In the U.S., we recognize two main party platforms: Republican and Democrat. Each party packages together specific positions on economic and social issues together into ideologies we call conservative and liberal. The desire for a small government, for example, is lumped with opposition to same sex marriage, while believing in a larger role for government is lumped together with support for abortion rights.
Do all people neatly fit into these two packages? And, if not, what are the consequences for electoral outcomes?
In the American Journal of Sociology, Delia Baldassarri and Amir Goldberg use 20 years of data (1984–2004) from the National Election Studies to show that many Americans have consistent and logical political ideas that don’t align with either major party’s ideological package. These voters, whom the authors call alternatives, are socially liberal and economically conservative (or vice versa).
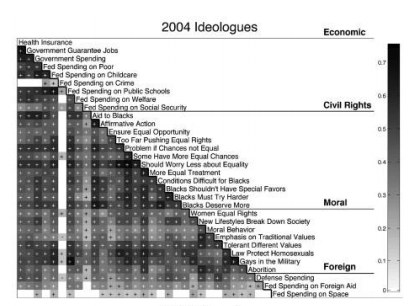
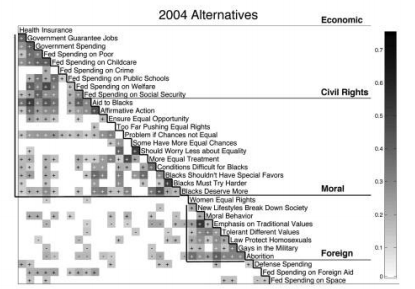
The images below show correlations between social and economic liberalism or social and economic conservativism. Strong correlations are dark and weak are light. The top image is of the opinions of ideologues — those who adhere pretty closely to the existing liberal and conservative packages — and the bottom images shows the opinions of alternatives.
In this data, being an alternatives is not just about being unfocused or uncommitted. Baldassarri and Goldberg show that their positions are logical, reasoned, consistent, and remain steady over time. The study makes it clear that the ties between economic and social issues made by the left and the right, which many people see as normal or natural, represent just two among the many belief systems that Americans actually hold.
When it comes to the ballot box, though, alternatives usually vote Republican. The authors write that the most conservative among the alternatives’ views tend to hold sway when it comes to picking a party. It appears that the salience of moral issues is not the primary reason for Republicans’ electoral success. Instead, for as-yet unknown reasons, alternative voters follow their more conservative leanings at the ballot, whether economic or social.
Cross-posted at The Reading List.
Jack Delehanty is a graduate student in sociology at the University of Minnesota. His work is about how social movement organizations can reframe dominant social narratives about inequality. In his dissertation, he explores how white Protestant-influenced discourses of poverty, family, and individual choice are being critically reshaped in the public sphere today.

Comments 3
Bill R — April 23, 2015
There are 5 categories of Americans as I see it today.
The Republican "base"
The Democratic "base"
Those who mindlessly mouth FOX New talking points
Those who mindlessly mouth Rachel Maddow talking points
The remaining 2/3rds of the country
A U.S. Parliament: Imagine All the Parties | Page Seven — May 12, 2015
[…] A Parliamentary System just ain’t going to happen in the U.S., but imagining it, illuminates the forces and fragments that shape American politics today. It also reminds us how inadequately the Left-Right, Liberal-Conservative, and Democrat-Republican dichotomies reflect the t…. […]