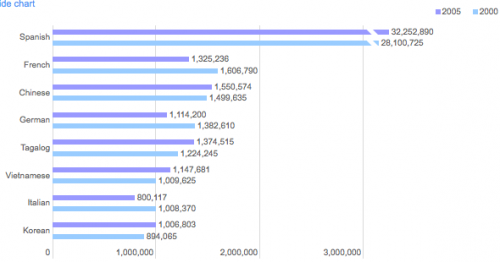
I was stuck by this image, which is being used by Environmental Defense as part of a “how you can stop global warming”-type promotion:

We see a cartoon anthropomorphized earth flexing its muscles happily while a tape measure is cinched around its quite unnaturally narrow waist. It’s an interesting collision between the longstanding metaphor of environmentalism as seeking the “health” of the environment, with the modern idea of obesity as iconic of poor health.
Unpacking the idea of ecological “health” as the goal of environmentalism is something I’ll mostly set aside here, except to note that it is a non-inevitable conceptualization (contrast the alternate framing of conservation/sustainability). The important thing to keep in mind is that the idea of ecological health involves conceptualizing the ecosystem, or even the entire planet, as a mega-organism — and in particular, a mega-human-body — for which health consists of an approximation to a particular ideal state. For a human body, health by this conception involves having all the normal parts (2 legs, both eyes, smooth skin, etc) functioning in the normal way.
What caught my eye about the ED ad was the change in the representation of what constitutes “health.” A quick Google image search on “sick earth” brings up lots of examples of the old way of representing health. We get lots of earths suffering from common cold and flu type symptoms — flushed, sweating, excreting mucus, and making use of thermometers and hot water pads.
The archetype of ill health here is infectious disease, an invasion by microbes that upsets the system’s functioning. The metaphorical parallels between viruses and pollution (including, in some cases, human beings) have been powerful for environmentalism.
But over the past few decades, we’ve acquired a new archetype for poor health: obesity. Being fat has become synonymous with being sick, and vice-versa. What I’m interested in here is not the scientific/medical question of how bad for you being fat really is (though I’ll admit to skepticism of the obesity panic on these grounds), but rather the sociological question of how obesity became the key trope in our discourse about health. Thus, a healthy earth can be easily represented as one that has slimmed down, because we all know that getting skinnier equals getting healthier. The metaphor is extended in the “Low Carbon Diet Guide” that the ad encourages you to download, which talks about how “counting carbs” should apply to carbon dioxide as well as carbohydrates. Interestingly, the guide sticks to energy conservation tips, thus both continuing environmentalists’ reluctance to address food habits as a contributor to climate change while mercifully avoiding blaming fat people for causing global warming by stuffing their faces.
An important element to the conceptualization of obestity as the archetype of ill health is the way it’s tied to ideas of personal responsibility. While genetics and social conditions play a huge role in determining who gets fat, our discourse about obesity promotes the idea that on the one hand you can control your own weight, and on the other fat people can be blamed for their condition. This is reflected in the content of ED’s Low Carbon Diet brochure, which is is a fairly standard compendium of personal behavioral changes that will make you a better, less-carbon-emitting, metaphorically slimmer person. Obviously this sort of thinking long predates the ecological-health-as-thinness metaphor, but there’s a synergy between them in terms of the emphasis on the small scope of personal control within a larger issue.
This is not the first, or most extreme, time environmentalists have tried to link up with the concern over obesity. But it was striking to me that the thin = healthy idea is so engrained that it can be used as a metaphor by causes outside of the public health field.
Stentor Danielson is a professor of Geography at Slippery Rock University in Pennsylvania. His research focuses on the relationship between humans and their environment. Specifically, he’s interested in how people understand the risk of wildfires. You can read more from Stentor at his blog, Debitage.