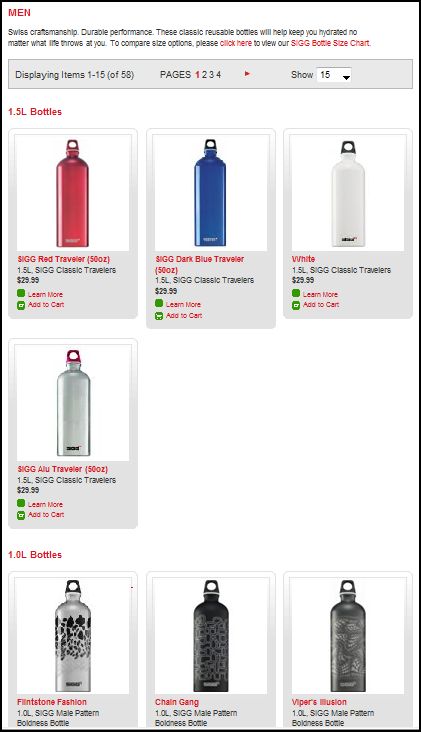
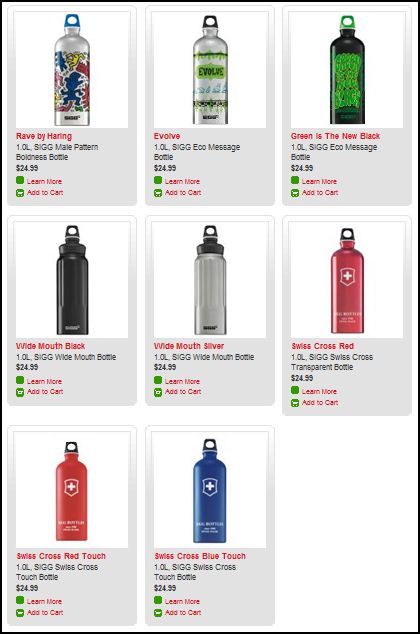
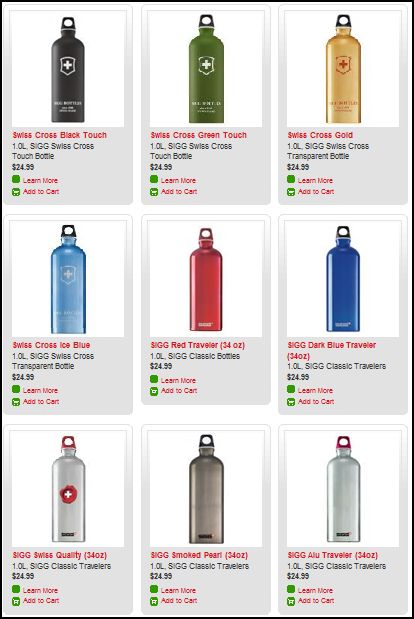
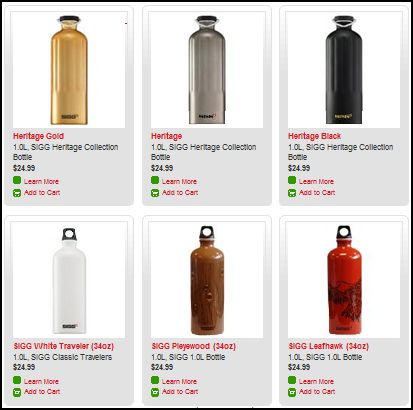
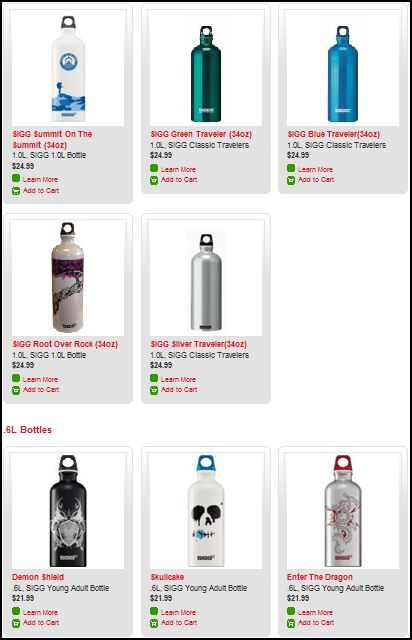
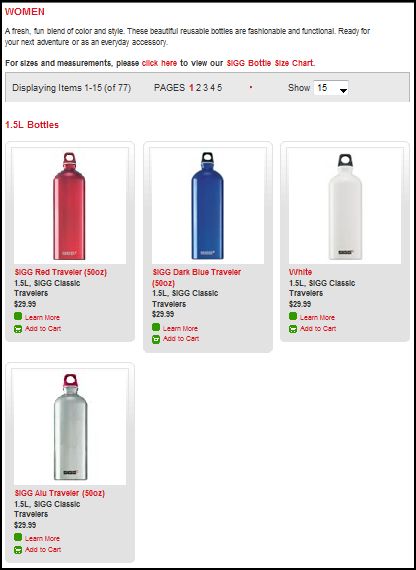
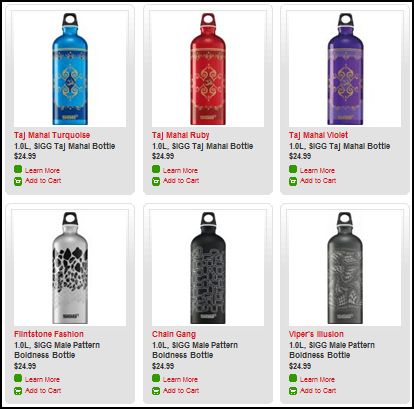
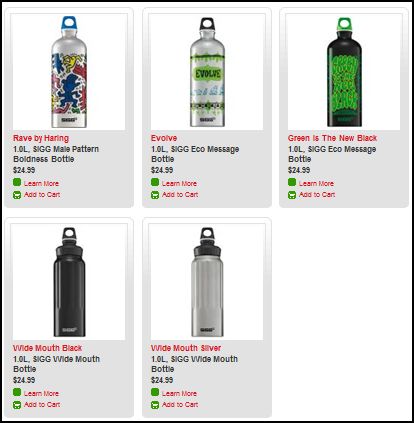
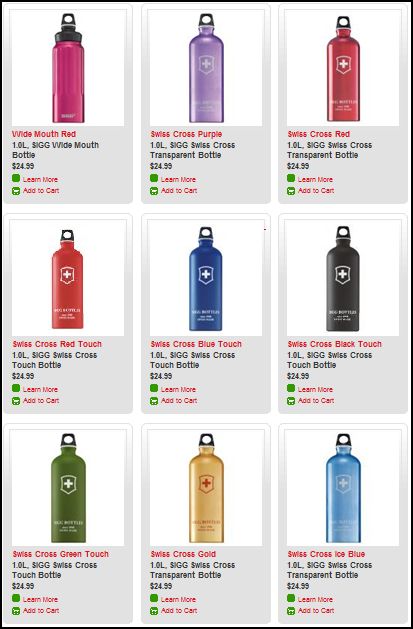
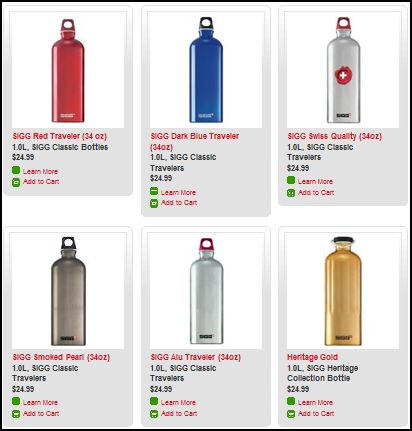
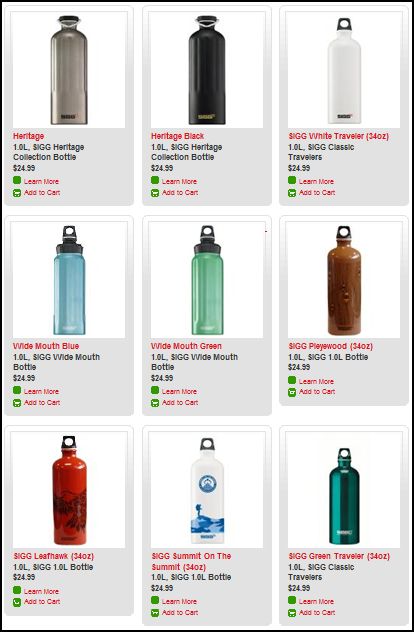
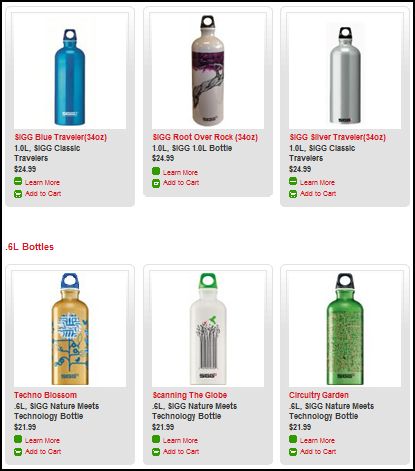
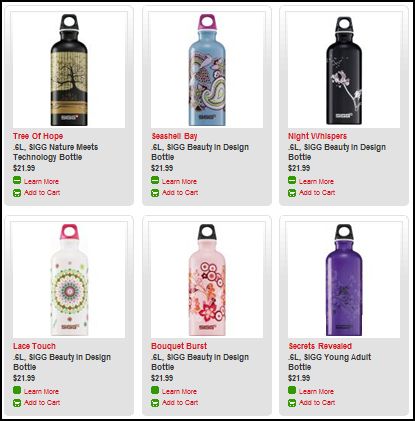
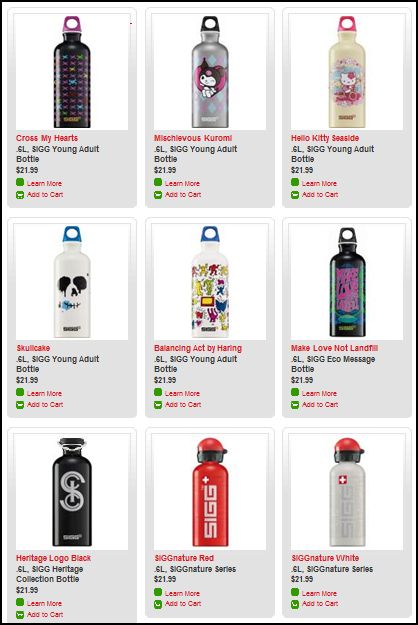
Stella P. sent in a link to the SIGG water bottle website, pointing to the fact that there are “women’s” and “men’s” collections. What’s interesting about the two collections isn’t just the reproduction of the gender binary and the gendering of water bottles, but the fact that the outcome of this bifurcation is actually less choice for men. There are 77 total water bottles in the women’s collection, but only 58 in the men’s. If you scroll through the options, you’ll see that women basically get to choose among ALL of the bottles, but men are not presented with any that (apparently) appear TOO feminine. This is a great example, then, of the way that patriarchy constrains men by pushing them away from items deemed girly.
Here are some screen shots of the men’s and women’s collections.
Women’s:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.