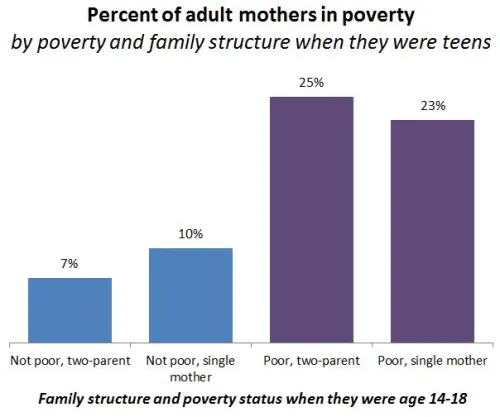
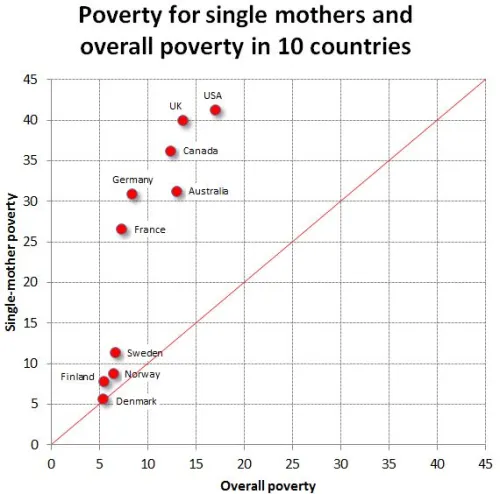
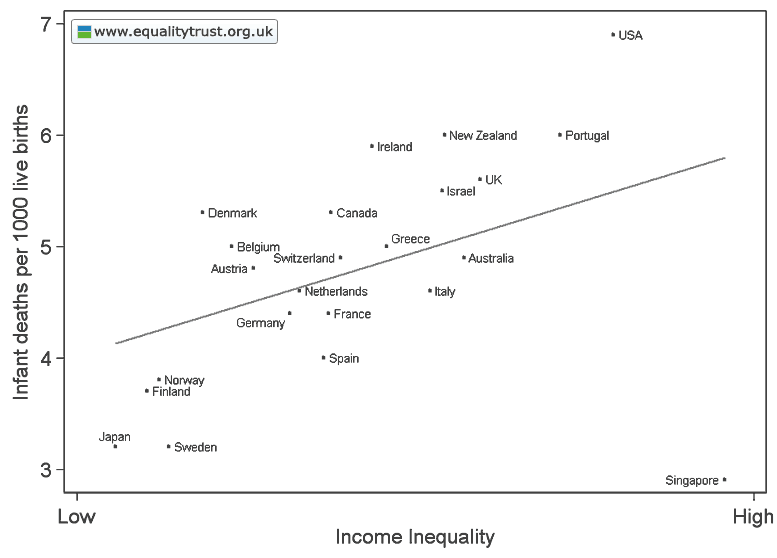
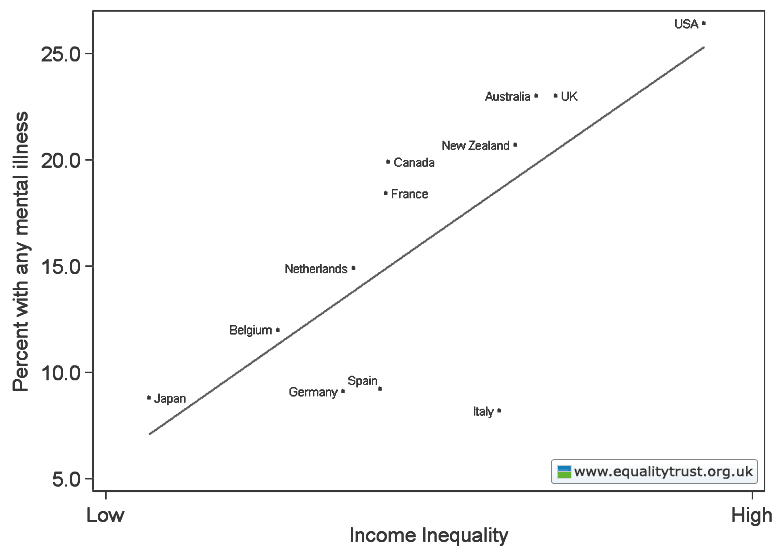
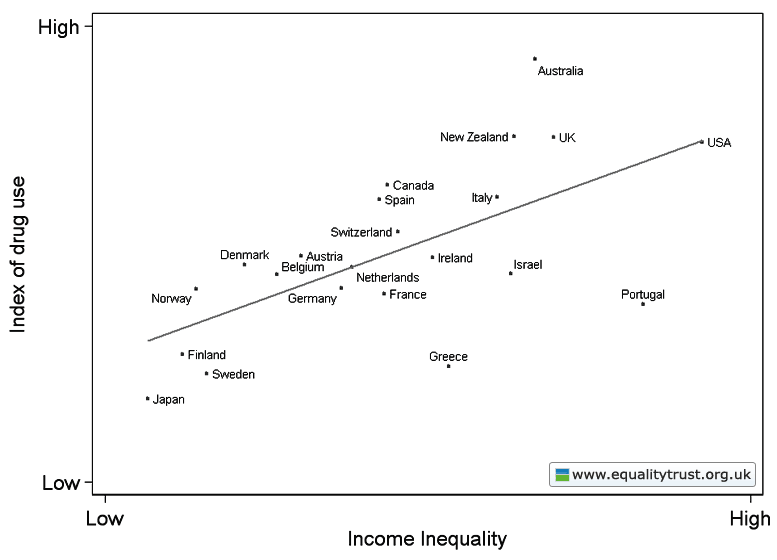
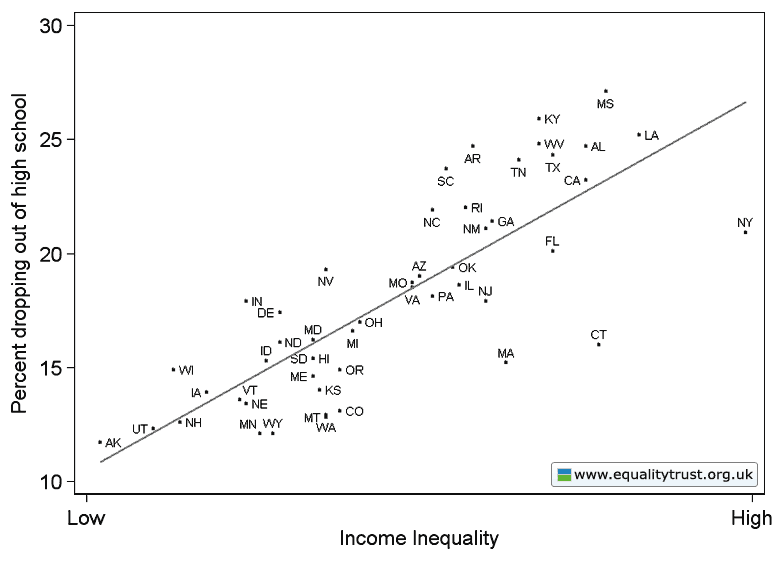
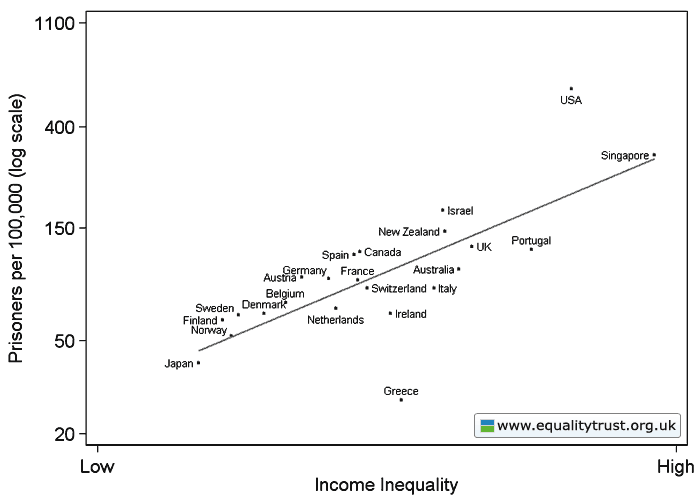
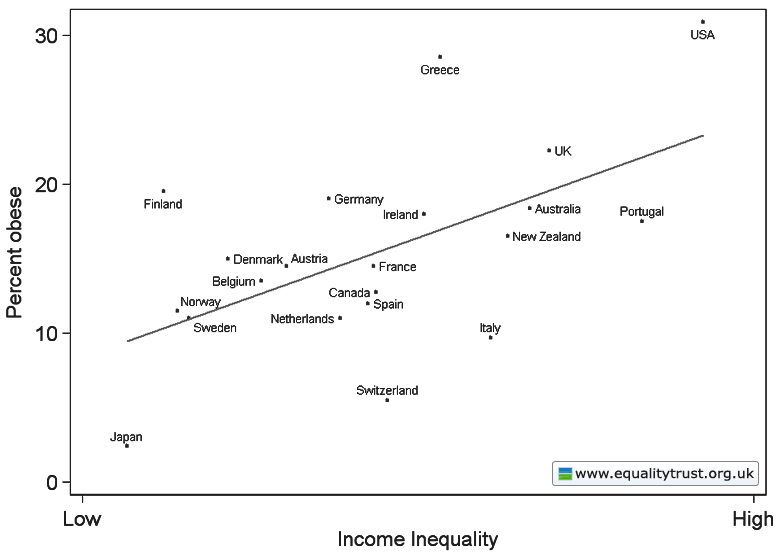
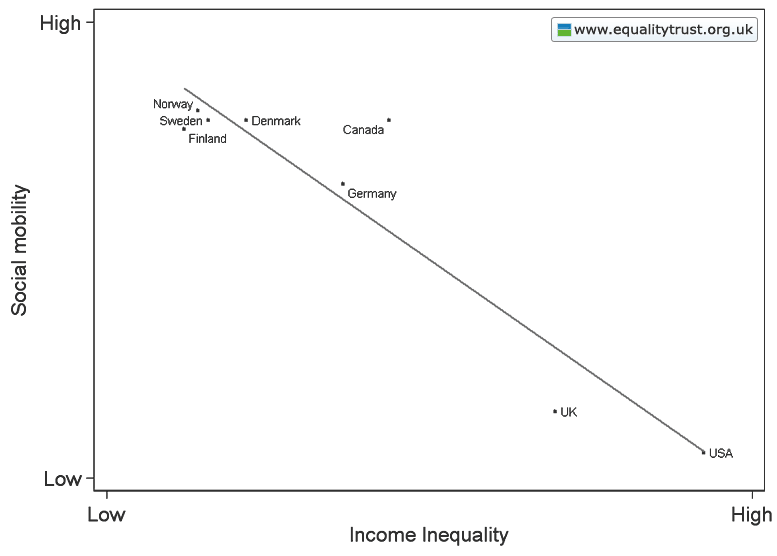
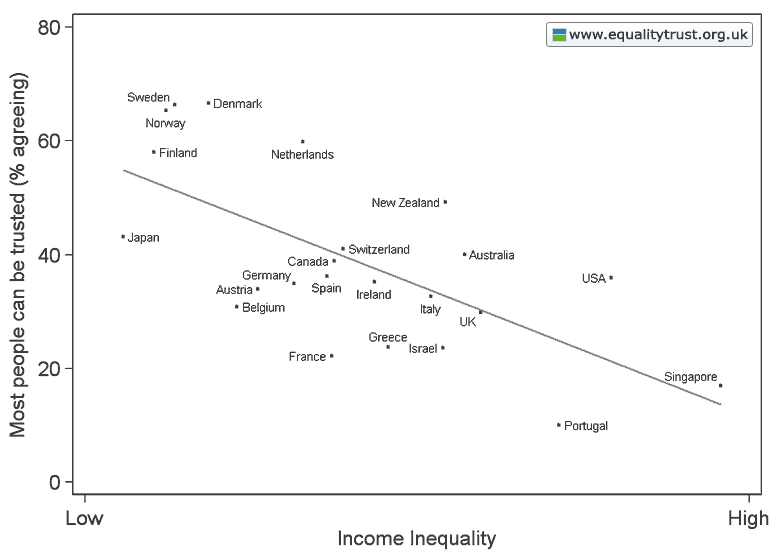
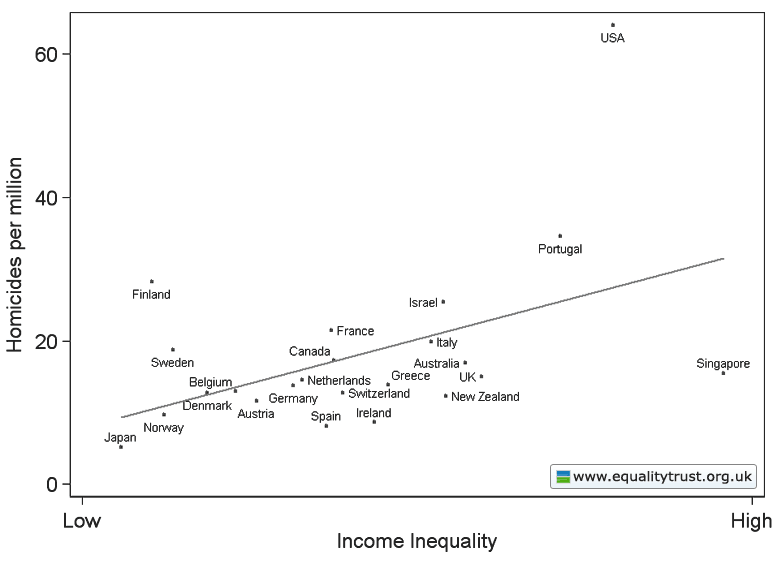
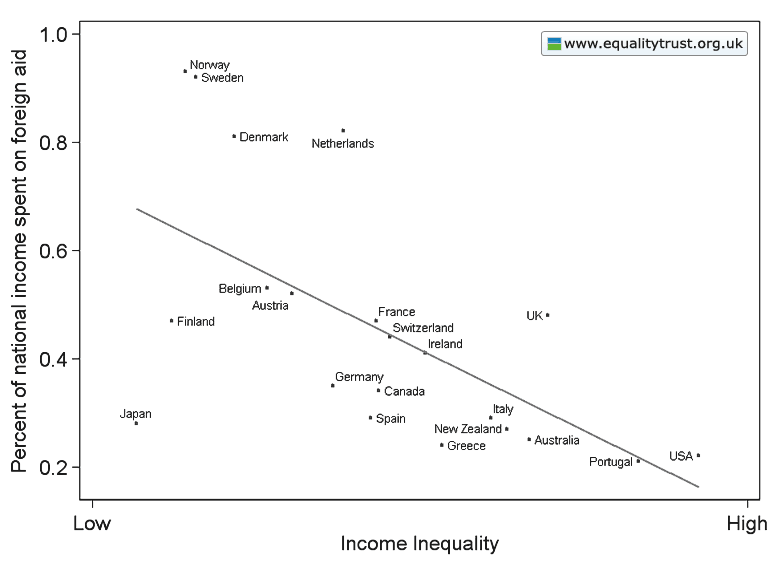
This weekend is commencement at my college, Occidental, and I thought it the perfect day to post new data on the job experiences of recent graduates. The data, a survey of 444 people in who graduated between 2007 and 2011, comes from a report out of Rutgers.
Just over half of the sample had a full-time job; 12% were un- or underemployed and looking for full-time work.
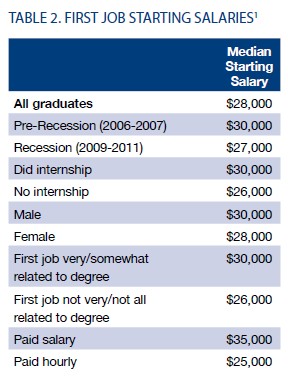
The recession appears to have depressed earnings by about $3,000. Pre-recession grads were making, on average, $30,000, while post-recession grads took in $27,000:
A third of students (35%) reported that their first job out of college was “not at all related” or “not very closely related” to their major. Almost half saw their first job as temporary and just “to get you by” (though this would drop to 36% when asked about their current job). Only half thought that their first job required a college degree.
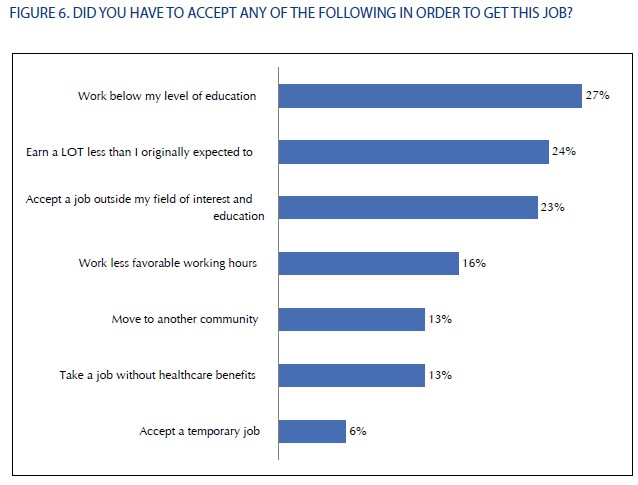
A significant proportion of students felt that they’d had to sacrifice something important to secure their job: 27% reported that they were working below their level of education, 24% took a job that paid less than they expected to earn, and 23% were working outside of their interests and training:
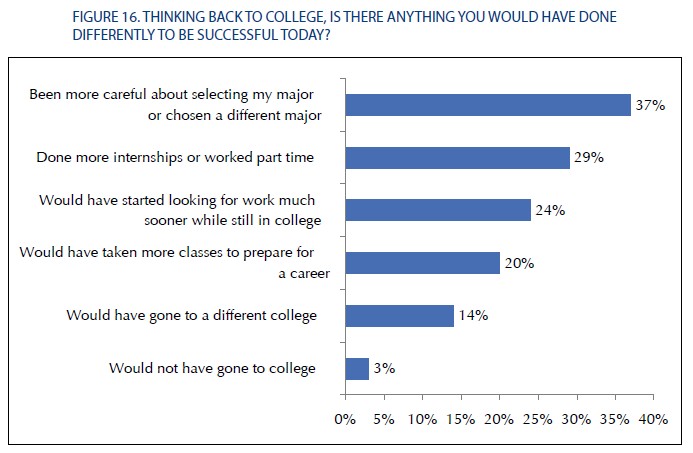
Many graduates would have done things differently. Notably a third said they would have re-thought their choice of major:
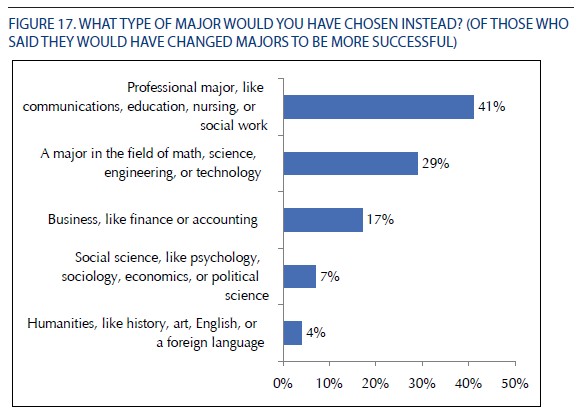
And most of them would have been more likely to have chosen a professional major (e.g., education or nursing) or one in a “STEM” field (e.g., science, technology, engineering, or math).
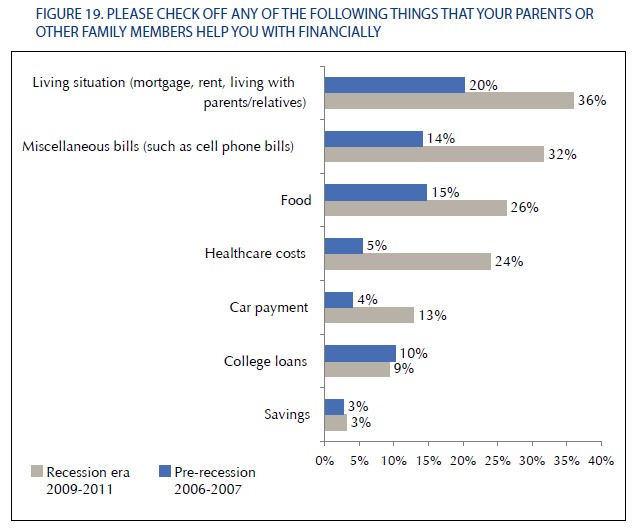
Recession-era grads are much more likely to be getting help from their parents, compared to pre-recession grads:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.