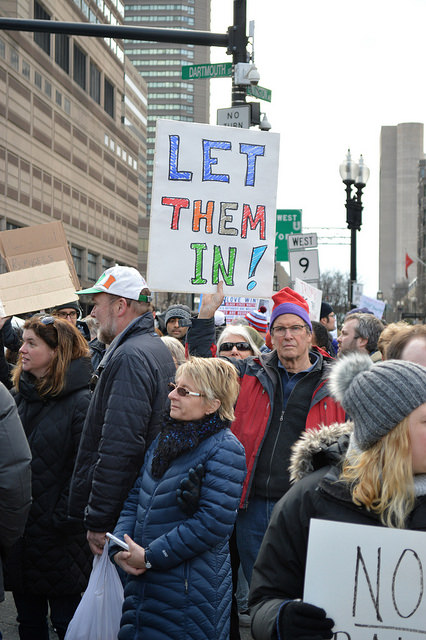
Throughout history, immigrant groups have been used as scapegoats for social problems — be it the continually unfolding European refugee crisis or the aftermath of the Holocaust. And those in favor of xenophobic policies, tend to encourage these negative sentiments against immigrants to garner support these types of policies. In the United States, many politicians demonize immigrants for their supposed violence, but a recent article in The New York Times features research that undermines the foundations of this contention. A team of researchers, led by sociologist Robert Adelman, examined 200 cities across the United States to uncover the relationship between immigration and crime trends over the course of several decades. Their study concluded that while immigration has risen in almost every city since the 1970s, crime has not:
“In 136 metro areas, almost 70 percent of those studied, the immigrant population increased between 1980 and 2016 while crime stayed stable or fell. The number of areas where crime and immigration both increased was much lower — 54 areas, slightly more than a quarter of the total. The 10 places with the largest increases in immigrants all had lower levels of crime in 2016 than in 1980. And yet the argument that immigrants bring crime into America has driven many of the policies enacted or proposed by the administration so far: restrictions to entry, travel and visas; heightened border enforcement; plans for a wall along the border with Mexico…But while the immigrant population in the county has more than doubled since 1980, overall violent crime has decreased by more than 50 percent.”
And while the researchers cannot use this evidence to establish whether an increase in immigration reduces crime, they clearly show that an immigration influx is not the disastrous picture painted by many news sources and politicians:
“In general, the study’s data suggests either that immigration has the effect of reducing average crime, or that there is simply no relationship between the two, and that the 54 areas in the study where both grew were instances of coincidence, not cause and effect. This was a consistent pattern in each decade from 1980 to 2016, with immigrant populations and crime failing to grow together.”