An extended version of this post also appeared at Ms.
I’ve been taking photographs of breast-cancer-research-and-prevention-branded products for a few months now. I was first driven to do so when I saw this at the Million Aire (private plane terminal) at the Burbank airport:
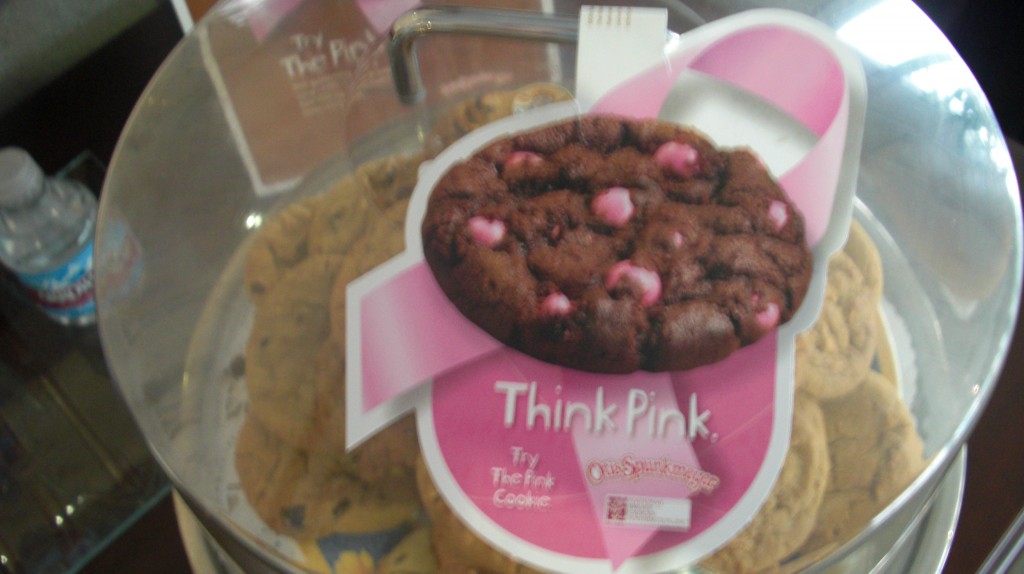

That’s right. You are looking at pink chocolate chips cooked into cookies to signify a commitment to reducing breast cancer-related morbidity and mortality.
Anti-breast cancer messages are, I think inarguably, the most widely product-linked disease-related message ever. I am constantly shocked by how many products have a breast cancer version. Here are some pictures I’ve taken over the last few months.
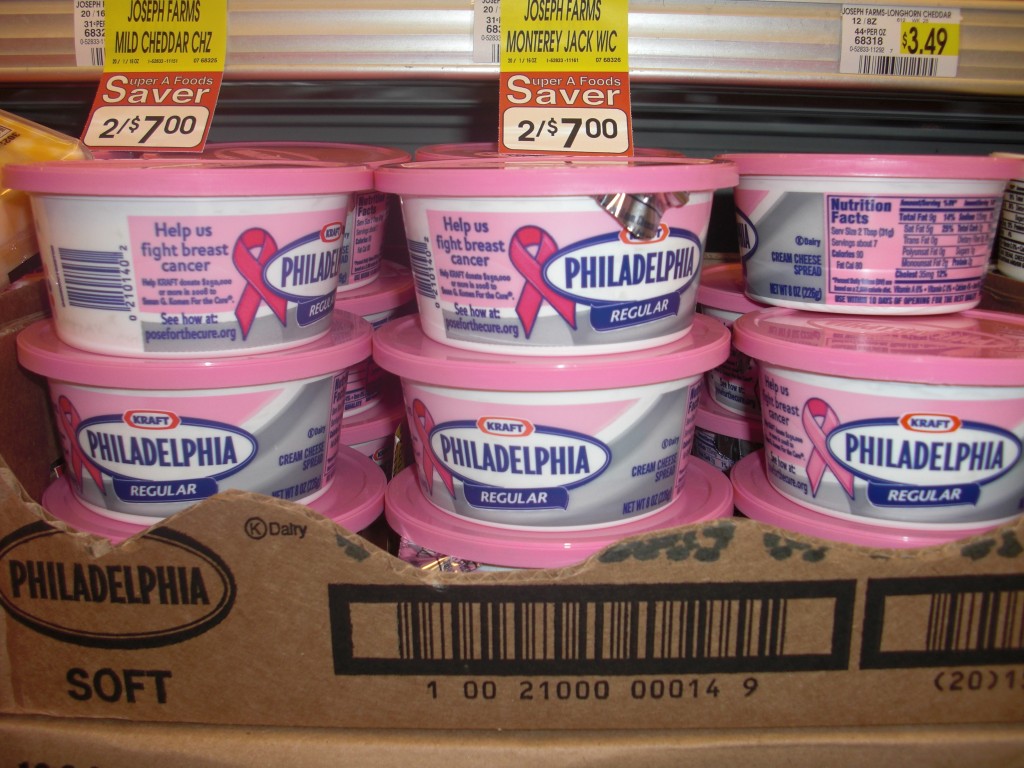
Cream cheese:

Padlock:

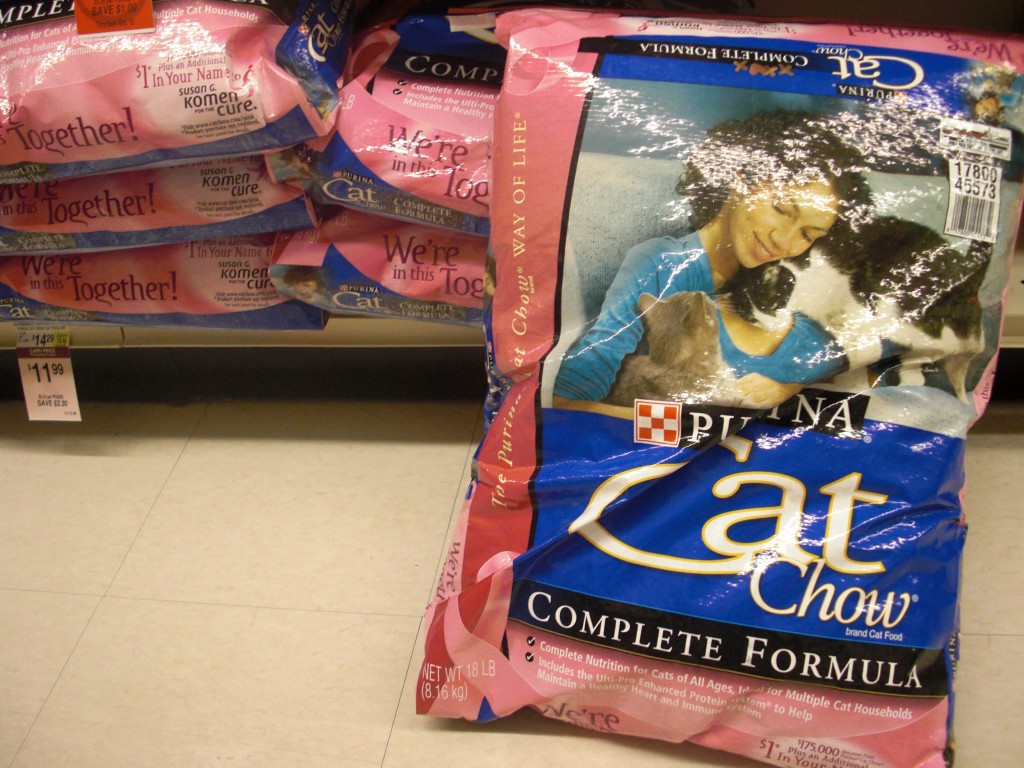
Cat food:

Gum:

Golf balls and tees:

Pots and pans:

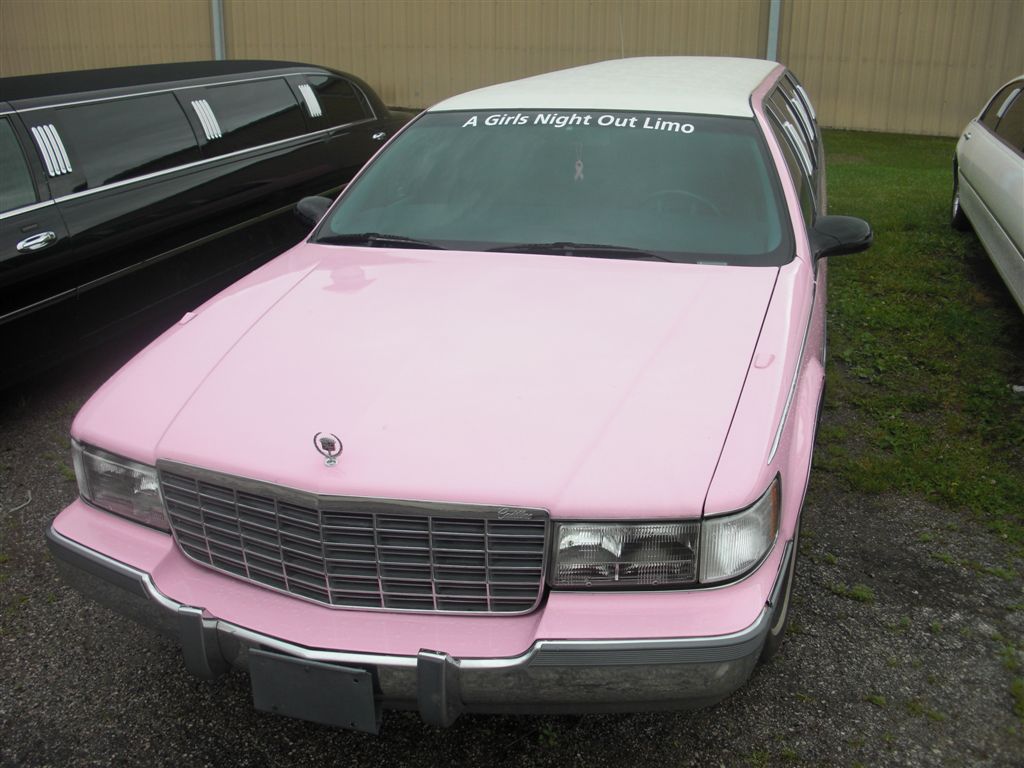
Steve W. sent in this picture of a pink “ladies night out” breast cancer-themed limo (note the pink ribbon hanging from the rear view mirror):

NEW (May ’10)! Renée Y. sent along this photo of breast cancer-awareness-themed grape tomatoes. I repeat: grape tomatoes.

We’ve discussed the commodification of activism extensively (see here, here, here, here, and here) and so I’m going to skip this point. Instead, I’d like the ask the following:
What does it mean when awareness of and funding for disease is subject to marketing? Is this really the most efficient or rational way to set health care priorities? I did a bit of research.
According to the CDC (2005 seems to be the latest available data), cancer is not the leading cause of death. Heart disease is the leading cause of death. Granted, cancer is a close second. In 2005, 652,091 people died of heart disease and 559,312 died of cancer. But not breast cancer, all cancers. In 2005, 49,491 people died of breast cancer. More than 10 times as many people died of heart disease.
And, if you want to prioritize cancers, more people are diagnosed with prostate cancer than breast cancer (source) and more people die from lung cancer (159,292), colon, rectal, or anal cancer (53,252), and lymphoid/hematopoietic cancers (55,028) (source).
So why such an emphasis on breast cancer? I’m not sure why. Certainly there is a massive social movement organization behind this anti-breast cancer marketing and people in charge have made a decision to take this approach. I think, also, the body parts and the presumed cause of disease matter. Do we have less sympathy (and would, therefore, a similar marketing campaign be less effective) for lung cancer because we think that lung cancer patients are to blame for their own disease? Would we find colo-rectal-anal cancer-themed cream cheese somehow less appetizing? Or prostate cancer-themed gum? Do lymphoid and hematopoietic cancers affect parts of the body that are simply less iconic?

“Save the lymph nodes” just doesn’t have quite the same ring?
I’m not trying to suggest that raising awareness of and funding research for breast cancer isn’t important, but I am interested in the strategies by which being “against” breast cancer is (literally) sold to us. And I’m curious about how this affects treatment and research funding, if at all, and the rationality of our resource distribution given the application of a marketing approach to (some) diseases (and not others). (Also in breast cancer marketing, see here, here, here, here, and here.)
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.