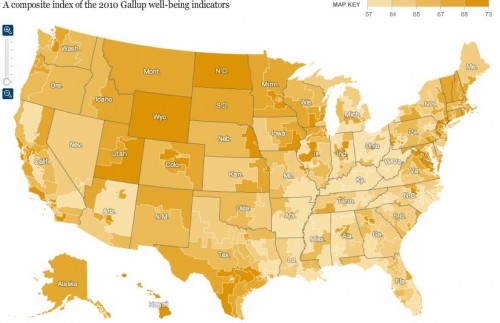
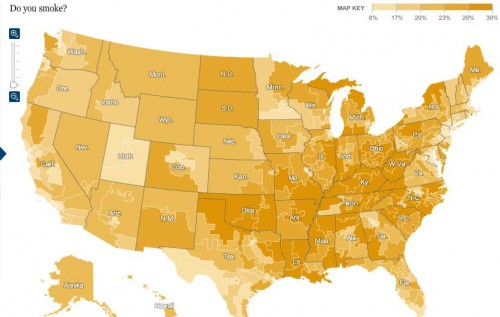
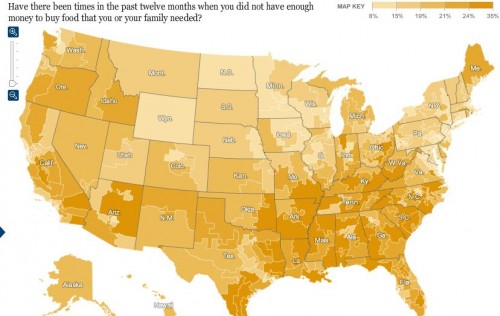
If I ran the Federal scary anti-smoking image warning program, I might show smokers the list of health-related terms that show up most in the states with the highest cigarette smoking rates.
If you take the smoking rates by state, and throw them into the Google Correlate hopper, you can see the 100 search terms that are most highly correlated with that reported smoking behavior. That is, the terms that are most likely to be used in high-smoking states and least likely to be used in the low-smoking states.
Is the result just a lot of noise? Maybe, but I don’t think so. Here are the smoking-related terms in the top 100:
- camel no 9
- cigarette coupon
- cigarette coupons
- marlboro coupons
- my time to quit
- safe cigarettes
- stopping smoking
- time to quit
- fire safe cigarettes
- ways to stop smoking
So that’s good for face validity — a list of random search terms isn’t likely to have all those smoking terms on it.
But after the smoking terms, the thing that jumps out is the health-related terms. We know from the Google flu tracker that people search for their symptoms. So these caught my eye.
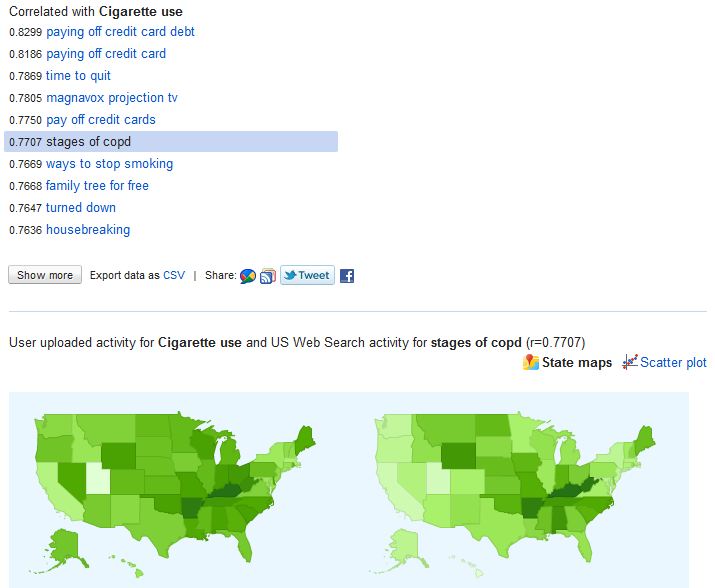
Here is a screen shot of the first page of results:
I selected “stages of copd” as the term to map. The map on the left is the smoking rates; the one on the right is the relative frequency of searches for “stages of copd.” That is, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a nasty disease the most common cause of which is smoking.
Here is the complete list of health-related terms among the top-100 correlates with smoking rates:
- stages of copd
- abnormal mammogram [the association between smoking and breast cancer remains controversial]
- aneurysm symptoms [more common among smokers]
- hardening of the arteries [exacerbated by smoking]
- jaw swelling
- red rash on legs [could be psoriasis, which smoking increases the risk of]
- swelling in neck
- swollen lymph node in neck
- pilonidal cyst pictures
Lymph node swelling, which is implicated in the jaw and neck searches, most often reflects infection — which smoking causes.
How strong are the connections? They’re not the strongest I’ve seen on Google Correlate. The “stages of copd” search is correlated with smoking rates at .77 on a scale of 0 to 1. It’s not uncommon to find correlations of .93 (which is the relationship between “quiche” and “volvo v70 xc”).
But considering the smoking rates come from a sample survey (the National Survey on Drug Use and Health) which includes random error, and states are somewhat arbitrary geographic units, that correlation seems pretty high to me. Here’s the scatterplot:
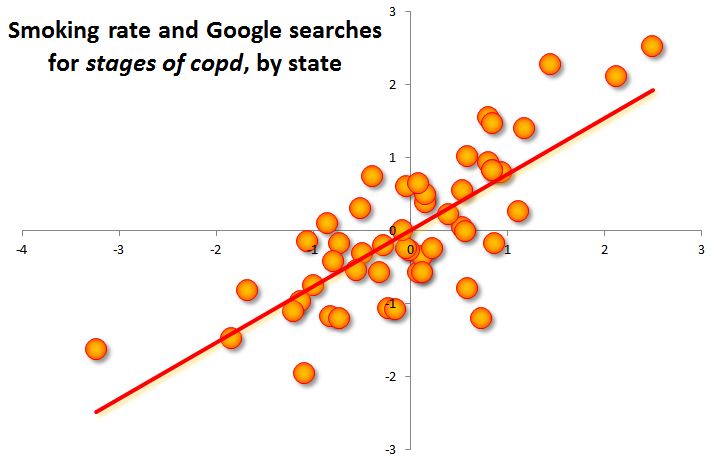 What is the correlation causality story here? I can’t say. But the simplest explanation is that these are the terms smokers (and maybe those who know or care for them) are most likely to Google relative to non-smokers — not that they are the most common searches smokers do, of course, but the searches that differentiate them from non-smokers. The simplest explanation is the best place to start.
What is the correlation causality story here? I can’t say. But the simplest explanation is that these are the terms smokers (and maybe those who know or care for them) are most likely to Google relative to non-smokers — not that they are the most common searches smokers do, of course, but the searches that differentiate them from non-smokers. The simplest explanation is the best place to start.
I like this list of conditions because in my experience smokers sometimes have the attitude of “you have to die of something.” But it’s not just the chance of dying that smoking increases — it’s a lot of possible forms of suffering along the way.
——————————
The Google Correlate tool is showing the great potential for using Internet search activity to investigate layers of behavior and meaning behind other observable social phenomena, such as race/ethnic composition, health behavior, and family patterns.














 I am hard pressed to imagine that such an ad would fly today. That these ads would not only be un-palatable, but impermissible, is evidence that the power of corporations is not absolute.
I am hard pressed to imagine that such an ad would fly today. That these ads would not only be un-palatable, but impermissible, is evidence that the power of corporations is not absolute.