Flashback Friday.
I heard stories this week about dung beetles and cuttlefish. Both made me think about the typical stories we hear in the media about evolved human mating strategies. First, the stories:
—————————-
Story #1 :The Dung Beetle
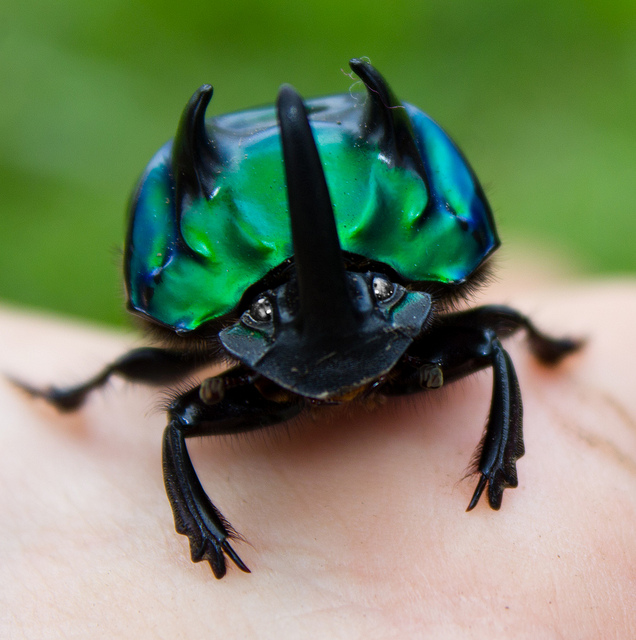

A story on Quirks and Quarks discussed the mating strategies of the dung beetle. The picture above is of a male beetle; only the males have those giant horns. He uses it to defend the entrance to a tiny burrow in which he keeps a female. He’ll violently fight off other dung beetles who try to get access to the burrow.
So far this sounds like the typical story of competitive mating that we hear all the time about all kinds of animals, right?
There’s a twist: while only male dung beetles have horns, not all males have horns. Some are completely hornless. But if horns help you win the fight, how is hornlessness being passed down genetically?
Well, it turns out that when a big ol’ horned male is fighting with some other big ol’ horned male, little hornless males sneak into burrows and mate with the females. They get discovered and booted out, of course, and the horned male will re-mate with the female with the hopes of displacing his sperm.
But.
Those little hornless males have giant testicles, way gianter than the horned males. While the horned males are putting all of their energy into growing horns, the hornless males are making sperm. So, even though they have limited access to females, they get as much mileage out of their access as they can.
The result: two distinct types of male dung beetles with two distinct mating strategies.
———————————
Story #2: The Giant Australian Cuttlefish
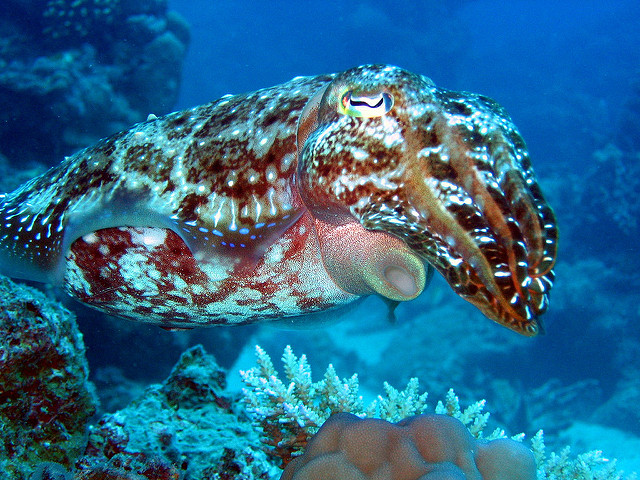

The Naked Scientists podcast featured a story about Giant Australian Cuttlefish. During mating season the male cuttlefish, much larger than the females, collect “harems” and spend their time mating and defending access. Other males try to “muscle in,” but the bigger cuttlefish “throws his weight around” to scare him off. The biggest cuttlefish wins.
So far this sounds like the typical story of competitive mating that we hear all the time about all kinds of animals, right?
Well, according The Naked Scientists story, researchers have discovered an alternative mating strategy. Small males, who are far too small to compete with large males, will pretend to be female, sneak into the defended territory, mate, and leave.
How do they do this? They change their color pattern and rearrange their tentacles in a more typical female arrangement (they didn’t specify what this was) and, well, pass. The large male thinks he’s another female. In the video below, the cuttlefish uses his ability to change the pattern on his body. He simultaneously displays a male pattern to the female and a female pattern to the large male on the other side.
———————————
So, can the crossdressing cuttlefish and dodge-y dung beetle tell us anything about evolved human mating strategies?
Probably not.
But I do think it tells us something about how we should think about evolution and the reproduction of genes. If you listen to the media cover evolutionary psychological explanations of human mating, you only hear one story about the strategies that males use to try to get sex. That story sounds a lot like the one told about the horned beetle and the large male cuttlefish.
But these species have demonstrated that there need not be only one mating strategy. In these cases, there are at least two. So, why in Darwin’s name would we assume that human beings, in all of their beautiful and incredible complexity, would only have one? Perhaps we see a diversity in types of human males (different body shapes and sizes, different intellectual gifts, etc) because there are many different ways to attract females. Maybe females see something valuable in many different kinds of males! Maybe not all females are the same!
Let’s set aside the stereotypes about men and women that media reporting on evolutionary psychology tends to reproduce and, instead, consider the possibility that human mating is at least as complex as that of dung beetles and cuttlefish.
Originally posted in 2010.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.