Cross-posted at Jezebel.
Today I have for you a round-up of ads that reinforce gendered expectations about parenting/housework — that women are predominantly responsible for them, and that moms and dads do them differently. Jennifer Thomas sent in this image from Target’s Fall 2010 coupon booklet:
She points out a couple of things. First, apparently moms buy things only for their daughters and dads buy things only for their sons. But even more interesting is what’s inside the baskets. Jennifer sums it up well:
Aside from a lamp and a soft doll, Mom’s basket…contains only domestic and “nurturing” items: detergent for baby’s delicate little clothing, diapers, infant medicine, and what looks like various cleaning sprays. Based on the contents of her basket, Mom’s role here is to care for and clean up after the child. Now take a look at Dad’s basket! I do see two bottles stuck in there [and maybe a blanket?], but more prominently displayed are chips, ice cream, and toys like a guitar and plastic golf clubs. If I had my choice based solely on this picture, I’d much rather be a dad than a mom!
Casey F. sent in an ad for the website Food on the Table, a shopping app, that clearly depicts moms as a family’s shopper:
And Eve P. and Kyle H. let us know about Amazon’s new Amazon Mom program:
Kyle was invited to join because he’d been busy ordering lots of stuff for his new child. Interestingly, despite its name, Amazon stresses that the program is for all parents and caregivers. Here’s a partial screenshot of the info page:
Part of the text:
Amazon Mom is open to anyone who is responsible for caring for a baby or young child–“Amazon Primary Caregiver” just didn’t have the same ring to it. Kidding aside, we chose this name because we noticed moms in social communities (like our Amazon discussion boards) looking to connect and share information about products and problems with other moms. We wanted a name that would let these groups know that this program was created with their unique needs in mind.
I suppose they’re right, “Amazon Primary Caregiver” is a mouthful. But what I find interesting is the way we accept the conflation of “parent” or “caregiver” with “mom” in a way that we don’t do with “dad.”
Finally, Kate H. sent in this Clorox ad, which reinforces the idea that women clean while men (are often incompetent fools who) need cleaned up after:
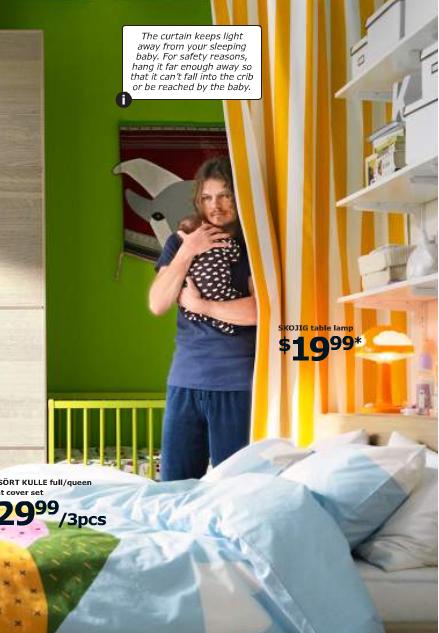
Leigh K., however, found an exception. A recent IKEA catalog included a number of images of men caring for both male and female children. This first one somewhat reinforces the “men can’t parent unsupervised!” trope, what with the kid on the left drawing on the door. Reader Elena says that’s probably meant to be a door painted with the chalkboard paint so it’s totally ok, and I do recall seeing a couple of other pages with kids using chalk, so nevermind my point there:
These two dads seem capable of parenting without any clear signs of disaster:
Leigh suggests that the images of involved, competent fatherhood might be the result of IKEA being a Swedish company. It’s possible that there’s an intentional ideological effort here to present men as caretakers (there is also at least one image of boys and girls playing with toys usually associated with the other gender). But also, IKEA markets itself as a somewhat youthful, hip brand, and showing non-traditional gender roles may fit well with that marketing strategy regardless of whatever larger social commitments to gender equality anyone at the company may or may not have. Whatever the reason behind it, the catalog — from a very large, profitable business (that apparently pays very little in taxes) — indicates that at least some companies think you can choose not to reinforce gendered parenting stereotypes and still manage to sell stuff.