As a feminist sociologist, I couldn’t help but notice how reality competition shows like Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson’s The Titan Games and American Ninja Warrior can teach us a lot about how society understands physical strength in relation to gender.
Each of these shows takes a different approach to including women in strength competitions. On The Titan Games, women compete against women, while men compete against men. For each round, there is a man and woman winner. Given this format, men and women get equal screen time throughout the show. We see pairs of women and men compete in the same competitions like the Herculean Pull—the most intense one-on-one game of tug-of-war you have ever seen. This same-gender competition can actually minimize gender differences to the audience. Even if the pairs of women are slower than the pairs of men on some events, competition times are not shown to the television audience, so this difference is not highlighted.
In contrast, in the original rules of Ninja Warrior, everyone competed and the highest ranked individuals moved on to the next round. This quickly resulted in few women being represented beyond the first round (although some women were advanced as “wildcards” at the producers’ discretion). On Ninja Warrior, the audience sees the ranks of all the competitors, so it is very clear how the women do in comparison to the men (not so well, for the most part).
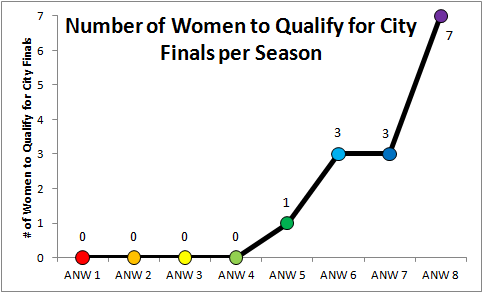
In 2017 (Season 9), the rules were modified to secure slots for women in later rounds. Interestingly, the rule change was in response to fan interest in seeing more women compete. Under the new rules, the top five women in qualifying rounds would advance and the top two women in the city finals would move on to national finals. This format results in some women moving forward based on performance in relation to all competitors and other women moving on based on their performance in relation to other women. For example, in Philadelphia qualifiers in Season 10, three women earned a spot in the city finals based on their overall rank in the competition and the next two highest-ranking women (although lower ranking than some men) also advanced to the City finals to attain the minimum of five women advancing.
From a feminist perspective, which approach is best for showing women’s strength in competition? Do you prioritize representation and visibility for women, giving equal time to men and women throughout the competition as in The Titan Games? Or do you prioritize eliminating gender as an organizing category, providing the opportunity for (some) women to be ranked higher than (some) men, and including the potential for participation of folks outside the gender binary as in the original Ninja Warrior rules? Or do you try to do both?
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/49994069/Screen_Shot_2016-06-30_at_10.05.58_AM.0.0.png)
This question matters because there are real stakes to the way we see strength in pop culture. The way we consider gender and physical strength affects many women, even those who are not elite athletes. For example, in my own research on the construction trades, many tradeswomen face assumptions and stereotypes about women’s physical ability that disadvantage them throughout their careers. It’s important to disrupt discourses about strength when they are leveraged to unnecessarily disadvantage women. Not all women (or men) have the physical ability to do construction work. But many do.
Strength competitions like these might seem to support stereotypes, but our scientific understanding of strength raises some troubling ideas about perceived “natural” differences of the body. Biological differences between men and women are not a clear as some would like to believe, this had led to problems with determining athletes’ genders for competition. In the US, large and muscular bodies are seen as desirable for men and problematic for women; this shapes who trains to complete in these types of competitions. If more women trained for strength-based competitions, we can assume the gap between men and women in these competitions would shrink, but not fully disappear. Similar trends have occurred in long distance running.
It’s difficult to imagine that anyone who has seen the women competitors on these shows could believe that women are not strong enough to do construction. Especially if you watched the first episode of The Titan Games and saw Tina Rivas, a sheet metal installer. And as she said about her work, “I am the only woman. So obviously that’s a little bit hard. But I can handle it.” Indeed.
Maura Kelly is an Associate Professor of Sociology at Portland State University. Her research and teaching interests include gender, sexualities, social inequality, work and occupations, and popular culture. Her current research is primarily focused on the experiences of women and people of color in the construction trades as well as policy and programs intended to increase the diversity of the construction trades workforce. She is the co-editor of the forthcoming book Feminist Research in Practice (Rowman & Littlefield 2019).

Comments 15
Brittany Lancaster — January 30, 2019
Really good article! Thank you for sharing.
Jenny — January 30, 2019
Really interesting article. Thanks to the Author.
Silent Ghost HD — February 2, 2019
If u want to watch movies and TV shows for free of cost and download them to watch later on, downlaod Silent Ghost HD from https://silentghosthd.com/
buat toko — February 22, 2019
sporty women are really cool :)
Agus Young | Digital Reviewer | caramembuatwebsiteku.com
vex 3 — July 20, 2020
The content is very practical, it gives me lots of new ideas, I like the content of your article very well. I hope you will have many new posts to share with readers.
fnaf
Luckrisia Bern — July 30, 2020
Thank you for the article! As a woman, I am always fighting for my rights and equality in the men's world. But sometimes men said that some things are just for them. I don't agree. I believe that we can play football, work hard or play games at different places like https://aussielowdepositcasino.com/house-of-pokies-casino/ easily.
lukat — August 23, 2020
A very meaningful event, I hope everything will go well happy wheels
bubble shooter — August 24, 2020
It's great to be here with everyone, I have a lot of knowledge from what you shared, to say thank you, the information and knowledge here helps me a lot.
mapquest driving directions
Jane Terry Fox — September 8, 2020
Show your gender power on any game that has a 200 welcome bonus that will help you start your gambling experience profitably! Good luck!
Lin — February 28, 2022
sgpslot Awesome write-up. I am a regular visitor of your web site and appreciate you taking the time to maintain the nice site. I will be a frequent visitor for a really long time.
asianbookie handicap
Kin — March 26, 2022
asianbookie bandar ust found your blog, I love nail art but have never asianbookie attempted to do anything like this myself!
Vell — March 30, 2022
Hey I really like your article and received many information from it!!
From Pragmatic Group
Alex reynolds — February 10, 2023
Even when I don't do much, Just keep going! quordle
navodayaresults5th.in — May 18, 2023
Navodayaresults5th strives to provide better service in various ways, and we do not sell or share your personal information with anyone else outside what you want to make public. We are very aware of email spam and navodayaresults5th.in make every effort to protect every email. Your letter may occasionally be seen by the public.respects its users in every manner, and we make every effort to keep them safe. In order to provide each and every user with superior service, information, and rich material, Navodayaresults5th
today quordle hint — June 21, 2023
Quordle has been available for purchase for a span of five months. Its successful outcome is the result of being released as an incomplete product. The daily game mode presents a fresh set of words for the Quordle puzzle every day at the stroke of midnight.
Today Quordle hint