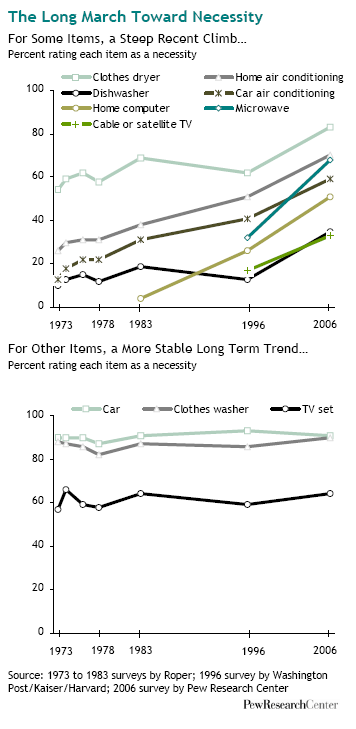
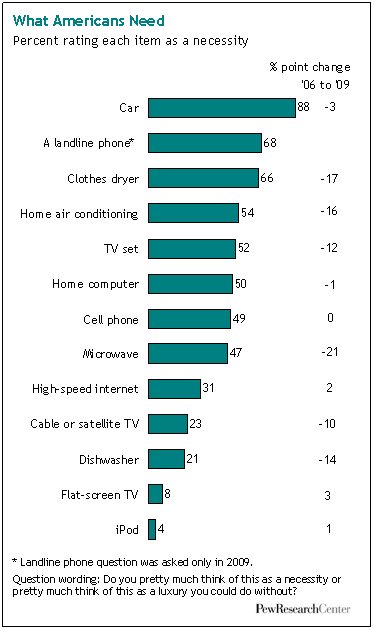
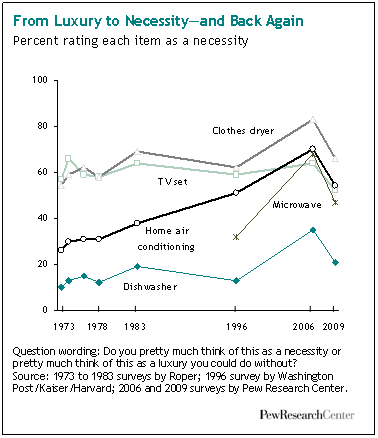
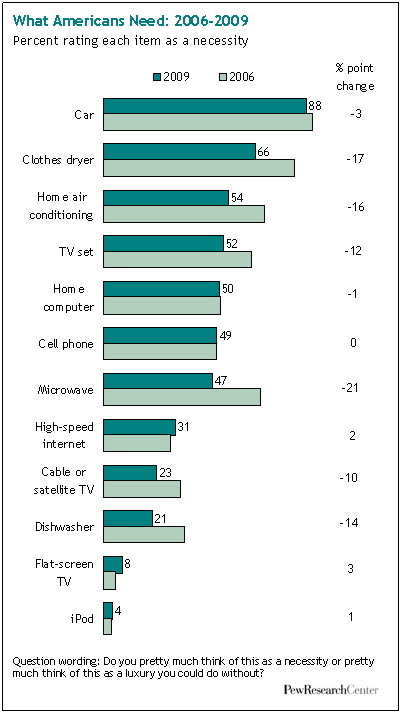
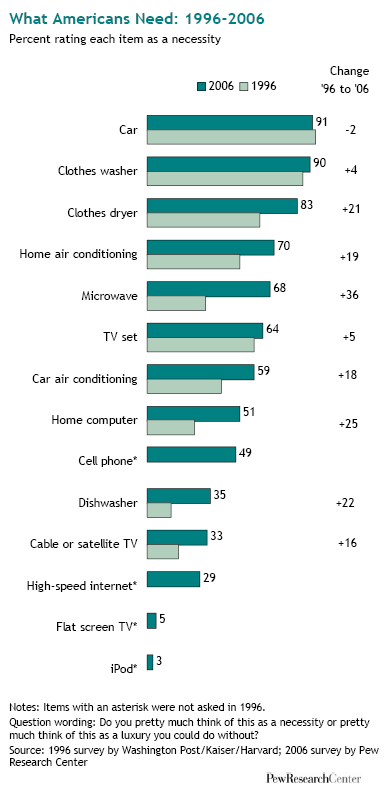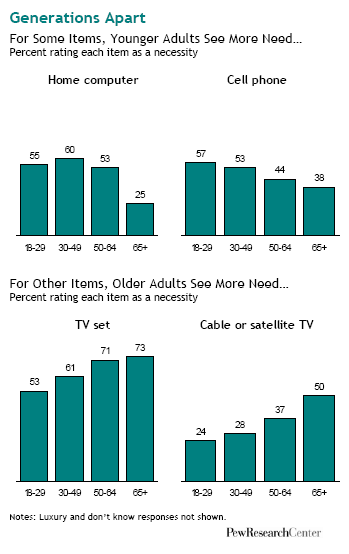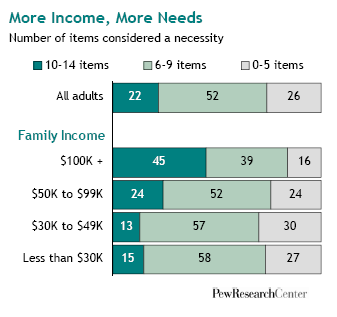Today Californians vote as to whether to legalize marijuana. Chris Uggen at Public Criminology explains:
This measure (1) legalizes various marijuana-related activities, (2) allows local governments to regulate these activities, (3) permits local governments to impose and collect marijuana-related fees and taxes, and (4) authorizes various criminal and civil penalties.
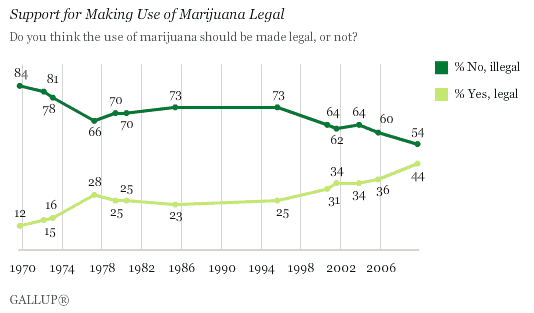
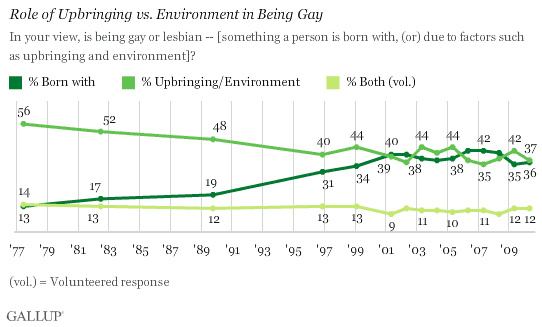
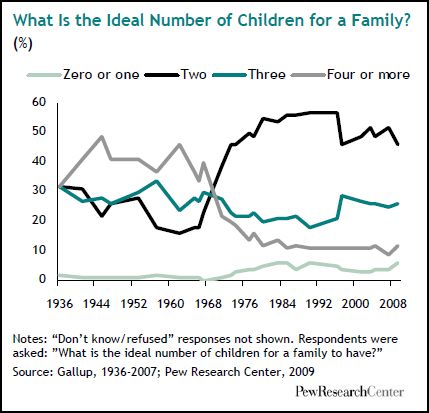
There is a chance that the measure will pass; Gallup polls of U.S. opinion show that support for legalization has grown over time:
What will happen if California becomes the first state to legalize marijuana is the stuff of speculation or, more generously, modeling. Uggen points to the work of scholars employed at the RAND Drug Policy Research Center (Beau Kilmer, Jonathan P. Caulkins, Rosalie Liccardo Pacula, Robert J. MacCoun, and Peter H. Reuter). According to their models:
(1) the pretax retail price of marijuana will substantially decline, likely by more than 80 percent. The price the consumers face will depend heavily on taxes, the structure of the regulatory regime, and how taxes and regulations are enforced;
(2) consumption will increase, but it is unclear how much, because we know neither the shape of the demand curve nor the level of tax evasion (which reduces revenues and prices that consumers face);
(3) tax revenues could be dramatically lower or higher than the $1.4 billion estimate provided by the California Board of Equalization (BOE); for example, uncertainty about the federal response to California legalization can swing estimates in either direction;
(4) previous studies find that the annual costs of enforcing marijuana laws in California range from around $200 million to nearly $1.9 billion; our estimates show that the costs are probably less than $300 million; and
(5) there is considerable uncertainty about the impact of legalizing marijuana in California on public budgets and consumption, with even minor changes in assumptions leading to major differences in outcomes.
In other words, it’s really hard to tell what the consequences of legalizing marijuana will be! Uggen urges caution.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.