Claude Fischer, author of Made in America (the blog and the book), recently posted about the trend in IQ test scores among Americans. He explains:
In general, contemporary Americans – and westerners in general – score higher than did people in the early- and mid-twentieth century… Indeed, there have been “massive gains” in scores over the twentieth century. This increase has been called the “Flynn Effect” after the scholar who first noted it.
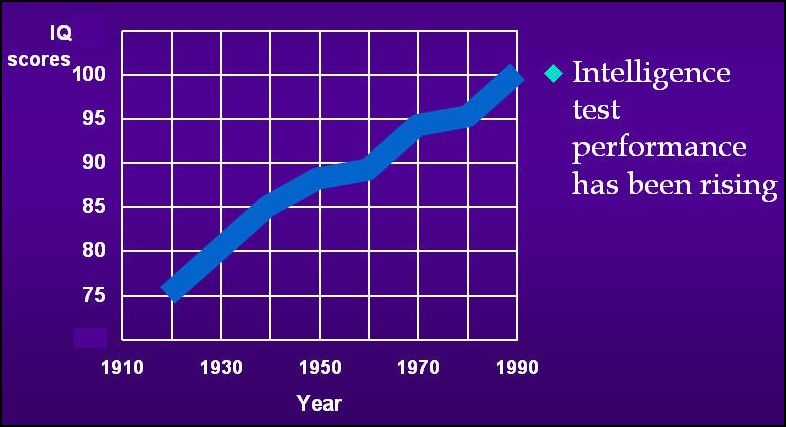
Fischer argues that the rise in intelligence test scores reflects training in abstract cognitive tasks (both in school and out) and improved health and nutrition:
Over the years, more Americans have become more extensively “trained” – knowingly or not – in the cognitive skills these tests measure, such as reading and decoding visual abstractions. Consider how modern children learn to “get” the alternating perspectives and visual meanings in television, video games, commercial logos, traffic signals, and the like… And modern children encounter far more writing, from schoolbooks to billboards to Facebook entries, than their ancestors did…
Another sort of explanation stresses improved health and nutrition, particularly in the womb and early in life. Not just sufficient calories, but sufficient nutrients like iodine and Vitamin C, are critical to growing minds (see, e.g., here.) Similarly, exposure to toxins, notably to lead in old paint and gasoline, reduces children’s cognitive skills. Thus, improved nutrition and health over the 20th century could explain some or all of the increase.
The rise in intelligence scores and the influence of our environments, suggests an interactive relationship between biology and society. We often think that intelligence is somehow “innate,” as if we are born with a certain IQ that is more or less inflexible. These scores suggest, however, that our potential for abstract thought, though it may be located in the biological matter of the brain, is actually quite malleable.
This, of course, is helpful for understanding differences in cognitive ability by socioeconomic class at one point in time, as well as historical changes.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.