The dominant firms in the U.S. and other major capitalist counties are happily making profits, but they aren’t interested in investing them in new plants and equipment that increase productivity and create jobs. Rather they prefer to use their earnings to acquire other firms, reward their managers and shareholders, or increase their holdings of cash and other financial assets.
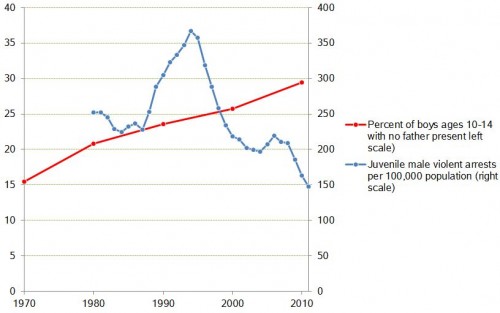
The chart below, taken from a Michael Burke post in the Irish Left Review, shows trends in both U.S profits and investment .
As you can see the increase in profits (in orange) has swamped the increase in investment (in blue) over the relevant time period; in fact, investment in current dollars has actually been falling.
Looking at the ratio between these two variables helps us see even more clearly the growth in firm reluctance to channel profits into investment. The investment ratio (investment/profits) was 62% in 1971, peaked at 69% in 1979, fell to 61% in 2000 and 56% in 2008, and dropped to an even lower 46% in 2012.
According to Burke, if U.S. firms were simply to invest at the level they did in 1979, not even the peak, the increase in investment in the American economy would exceed $1.5 trillion, close to 10% of GDP.
The same dynamic is observable in the other main capitalist economies:
In 1995 the investment ratio in the Euro Area was 51.7% and by 2008 it was 53.2%. It fell to 47.1% in 2012. In Britain the investment ratio peaked at 76% in 1975 but by 2008 had fallen to 53%. In 2012 it was just 42.9% (OECD data).
So what are firms doing with their money? As Burke explains:
The uninvested portion of firms’ surplus essentially has only two destinations, either as a return to the holders of capital (both bondholders and shareholders), or is hoarded in the form of financial assets. In the case of the U.S. and other leading capitalist economies both phenomena have been observed. The nominal returns to capital have risen (even while the investment ratio has fallen) and financial assets including cash balances have also risen.
So, with firms seeing no privately profitable outlet for their funds, despite great societal needs, their owners appear content to reward themselves and sock away the rest in the financial system. In many ways this turns out to be a self-reinforcing dynamic. No wonder things are so bad for so many.
Cross-posted at Reports from the Economic Front.
Martin Hart-Landsberg is a professor of economics at Lewis and Clark College. You can follow him at Reports from the Economic Front.