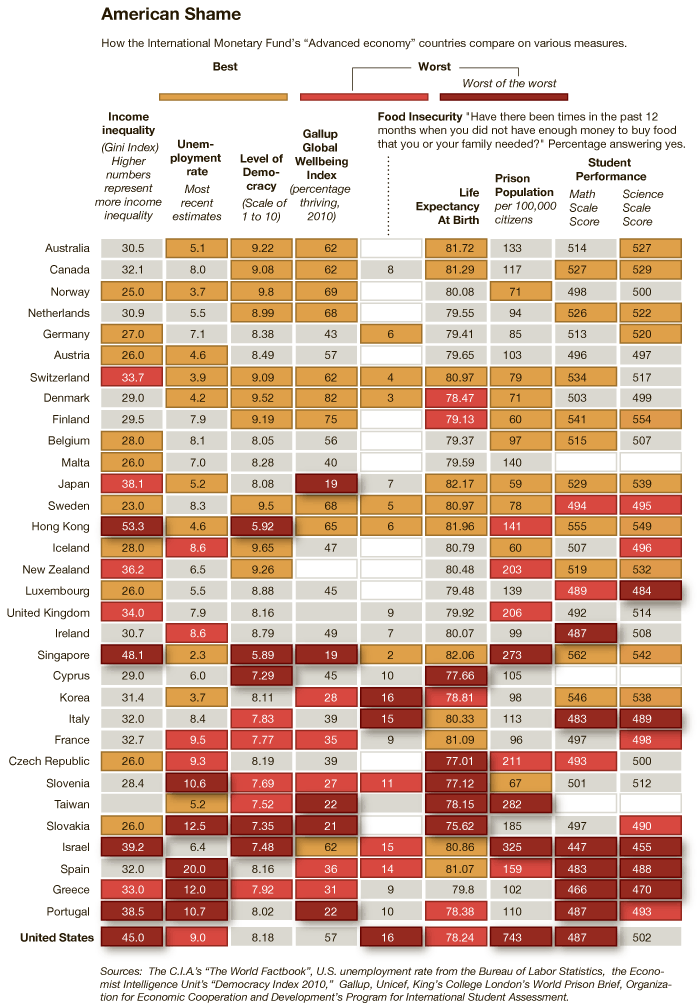
An infographic accompanying an article at the New York Times reveals how “advanced economies” compare on various measures of equality, well-being, educational attainment, and more. To illustrate this, for each measure countries that rank well are coded tan, countries that rank poorly and very poorly are coded orange and red respectively, and countries that are in the middle are grey. The countries are then ranked from best to worst overall, with Australia coming in #1 and the United States coming in last. You might be surprised how some of these countries measure up.
Thanks to Dmitriy T.M. for the link.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.

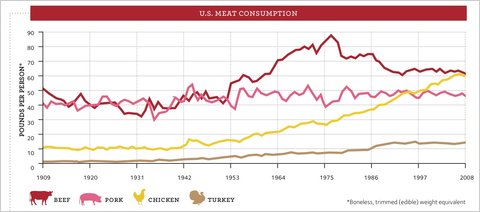
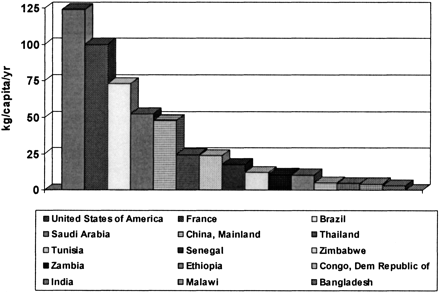
.jpg)