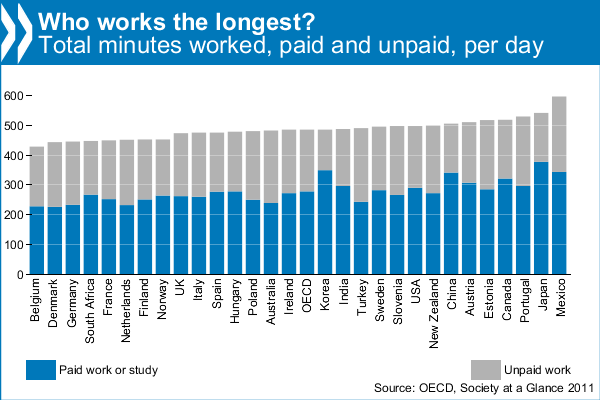
Note: Since I posted this, Philip Cohen has brought up concerns about the National Marriage Project’s data and analysis in another study. You might want to take a look at his post.
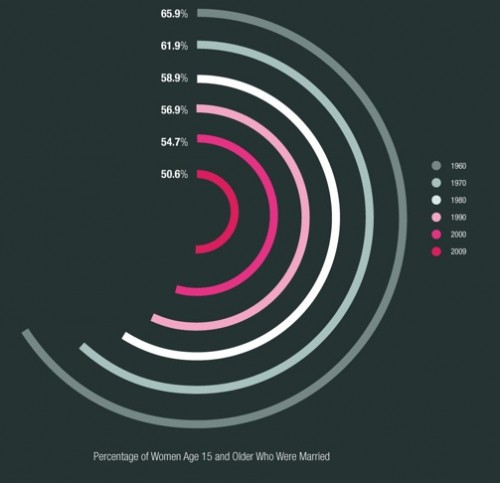
Patricia P. sent in an infographic illustrating trends in marriage, divorce, and cohabitation over the last several decades, based on data from the National Marriage Project at the University of Virginia. I found several of the images to be a bit cluttered and unclear, but this one neatly summarizes the percent of women over age 15 who were currently married, 1960-2009:
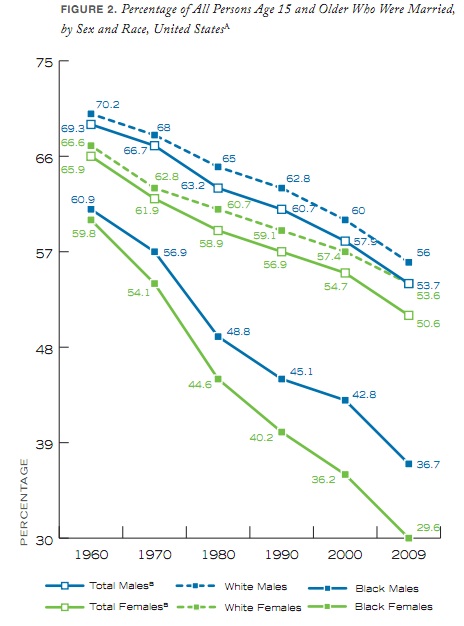
I looked through the full 2010 The State of Our Unions report. This graph, showing the percent of those aged 15 or older who were married from 1960-2009, shows that marriage has become less common for both men and women, Blacks and Whites (based on U.S. Census Data):
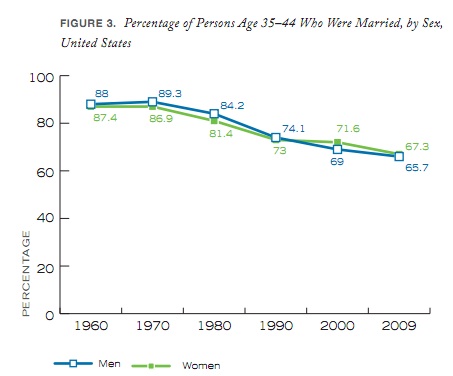
Of course, this is in large part because people in the U.S. are getting married later; not only do we not really expect a 15-year-old to be married, we’d be rather horrified if they were. If we look only at adults aged 35-44, we do see a significant decrease in marriage between 1960 and 2009, but still, about 2/3 were married:
The report also includes a graph of the percent chance that a couple will divorce or separate within 10 years, broken down by education, for the early ’70s and the late ’90s (for first-marriage couples only). Least educated is defined as having less than a high school diploma; the moderately educated graduated high school but have less than a 4-year college degree; and the highly educated have a 4-year college degree or more:
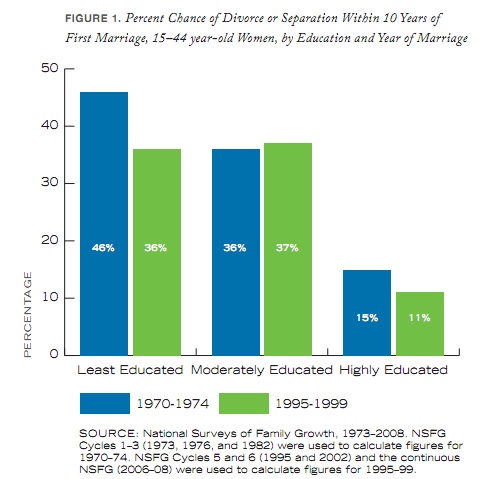
Note that for both the least and most educated, the risk of divorce actually went down — though those with the least education are over three times as likely to separate/divorce than the highly educated.
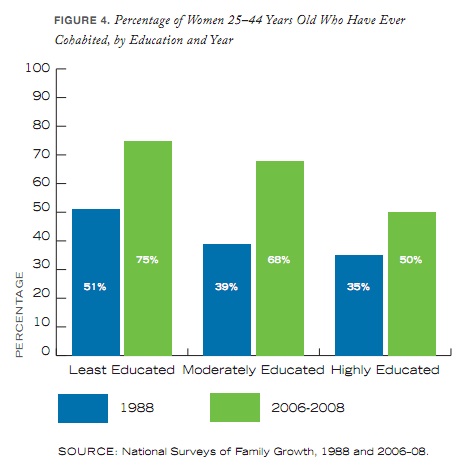
On the other hand, rates of cohabitation have gone up:
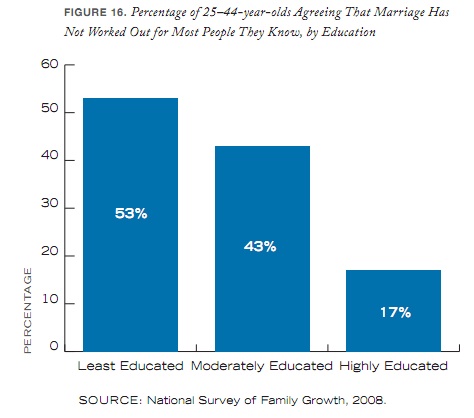
Perceptions of marriage, not surprisingly, also vary by educational level, with the highly educated feeling significantly more positively about marriage than the less educated population. Asked if they agreed that marriage hadn’t worked out for “most people” they know, 53% of the least educated and 43% of the moderately educated said yes, while only 17% of those with at least college degrees felt similarly:
So the overall trend appears to be a growing gap between the highly educated and those with less than a 4-year college degree, with the moderately educated looking more similar to those with less than a high school diploma in terms of their marriage, divorce, and cohabitation behaviors. If you’re interested in this topic, check out the full report.