Today I bring you one example of how medical technology and body modification are converging.
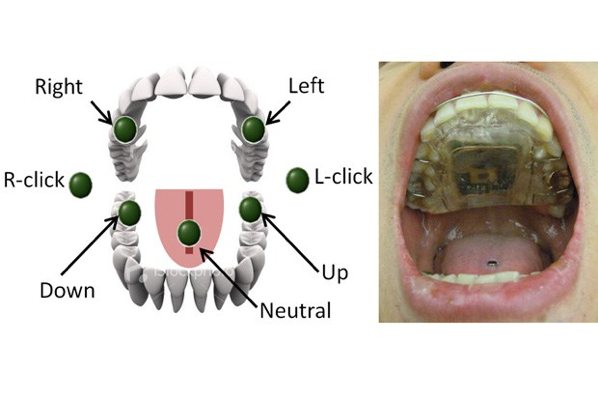
The image above comes from the Georgia Institute of Technology, where they have engineered a new form of wheelchair mobility through the use of a tongue piercing. The Tongue Drive System uses a dental plate that captures the movement of the tongue piercing below, which is fashioned with a tiny magnet on top. more...