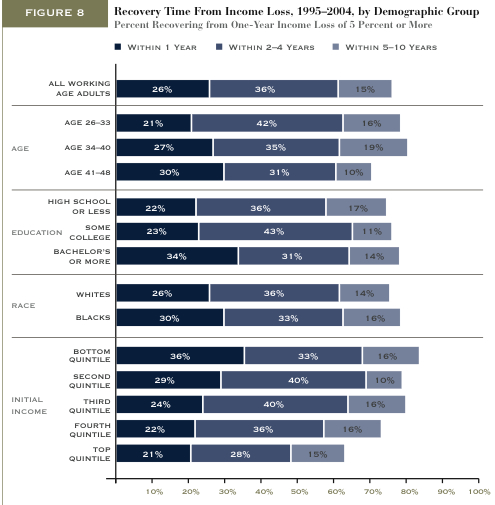
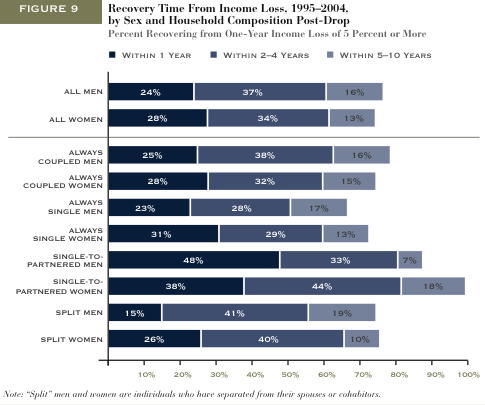
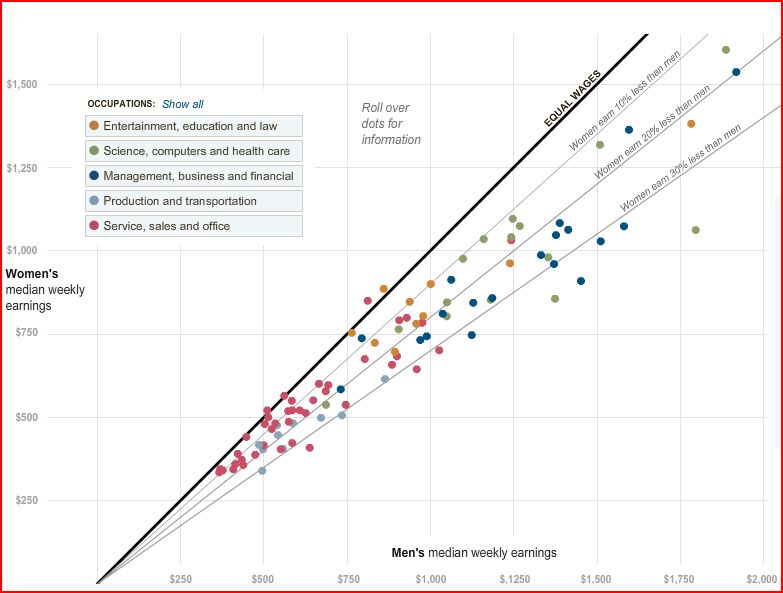
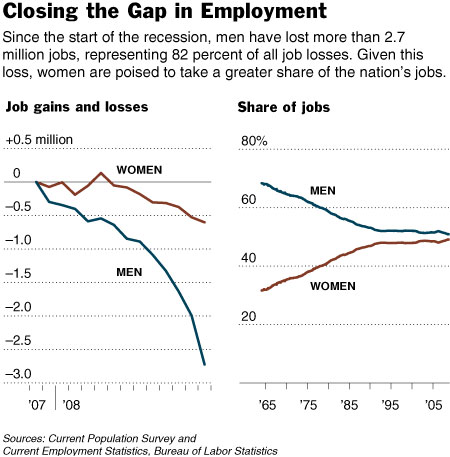
The figure below, borrowed from U.S. News and World Report, shows that the wage gap between women and men, for nearly all age groups, has narrowed significantly between 1979 and 2008. It also shows that the wage gap is smallest for men and women aged 20-24, grows for men and women aged 25-34, grows even further for men and women aged 35-44, and remains steady after that.
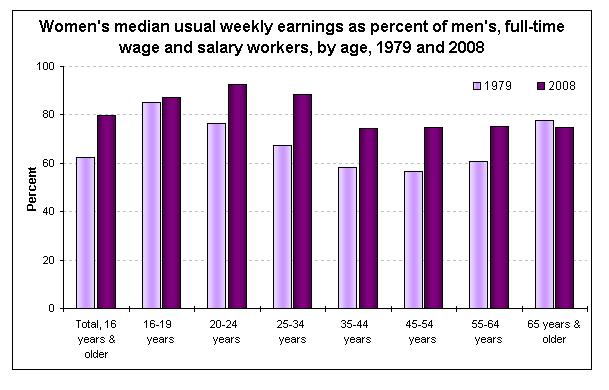
These data are for men and women in the same jobs working full time. So what would explain this change? Sociologists have found that much of the growth in the wage gap over the life course is due to the fact that women are held disproportionately responsible for childcare and housework (see some data here). As men and women start to have children, women (whether by choice or necessity) find themselves sacrificing their careers more so than men. On the flip side, mothers are discriminated against by employers more often than fathers and women without children. (See, for example, this clip of Gov. Rendell commenting that Janet Napolitano is a good candidate for secretary of Homeland Security because she has no family.) That’s why you see the wage gap increasing during prime childbearing years (25-44), but not afterward.
For more on the wage gap, see our posts on the wage gap for college grads, comparing different kinds of wage gaps, the role of job segregation, gender and the wage gap in different professions.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.