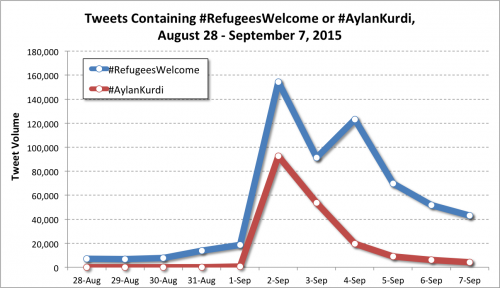
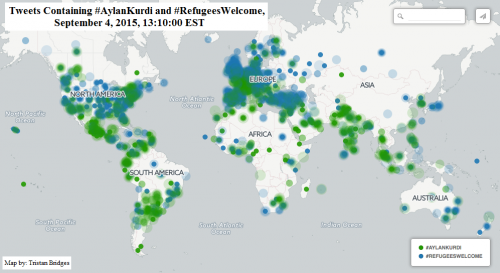
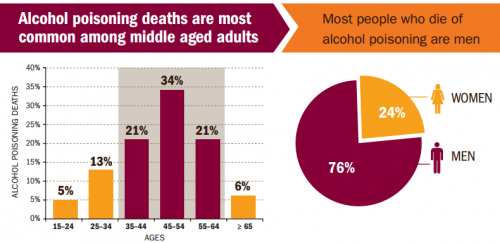
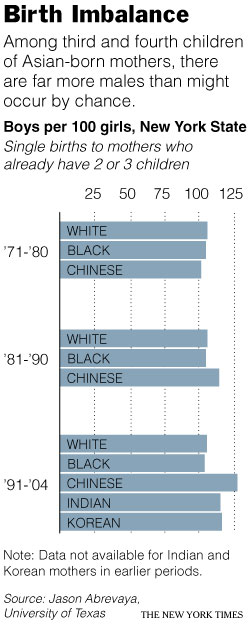
One explanation for Trump’s popularity on the political right is that supporters are attracted to him because they feel invisible to “establishment” candidates and Trump, as an “outsider” is going to “shake things up.” A survey of 3,037 Americans completed by RAND, weighted to match the US (citizen) population, suggests that there is something to this.
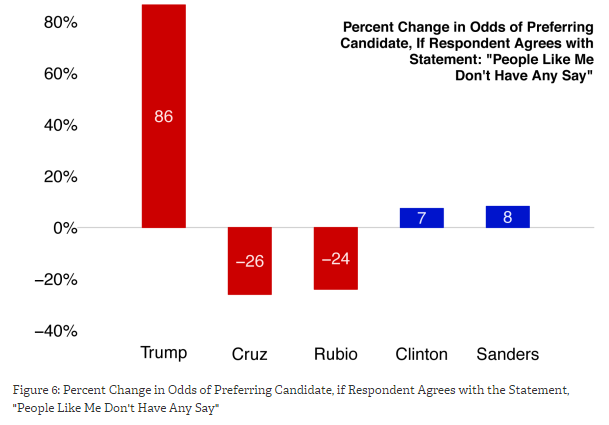
About six months ago, RAND asked respondents if they agreed with the statement “people like me don’t have any say about what the government does.” Responses among likely Democratic voters didn’t significantly correlate with support for either Sanders or Clinton and those among likely Republican voters didn’t significantly correlate with support for Rubio or Cruz, but responses did correlate dramatically with a preference for Trump. All other things being equal, people who “somewhat” or “strongly” agreed with the statement were 86% more likely to prefer Trump over other candidates.
“This increased preference for Trump,” RAND explains, “is over and beyond any preferences based on respondent gender, age, race/ethnicity, employment status, educational attainment, household income, attitudes towards Muslims, attitudes towards illegal immigrants, or attitudes towards Hispanics.”
Whatever else is driving Trump voters, a sense of disenfranchisement appears to be a powerful motivator.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.