When my primary care physician, a wonderful doctor, told me he was retiring, he said, “I just can’t practice medicine anymore the way I want to.” It wasn’t the government or malpractice lawyers. It was the insurance companies.
This was long before Obamacare. It was back when President W was telling us that “America has the best health care system in the world”; back when “the best” meant spending twice as much as other developed countries and getting health outcomes that were no better and by some measures worse. (That’s still true).
Many critics then blamed the insurance companies, whose administrative costs were so much higher than those of public health care, including our own Medicare. Some of that money went to employees whose job it was to increase insurers’ profits by not paying claims. Back then we learned the word “rescission” — finding a pretext for cancelling the coverage of people whose medical bills were too high. Insurance company executives, summoned to Congressional hearings, stood their ground and offered some misleading statistics.
None of the Congressional representatives on the committee asked the execs how much they were getting paid. Maybe they should have.
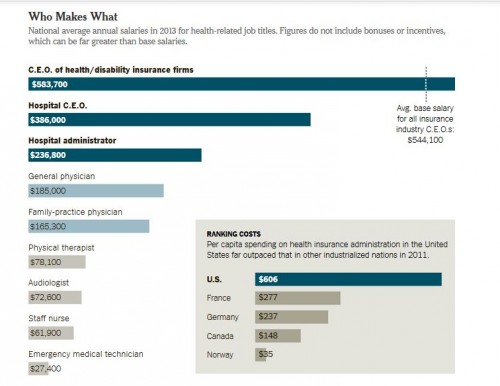
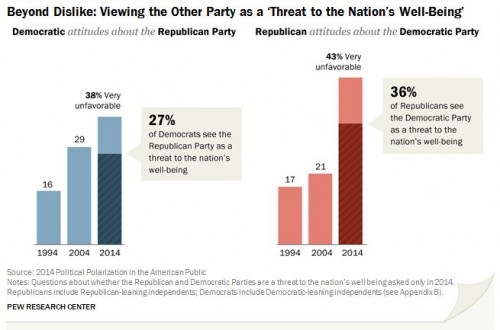
Health care in the U.S. is a $2.7 trillion dollar business, and the New York Times has an article about who’s getting the big bucks. Not the doctors, it turns out. And certainly not the people who have the most contact with sick people — nurses, EMTs, and those further down the chain. Here’s the chart from the article, with an inset showing those administrative costs.
As fine print at the top of the chart says, these are just salaries — walking-around money an exec gets for showing up. The real money is in the options and incentives.
In a deal that is not unusual in the industry, Mark T. Bertolini, the chief executive of Aetna, earned a salary of about $977,000 in 2012 but a total compensation package of over $36 million, the bulk of it from stocks vested and options he exercised that year.
The anti-Obamacare rhetoric has railed against a “government takeover” of medicine. It is, of course, no such thing. Obama had to remove the “public option”; Republicans prevented the government from fielding a team and getting into the game. Instead, we have had an insurance company takeover of medicine. It’s not the government that’s coming between doctor and patient, it’s the insurance companies. Those dreaded “bureaucrats” aren’t working for the government of the people, by the people, and for the people. They’ve working for Aetna and Well-Point.
Even the doctors now sense that they too are merely working for The Man.
Doctors are beginning to push back: Last month, 75 doctors in northern Wisconsin [demanded] . . . health reforms . . . requiring that 95 percent of insurance premiums be used on medical care. The movement was ignited when a surgeon, Dr. Hans Rechsteiner, discovered that a brief outpatient appendectomy he had performed for a fee of $1,700 generated over $12,000 in hospital bills, including $6,500 for operating room and recovery room charges.
That $12,000 tab, for what it’s worth, is slightly under the U.S. average.
Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.