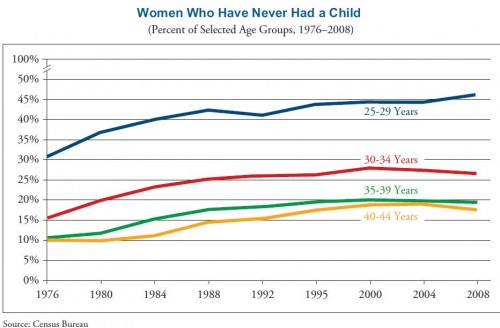
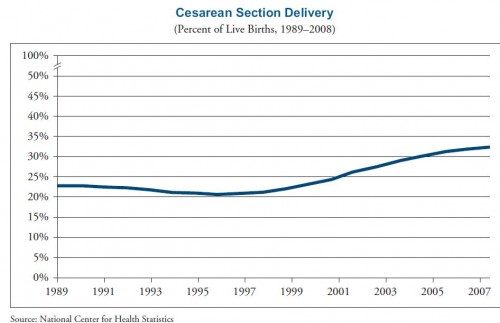
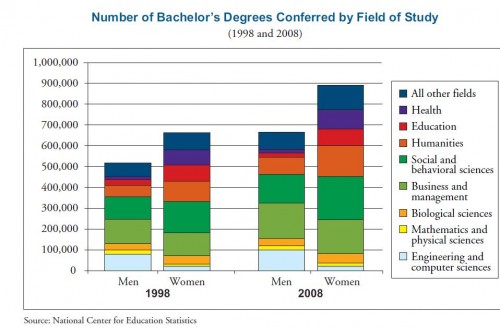
Sociology PhD candidate Kjerstin Gruys recently guest posted about her effort to shun mirrors for one year in the hopes of improving her body image. As any really interesting and challenging project should, it’s begun to get some major media coverage, including a story at Yahoo News. When a political project starts getting mass media attention, though, it risks being contextualized and even co-opted by the status quo. This is a case in point.
Interspersed among the article about Gruys’ project are links, an effort on the part of the website to get readers to spend more time on its pages and the pages of its advertisers. These are probably randomly generated according to the content of the article. So, since Gruys’ project is about her feelings about her body and avoiding mirrors for six months before and after her wedding day, the links center around beauty and weddings. The first two links nestled in among the first few paragraphs read “Are you Satisfied with Your Face?” and “A Wedding Dress to Fit Your Body Shape.”
By publicizing her project, Kjerstin is trying to make the personal political. But one of the only means of drawing awareness to her work includes losing control of how it’s talked about and delivered. While she wants women to feel better about themselves, and some may be inspired by her project, in some ways this is also another instance of the mass media reminding women to think about the appearance of their face and body. The inserted links, further, can be read as upholding the very standards that Gruys is trying to combat. And in at least some cases, they do. The “Are you Satisfied with Your Face?” link, in this vein, goes to a site sponsored by super-beauty project corporation L’Oreal.
Thanks to my student, Kirsten Easton, for sending along this link!
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.