Originally posted in 2010. Re-posted in honor of Women’s History Month.
When I teach gender I always talk about the ways in which societies actively construct ideas that men and women have very different bodies, capable of different things. In the U.S., our gender ideology includes the belief that female bodies are weaker than male ones, more fragile. Particularly in the Victorian Era, this belief led doctors to discourage physical activity by women. Among a range of other concerns, doctors argued that physical exertion in women might cause their organs (particularly the reproductive organs) to become dislodged and wander around the body, causing all types of problems. I know I’d certainly be distressed if my uterus migrated and I ended up pregnant and carrying a fetus in, say, my elbow.
A result of this, of course, is that (White) women were discouraged from being physically active and taking part in sports. This, combined with heavy clothing and corsets that actually did shove organs around, led to the condition that the medical community claimed already existed: women’s bodies were less capable of physical exertion than men’s and they were more likely to faint (corsets often making it difficult to breathe adequately). It’s a self-fulfilling prophecy: if you believe women’s bodies are weaker than men’s and thus discourage or even prohibit women from being physically active, you create differences in physical capability and fitness that you can then claim prove you were right all along.
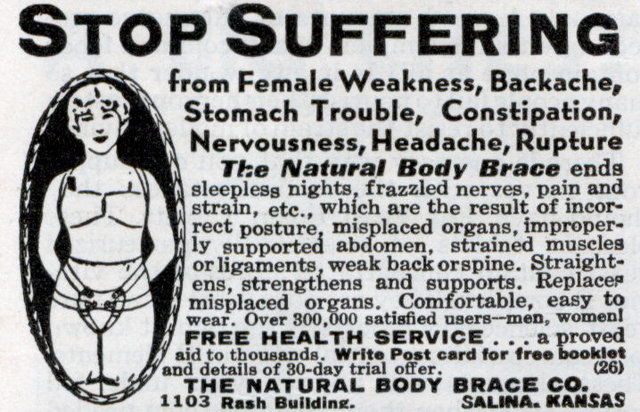
James T. found this awesome ad for a product that, among other amazing things, ends “misplaced organs” and will even move them back where they belong (from Modern Mechanix). The ad (from 1934) says that satisfied users include both men and women, but concerns about misplaced organs were a concern applied predominantly to women:
Medical practitioners weren’t just worried about physical exertion. They believed mental activity could be harmful to women as well; perhaps all that thinking meant the brain would take blood away from the reproductive organs and lead to infertility. A common diagnosis for women was “hysteria,” a general term that could be applied to almost any woman. A common “cure” for hysteria was bed rest, preventing both physical and mental activity. The diagnosis of hysteria served as a justification for severely limiting women’s activities, drawing on the ideology of the fragile female body. Charlotte Perkins Gilman wrote the classic short story “The Yellow Wallpaper” after her own experience of being forced to stay in bed with no mental stimulation, not even books.
Hysteria was also often associated with sexual problems, including a lack of interest in sex. The cure for this was “vaginal massage,” which was exactly what you think it was. This was done manually in doctors’ offices, but eventually mechanical vibrators became widely available, allowing women to treat their hysteria more cheaply and at home, and reducing the time it took to produce a “paroxysm”.
I find it fascinating that the construction of (middle/upper class White) women as “hysterical” and often sexually repressed and frigid made it acceptable for them to purchase a product that allowed them to sexually satisfy themselves at a time when masturbation was still widely vilified, and excuse it on the grounds that it was medically prescribed.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.