When thinking about how media coverage affects public perceptions, many people think of it in terms of an “injection model”–that is, media outlets “inject” ideas into a passive public, directly affecting what they think (or, anyway, what everyone else thinks, since most people are convinced that they personally aren’t affected). Many researchers have argued this model depicts media audiences as having little agency when it comes to interpreting things they read or hear. People do ultimately decide what they think of issues, though the media play a large role in defining what issues are worth thinking about.
I have spent the last several days being mystified and annoyed by the number of news stories I’ve heard about Tiger Woods and his wreck and apparent affairs. I do not understand why this is national (and even international) news, and why news outlets from Fox to NPR found it worthwhile to have on commentators to talk about the fact that an athlete cheated on his wife.
Upon hearing my grumbling, my friend Larry (of The Daily Mirror) sent in this Google trends graph showing searches for “Tiger Woods” and “Afghanistan” during the last month:
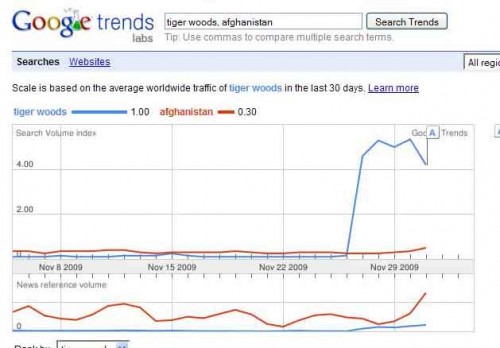
The top graph shows searches for those terms; the bottom graph shows the frequency of them in news stories distributed by Google News. What was interesting to me is that news coverage has actually been higher for Afghanistan, with the gap growing during the days following the Tiger Woods story, but searches have followed the opposite pattern, with the enormous spike in searches for Tiger Woods in the last few days. It’s possible that TV media outlets have covered the Tiger Woods issue more than print media, so that could show a different trend.
But from what we see here, it appears that public interest isn’t being driven solely by media coverage, and any increases in news stories about Tiger Woods may be a response to an appetite for more information. That doesn’t mean media coverage doesn’t play a large part in framing public discourse–after all, we wouldn’t even know about the Tiger Woods story if it didn’t get some initial media coverage–but media outlets don’t decide what to cover in a complete vacuum, with the ability to get the public interested in any story they report on.
UPDATE: Larry sent in this image that contrasts searches for those terms with searches for “porn”:
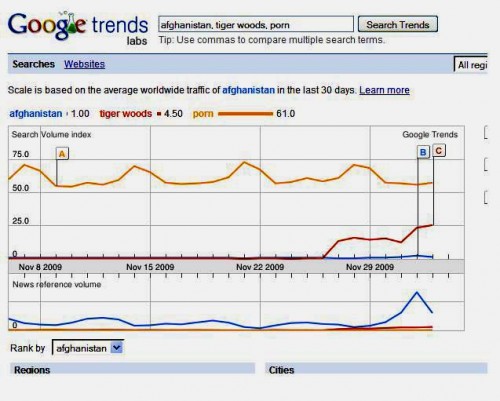
Sigh.
Also see our posts on CNN questioning whether Jon and Kate’s divorce was getting too much coverage, which missing children get media coverage, the media shape reality, and coverage of Obama and Clinton.





