Netflix made a big splash in “true crime” with its series Making a Murderer, chronicling the investigations and trials of Wisconsin man Steven Avery. Exonerated after 18 years in prison for sexual assault in 2003, Avery was arrested for a new crime—murder—in 2007. Public debate about the documentary revolves around whether Avery’s innocent, potential misconduct in the justice system, and the ethics and consequences of documentary “vigilante justice,” but there is little doubt Avery was wrongfully convicted the first time around, in 1985. Social science helps us understand the more systematic consequences of incarceration and exoneration that cultural phenomena like Making a Murderer, the Serial podcast, and even the upcoming miniseries “The People v. O.J. Simpson: American Crime Story” bring to our attention.
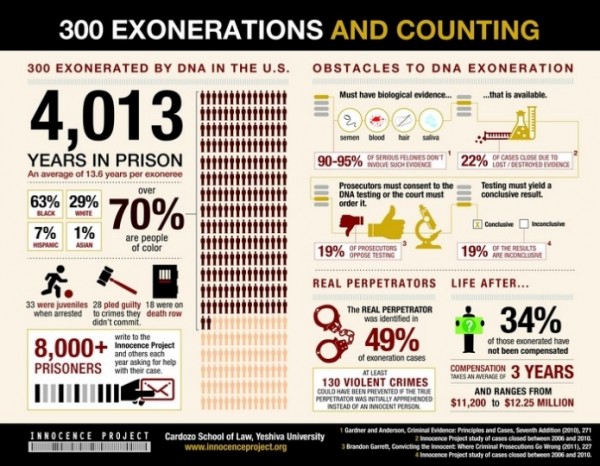
Pop culture tends to focus on errors, like witness misidentification and shoddy forensics, but those are not the only things that lead to wrongful convictions. Sociological research shows blacks and Hispanics are at a higher risk, and these groups are, in fact, overrepresented in samples of exonerees. Black exonerees suffer longer periods of incarceration between their conviction and exoneration than other groups. And exonerations often raise questions about the criminal justice system’s authority and legitimacy in the eyes of the public.
- Brandon Garrett. 2011. Convicting the Innocent. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Marvin Zalman, Matthew J. Larson, and Brad Smith. 2012. “Citizens’ Attitudes Toward Wrongful Convictions,” Criminal Justice Review 37(1): 51-69.
- Maeve Olney, and Scott Bonn. 2015. “An Exploratory Study of the Legal and Non-Legal Factors Associated With Exoneration for Wrongful Conviction: The Power of DNA Evidence,” Criminal Justice Policy Review 26(4): 400-420.
Exonerees, even those who aren’t in a media spotlight, face practical problems after they are released from prison. The stigma of having served time diminishes chances in the employment and housing markets, even for those who are exonerated. Like others experiencing reentry after incarceration, exonerees also face unmet needs with regard to physical, dental, and mental healthcare, as well as the myriad challenges of rebuilding social networks and reintegrating to everyday life.
- Devah Pager. 2003. “The Mark of a Criminal Record,” American Journal of Sociology 108(5): 937-975.
- Adina M. Thompson, Oscar R. Molina, and Lora M. Levett. 2011. “After Exoneration: An Investigation of Stigma and Wrongfully Convicted Persons,” Albany Law Review 75(3): 1373-1413.
- Kimberley A. Clow, and Amy-May Leach. 2015. “Stigma and Wrongful Conviction: All Exonerees are Not Perceived Equal,” Psychology, Crime & Law 21(2): 172-185.
- Saundra D. Westervelt and Kimberly J. Cook. 2012. Life after Death Row: Exonerees’ Search for Community and Identity. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.

Comments