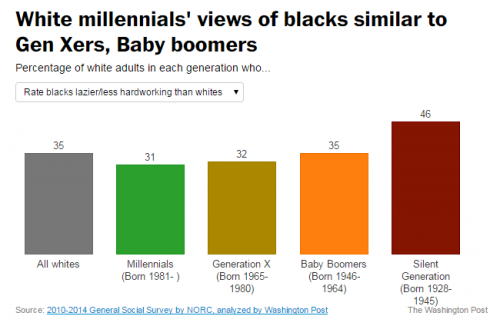
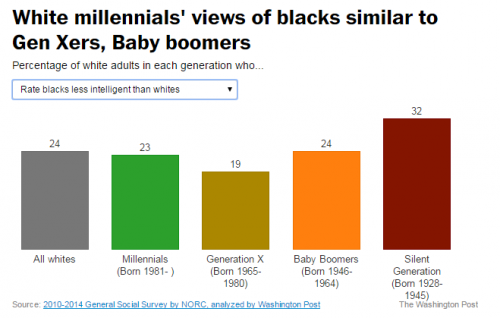
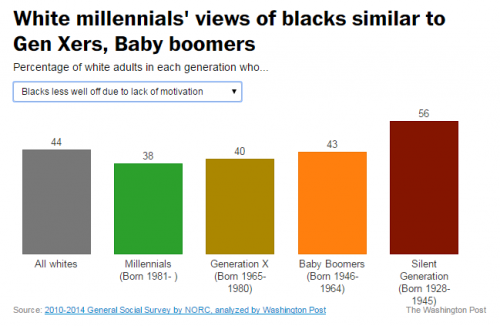
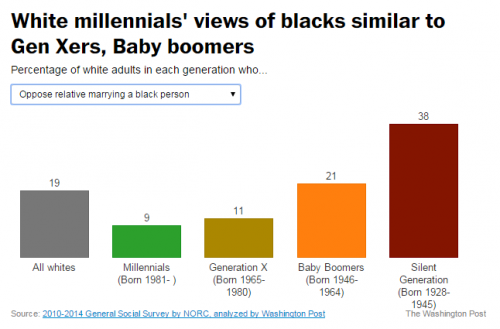
There is a whole social science to the optimal balance of victory and defeat in social movements and social change. Consider two political cartoons by Mike Luckovich. One, from June 21, counterposes a person carrying a sign saying “black lives matter” and a Confederate flag subtitled “S. Carolina rebuttal.” Another, from June 25, features a black man weighted down by chains and padlocks saying “voter ID laws,” inequality,” “police brutality,” and “mass jailings.” A white man in front of him jumps up high and lifts his arm, saying “The Confederate flag’s coming down, high five!”
Did he really just demand the removal of the Confederate flag and then mock people who would celebrate its removal? Is that how much things change in a week? But in periods of social change, moving the goal posts is what it’s all about. And there’s nothing wrong with that.
The Charleston massacre was a horrific reminder of how it seems some things never change. But they do change. Dylann Roof was caught and may be put to death, legally. And it turned out that, not only had the Confederate flag only been flying at the South Carolina capitol for a few decades, but it actually could be taken down in response to public outrage. And yet, that’s not the end of racism.
Anthea Butler, a religion and Africana studies professor at Penn, who wrote an op-ed in the Washington Post, was on the On Point radio show. She was talking to host Tom Ashbrook, when she got this:
Tom Ashbrook: If you ask me, I understand that feeling and that vivid response. At the same time, I, and maybe you, Anthea Butler, Dr. Butler, don’t want to lose, or not recognize, or lose the progress that has been made. And this is nowhere near paradise…
Anthea Butler: But what kind of progress? What kind of progress? This is what we keep talking about. And I don’t understand, when you say, “We’ve made progress.” How have we made progress when the president of the United States has been constantly questioned because he is partially a Black man? And so you talk progress — and this is the kind of talk we’re going to hear all week long after this.
TA: But he’s president, madam.
AB: He is president.
TA: Well, that’s a pretty big deal…
AB: That is a big deal, but to some people in this country, like Dylann Roof, that is the end of this country. That’s why you had the kind of phrase that he said, that all your politicians, the right Republican politicians have been saying, “Take our country back.” And so, I want to talk about the rhetoric that’s happened…
Ashbrook has a point about progress, of course, but it’s just the wrong time to say that, days after a racist massacre that seems as timeless as a Black-churches burning. At that moment there could be no progress.
For whatever reason, Ashbrook turned to progress on the interpersonal level:
TA: We did see White people in South Carolina, in Charleston, pour into the churches alongside African Americans over this weekend.
AB: Yes we did. But you need to understand the distinction here. I don’t doubt that there are well-meaning, good White people, good White Christians, who are appalled at this. I understand that. But when you have a structural system that continues to do this kind of racial profiling, the kinds of things that are going on with the police in this country, the kinds of issues that we’ve had. The problem becomes this: you can talk about progress all you want, but reality is another thing altogether.
Again, it’s progress, but focusing on it at that moment is basically #AllLivesMatter. President Obama also tried to keep his eyes on the prize, in his appearance on the WTF podcast:
Racism, we are not cured of it. And it’s not just a matter of it not being polite to say “nigger” in public. That’s not the measure of whether racism still exists or not. It’s not just a matter of overt discrimination. Societies don’t, overnight, completely erase everything that happened 200 to 300 years prior.
Outrage ensued about his use of “nigger,” but White House Press Secretary Josh “earnest non-racist white guy” Earnest doubled down:
The President’s use of the word and the reason that he used the word could not be more apparent from the context of his discussion on the podcast. The President made clear that it’s not possible to judge the nation’s progress on race issues based solely on an evaluation of our country’s manners. The fact is that we’ve made undeniable progress in this country over the last several decades, and as the President himself has often said, anyone who lived in this country through the ‘50s and the ‘60s and the ‘70s and the ‘80s notes the tremendous progress that we’ve made. That progress is undeniable. But what’s also undeniable is that there is more work that needs to be done, and there’s more that we can do. And the fact is everyone in this country should take some inspiration from the progress that was made in the previous generation and use that as a motivation and an inspiration to try to make further progress toward a more perfect union.
Now is no time to talk about progress, some say. With Black church members being gunned down and churches burning, and one appalling, outrageous video after another showing the abuse of Black citizens by police, having a Black president is not a victory. So much so that maybe he’s not really Black at all. Frank Roberts writes of Obama’s “Amazing Grace” moment:
With Obama … blackness has been reduced to a theatrical prop; a shuck-and-jive entertainment device that keeps (black) audiences believing that the President “feels their pain” — at precisely the same time that he fails to provide a substantive policy response to black unemployment, over-incarceration, and/or racialized state violence.
The social scientist in me objects, because the rate of progress is not determined by the victory or tragedy of the moment, or by the blackness of a man. And Obama probably has done more than any other president (at least recently) to address Black unemployment, incarceration, and racialized state violence. That’s not a moral or political statement — and it doesn’t imply “enough” — it’s an empirical one.
Movements use good news for legitimacy and bad news for urgency. When something goes well, they need to claim credit and also make sure their supporters know there is more work to be done. When something awful happens they place the troubles in the context of a narrative of struggle, but they don’t want to appear powerless because that saps support and undermines morale.
An extended version of this post is at Family Inequality.
Philip N. Cohen is a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park. He writes the blog Family Inequality and is the author of The Family: Diversity, Inequality, and Social Change. You can follow him on Twitter or Facebook.