Everyone has been talking about last week’s Senate testimony from Christine Blasey Ford and Supreme Court nominee Brett Kavanaugh. Amid the social media chatter, I was struck by this infographic from an article at Vox: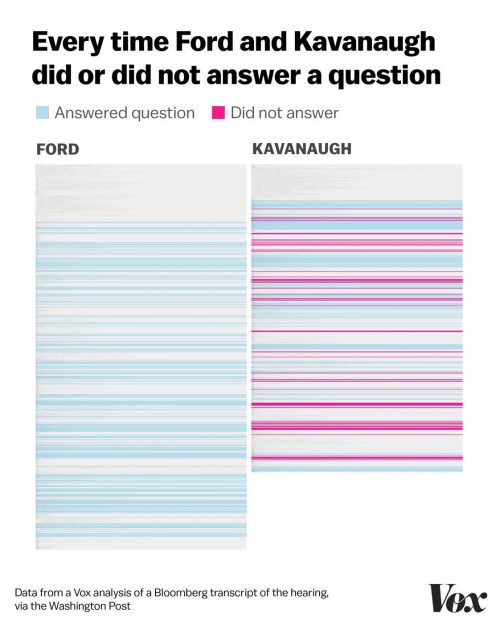
Commentators have noted the emotional contrast between Ford and Kavanaugh’s testimony and observed that Kavanaugh’s anger is a strategic move in a culture that is used to discouraging emotional expression from men and judging it harshly from women. Alongside the anger, this chart also shows us a gendered pattern in who gets to change the topic of conversation—or disregard it altogether.
Sociologists use conversation analysis to study how social forces shape our small, everyday interactions. One example is “uptalk,” a gendered pattern of pitched-up speech that conveys different meanings when men and women use it. Are men more likely to change the subject or ignore the topic of conversation? Two experimental conversation studies from American Sociological Review shed light on what could be happening here and show a way forward.
In a 1994 study that put men and women into different leadership roles, Cathryn Johnson found that participants’ status had a stronger effect on their speech patterns, while gender was more closely associated with nonverbal interactions. In a second study from 2001, Dina G. Okamoto and Lynn Smith-Lovin looked directly at changing the topic of conversation and did not find strong differences across the gender of participants. However, they did find an effect where men following male speakers were less likely to change the topic, concluding “men, as high-status actors, can more legitimately evaluate the contributions of others and, in particular, can more readily dismiss the contributions of women” (Pp. 867).

The important takeaway here is not that gender “doesn’t matter” in everyday conversation. It is that gender can have indirect influences on who carries social status into a conversation, and we can balance that influence by paying attention to who has the authority to speak and when. By consciously changing status dynamics —possibly by changing who is in the room or by calling out rule-breaking behavior—we can work to fix imbalances in who has to have the tough conversations.
Evan Stewart is an assistant professor of sociology at University of Massachusetts Boston. You can follow his work at his website, or on BlueSky.
Comments 10
sandra hamlin — December 17, 2018
My goodness how can anyone focus on the discussion when the fashion is impacting her ability to present a smooth argumentative debate
Ekspedisi Surabaya Ke Sulawesi Selatan — August 9, 2020
Trouble Is My Business 2018 is a neo noir/film noir style starring Tom Konkle,Brittney PowellThis is a masterpiece movie
a great film.A wonderful noir story,I grew instantly
a knew and true appreciation for this epic film noir/neo
noir film, and the back ground music is fantastic.This
timeless masterpiece film into the noir world it's going to be a classic movie,
a true epic film with wonderful true drama noir style actors.
For screenwriters who come across this, take the following pointers on board:Contrasting Characters:
This great film has great characters and true drama noir
style actors distinction and this film has all of
that and very much more.Trouble Is My Business
starring Tom Konkle,Brittney PowellThis neo noir film style is going to be one
of the classic movie of all times that will continue to
live with humanity,thoughout every generation and they will
all say, "Oh that was 10 out of 10,with two thumbs up"..When you watch this film you will know the
world inside of being a private eye and the smarts that
goes along with it,in fact smartness is the only thing that
can keep them alive in most cases. I've seen this film
several times, and want to be captured by its spell every time.I enjoyed this film and adore all things about film noirs and neo noirs and
bow down in awe to the film's wonderful cast.Writers/Actors:
Tom Konkle,Brittney Powell are truly great in this film together.Director:Tom Konkle is a
great director,the camera shows just how emotional the life of a
detective real is and brings out true noir style.Detective
Roland Drake(Tom Konkle) falls for two sisters from the Montemar family.
One woman is dead and the other wants to kill him.Families will talk about the differences between movies made within the last few years and movies of the 1940s
like The Big Sleep and other film noirs.This neo film is
a marvel of convoluted, unexplained plot threads that miraculously add up to one of the great pleasures of cinema.
Usually categorized under the film noir umbrella for its shadowy photography and emphasis on the menace of the underworld,
"Trouble Is My Business" mixes its cynicism with enough dry humor to almost lend it a sense
of optimism.The bad guys go down and the detective gets the
girl,even if it's not entirely clear whether she's trustworthy.The real treat is Tom Konkle,who seems game to play tough guy but also self-deprecating role.A true wonderful actor.The movie is a great example of the importance of emphasis and editing with a great story line.
"Trouble Is My Business" Passion, murder,and betrayal,just another
day at the officeis a must see either on the big screen or on dvd.You will not be disappointed and you will want more
after seeing this film.
Ekspedisi surabaya — April 22, 2021
Nice article
Max Harding — March 29, 2022
I was recently talking to a friend who is a senior executive at one of the most important companies in the world. He's very, very smart and very busy. We talked about what it's like to be considered an expert in business, and how that changes things. One thing he said was that if you're perceived as a person of influence, people are much more likely to let you change the subject when you want to. So, I hired professional bio writing services to write more about it as it seems interesting. If you're an important person with a lot going on — and if you can project as much — people will tend to let you get away with changing the subject.
David Willy — April 4, 2022
Thanks for sharing [this](http://www.google.com) article.
Maxyc — July 27, 2022
I used to trust complex tasks to professionals too, especially if there is no time at all.
Bartholome Bradtke — November 26, 2023
I will refrain from engaging in any further discussion and patiently await the outcome of the vote in geometry dash 23.
Mark Spitz — August 8, 2024
The variety of games available on papa's games is truly impressive!
Jack Son — June 17, 2025
The players of Templer Run have access to a variety of goods, such as bulletproof masks, speed boosts, and high leaps, which enable them to run faster and conquer obstacles more successfully in the exciting race that never ends.
Dinosaur Game — July 2, 2025
That sounds like a fun, old-school detective flick! I love movies that don't take themselves too seriously. Tom Konkle sounds fantastic. Sometimes, when I'm feeling stressed at work and need a quick mental break, I play the Dinosaur Game on Chrome. It's surprisingly absorbing and helps me reset. I might need to add "Trouble Is My Business" to my watchlist for a more cinematic escape!