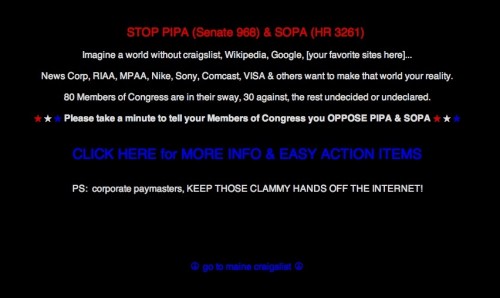
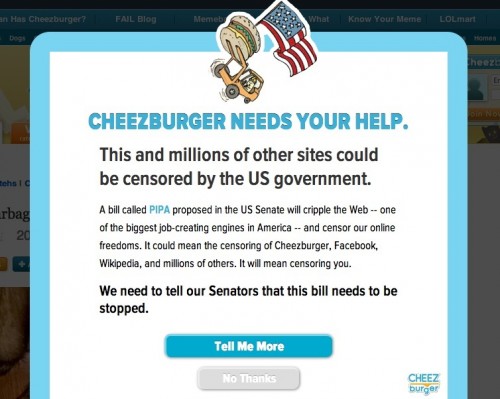
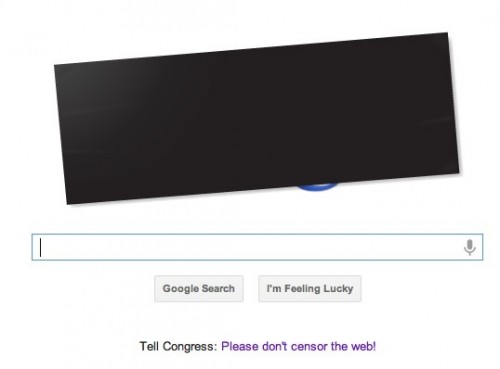
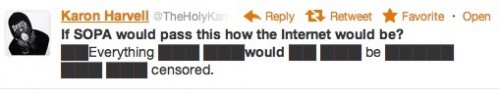
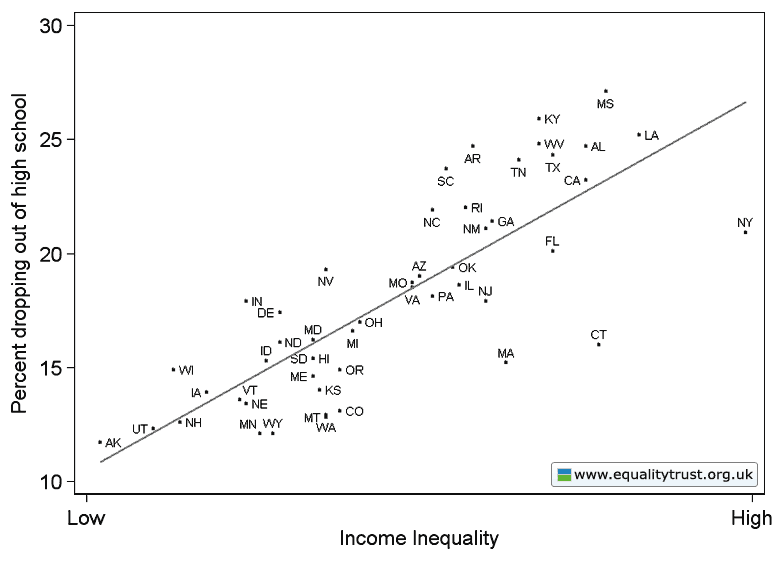
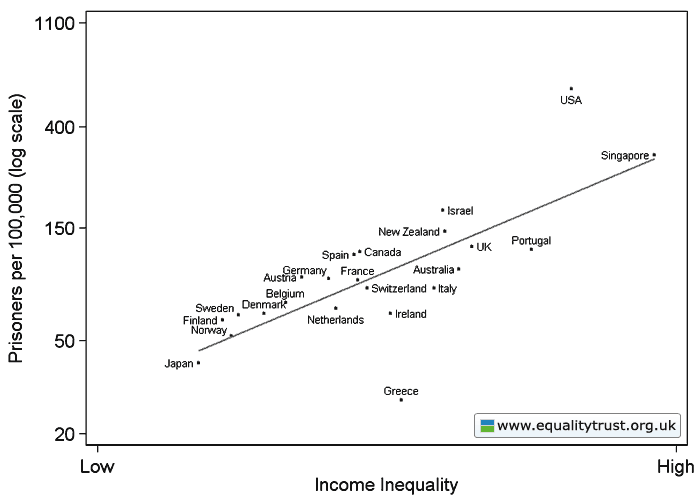
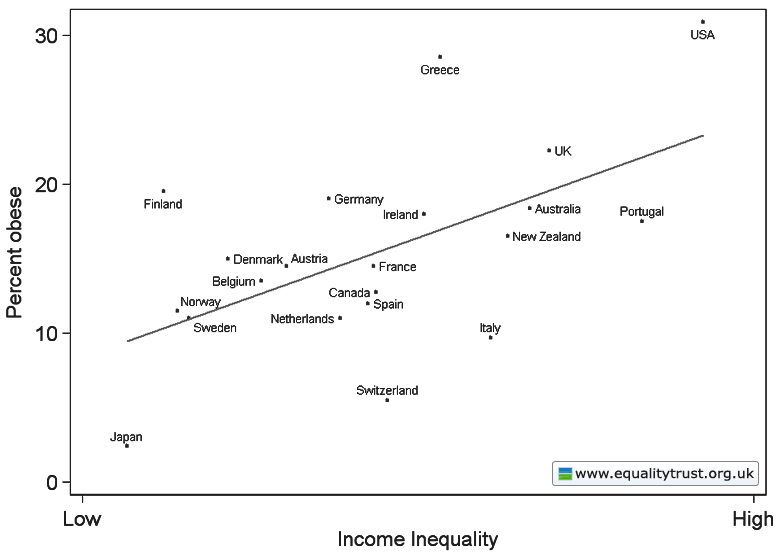
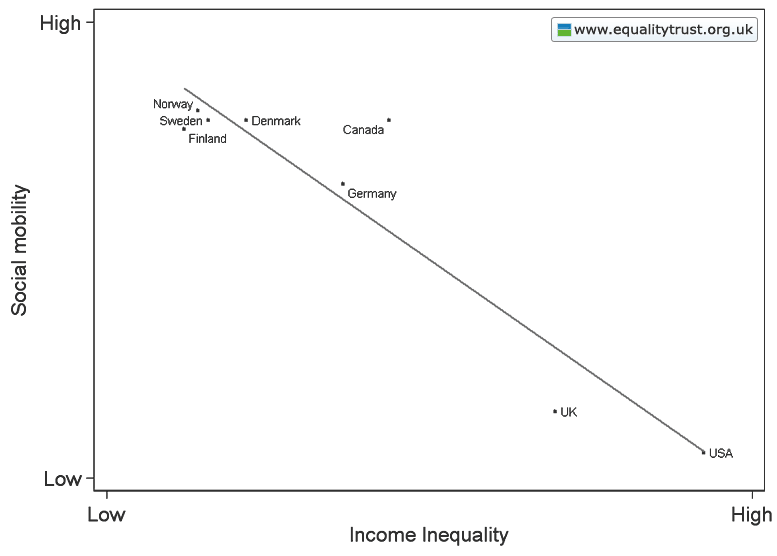
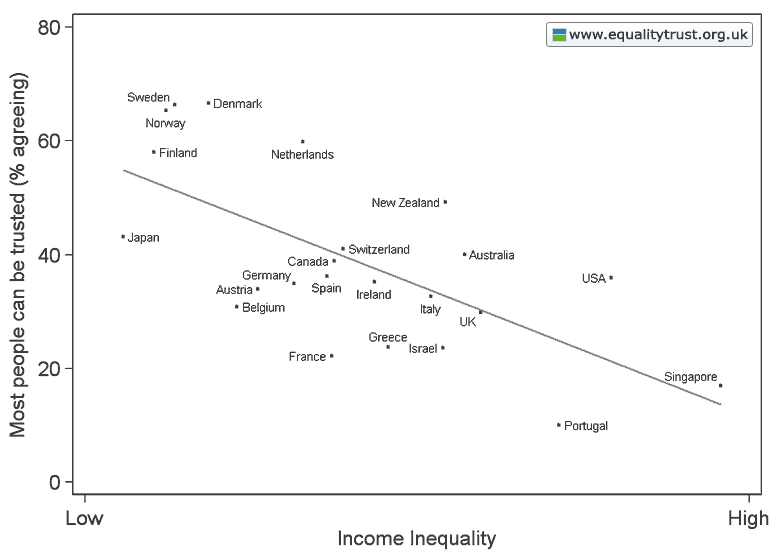
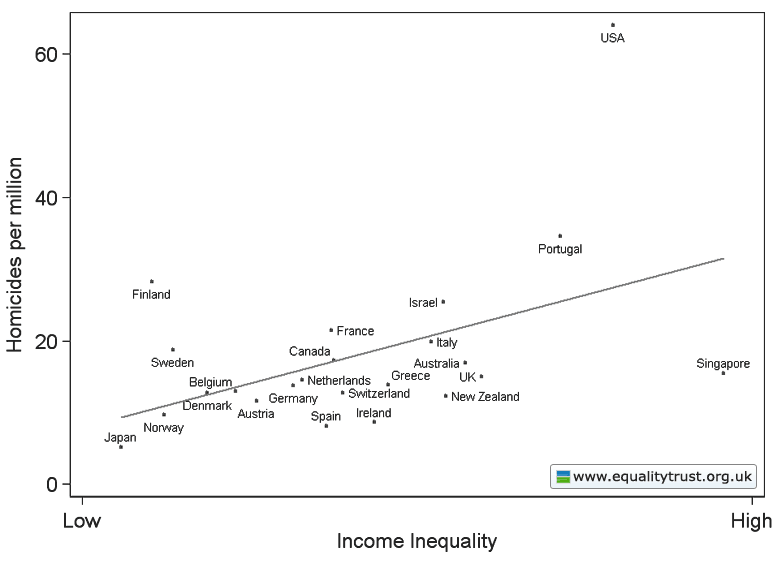
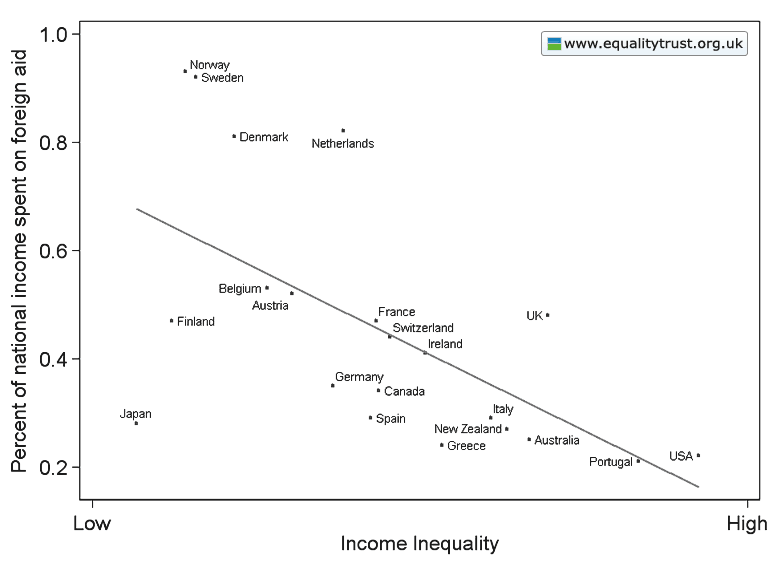
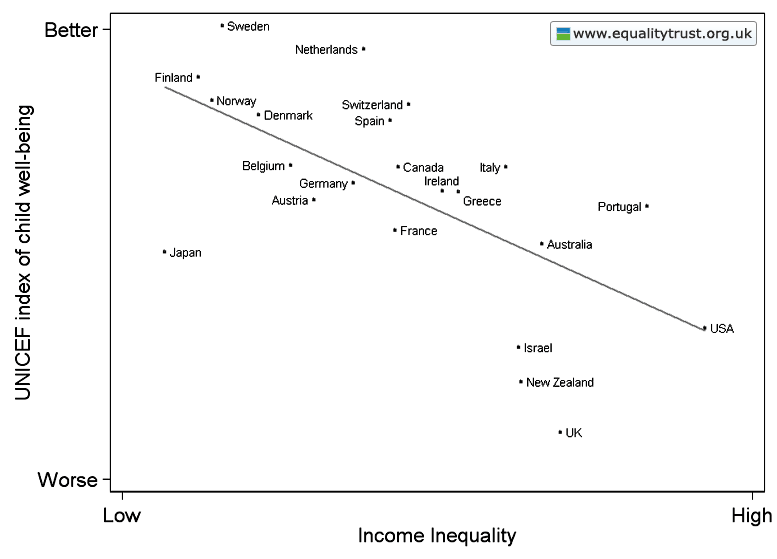
Dr. Bethany Pope sent in a segment from a National Geographic show about animals’ sexual behavior. The clip is an amazingly gendered discussion, describing animals’ motivations and behaviors through the lens of what is considered normative masculine and feminine sexual behavior, the correct place of males and females in the social hierarchy, and the assumption that males and females are locked in a zero-sum game. The anthropomorphizing of other species begins at the outset, when we learn female hyenas want “more than equal rights, they want to beat males at their own game.” In fact, “Africa’s plains are among the most macho places on earth…they’re testosterone-fueled battlefields,” filled with “swaggering” males. Bethany sums up the tone regarding hyenas, saying, “The documentary presents them as an abomination, usurping male gender roles.” Indeed, at about a minute in we learn that hyenas “seem mixed up.” A hyena “swaggers,” “confident” and “cocksure,” its penis swinging “low and proud.” But what’s this? The swaggering, cocksure hunter “has a secret”! That’s not a penis, it’s an enlarged clitoris; our hero is a she! Not only that, there’s not a penis anywhere to be found, as this is an all-female pack; “these female are some of the most masculine in the world — and they like to sniff each other an awful lot, too. Compounding the “confusion,” they have a “bulging” sac, like a scrotum. And not only are female hyenas masculinized, but the poor males are emasculated, reduced to being “subservient, servile, and scared.” It is rather stunning example of anthropomorphizing the natural world and applying gendered norms of sexuality to other species, and worth sitting through the full six minutes to get the full effect (the video might not be safe for some workplaces; there are a lot of lingering shots of penises and clitorises. A lot.):
Dr. Bethany Pope sent in a segment from a National Geographic show about animals’ sexual behavior. The clip is an amazingly gendered discussion, describing animals’ motivations and behaviors through the lens of what is considered normative masculine and feminine sexual behavior, the correct place of males and females in the social hierarchy, and the assumption that males and females are locked in a zero-sum game. The anthropomorphizing of other species begins at the outset, when we learn female hyenas want “more than equal rights, they want to beat males at their own game.” In fact, “Africa’s plains are among the most macho places on earth…they’re testosterone-fueled battlefields,” filled with “swaggering” males. Bethany sums up the tone regarding hyenas, saying, “The documentary presents them as an abomination, usurping male gender roles.” Indeed, at about a minute in we learn that hyenas “seem mixed up.” A hyena “swaggers,” “confident” and “cocksure,” its penis swinging “low and proud.” But what’s this? The swaggering, cocksure hunter “has a secret”! That’s not a penis, it’s an enlarged clitoris; our hero is a she! Not only that, there’s not a penis anywhere to be found, as this is an all-female pack; “these female are some of the most masculine in the world — and they like to sniff each other an awful lot, too. Compounding the “confusion,” they have a “bulging” sac, like a scrotum. And not only are female hyenas masculinized, but the poor males are emasculated, reduced to being “subservient, servile, and scared.” It is rather stunning example of anthropomorphizing the natural world and applying gendered norms of sexuality to other species, and worth sitting through the full six minutes to get the full effect (the video might not be safe for some workplaces; there are a lot of lingering shots of penises and clitorises. A lot.):
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.