I happened upon a list of figures that display lots of information about who majors in science and engineering (S&E), all available at the NSF page on Women, Minorities, and Persons with Disabilities in Science and Engineering. All are for institutions in the U.S. only, as far as I can tell.
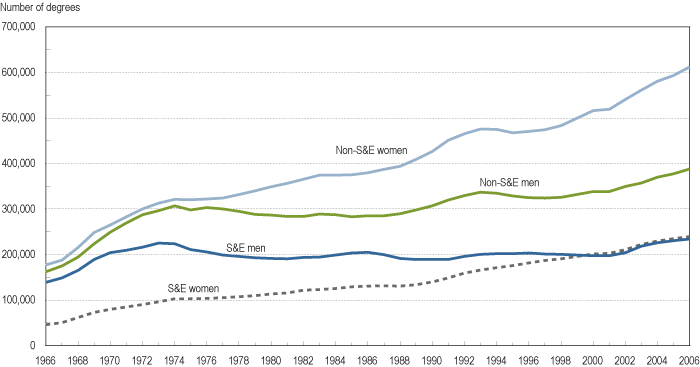
Here we see the number of bachelor’s degrees in S&E and non-S&E fields, by sex:
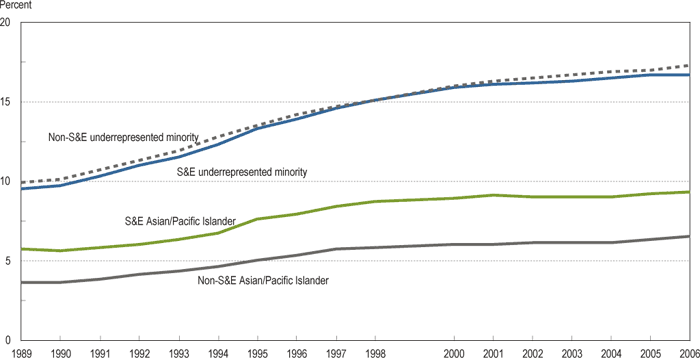
Percent of S&E and non-S&E bachelor’s degrees earned by racial minorities:
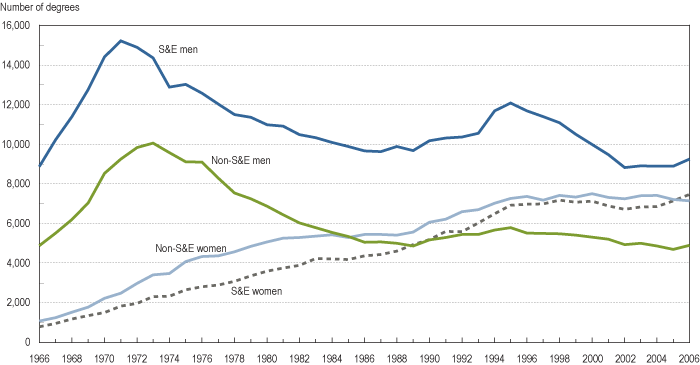
Number of doctoral degrees earned by sex:
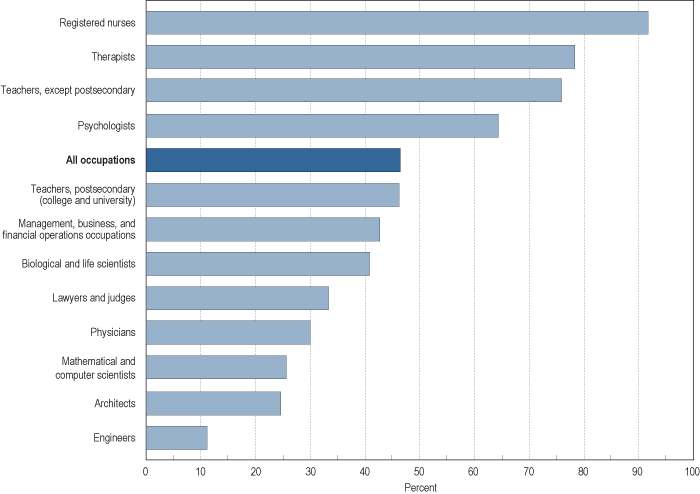
Percent of female workers in selected occupations in 2007:
Percent of S&E Ph.D.-holding employees at 4-year colleges and universities that are women:
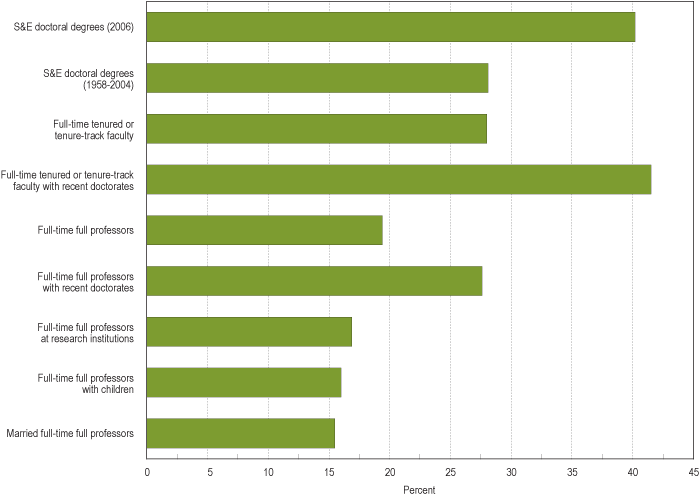
Notice that while women are pretty well represented among “full-time tenured or tenure-track faculty,” they make up barely 15% of “full-time full professors with children,” “married full-time full professors,” and “full-time full professors at research institutions.” Some of this may be a matter of time, in that because being promoted to full professor takes years, an increase in the number of women getting Ph.D.s in a particular field will take a while to show up as a similar increase in number of women as professors in that field, everything else being equal.
But everything else isn’t equal. Women, even highly-educated ones, still do the majority of childcare and housework, and are more likely than men to consider how potential jobs could conflict with future family responsibilities when they are deciding what type of career to choose. So the lower proportion of female full professors at research institutions is likely a combination of some old-school unfriendliness to women in some departments, but also of women opting out of those positions–that is, deciding that the time and energy required to get tenure in a science/engineering department at a research school would conflict too much with family life, so they pursue other career options (for instance, women make up a higher proportion of faculty at community colleges, which are often perceived as being easier to get tenure at, since you don’t necessarily have to do lots of publishing–though anyone who has ever taught 5 courses a semester may question the assumption that it takes less time and work to teach than to publish).
And of course some women try to combine a tenure-track job with their family responsibilities and find it difficult, and either leave academia voluntarily or are turned down for tenure because they have not published enough or are not see as adequately involved and committed. Because of inequalities in the family, men are less likely to face those situations, though certainly some do.
I wish the report had a graph for non-S&E faculty, although it might just depress me.
UPDATE: Commenter Sarah says,
Check out the report “Women in Science: Career Processes and Outcomes” by Yu Xie and Kimberlee A. Shauman. They find no evidence to support the hypothesis that women are under-represented at the tenure level due to a lag between getting PhDs and acquiring tenure track positions. In the life sciences, women have been getting PhDs at the same rate as men for many years now, but inequality persists at the tenure-track level. Xie and Shauman find that a variety of social factors are responsible for actively hindering women at the highest levels of academia.

Comments 13
Anonymous Coward — April 3, 2009
Just checking, but are those stats for woman the USA, or are they worldwide?
Gwen — April 3, 2009
I'm pretty sure it's just for the U.S.
Television Career — April 4, 2009
[...] Sociological Images ? WOMEN/MINORITY PH.D.S IN SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING By gwen about this blog. Media Inquiries. We are happy to speak with members of the media. Please inquire with Lisa Wade (lwade@oxy.edu) and Gwen Sharp (sharp.gwen@gmail.com). … Women, even highly-educated ones, still do the majority of childcare and housework, and are more likely than men to consider how potential jobs could conflict with future family responsibilities when they are deciding what type of career to choose. So the lower proportion of female full professors at … Comments for Sociological Images - http://thesocietypages.org/socimages/ [...]
Anonymous — April 4, 2009
I have been visiting PhD programs and out of the 6 I visited, one had a women's event where the female professors, grad students, and prospects could talk about women and academia. We chatted about the job search with two professionals and babies, mostly. The school was particularly proud of their support for women and family, but the entire time I kept thinking - don't men have families? Wouldn't the male prospects be interested in time off for taking care of babies as well? I thought it was nice they had a space for women to talk about these issues, but in doing so it still framed balancing life and work as a "women's issue" solely.
zoelouise — April 4, 2009
"Some of this may be a matter of time...an increase in the number of women getting Ph.D.s in a particular field will take a while to show up as a similar increase in number of women as professors in that field, everything else being equal."
It doesn't happen, though. In social, behavior, and life sciences, women have been 20-30% of the pipeline for 20-30 years, and still their numbers as tenured professores are about 15%.
"So the lower proportion of female full professors at research institutions is likely a combination of some old-school unfriendliness to women in some departments, but also of women opting out of those positions."
Please do not undersell bias. It is still out there and going strong. It may bot even be intentional in many cases. But to get ahead in science, one must be recognized by one's peers. Unfortunately, it is human nature, often unconsciously, to pick folks most like ourselves, and folks with whom we are comfortable. for men, who have these jobs, the easiest choice to join the ranks is another man. I got my tenure track job basically because the department chair has a high opinion of my PhD professor, not because of my natural talent.
If you haven't yet, please look at the report from the National Acadeimies of Science about this. If you go to this page; http://www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=11741
you can find the option to view the PDF executive summary of the report for free. I hope you will have a look at it. I don't think women "opt out" as often as the "give up".
sarah — April 4, 2009
Gwen--
Check out the report "Women in Science: Career Processes and Outcomes" by Yu Xie and Kimberlee A. Shauman. They find no evidence to support the hypothesis that women are under-represented at the tenure level due to a lag between getting PhDs and acquiring tenure track positions. In the life sciences, women have been getting PhDs at the same rate as men for many years now, but inequality persists at the tenure-track level. Xie and Shauman find that a variety of social factors are responsible for actively hindering women at the highest levels of academia.
http://www.amazon.com/Women-Science-Career-Processes-Outcomes/dp/0674018591/ref=sr_1_9?ie=UTF8&s=books&qid=1238889569&sr=8-9
Gwen Sharp, PhD — April 5, 2009
Sarah--thanks so much for the link, that's awesome.
Zoelouise--I definitely agree with you about bias. My statement about "opting out" was that in many cases women have been socialized into assuming they will have family responsibilities and sort of pre-"give up"--they (accurately) suspect that many types of workplaces/jobs aren't family-friendly, other people suggest other options (I know a woman who had a Dean CANDIDATE--a man NOT EVEN HIRED to oversee her area, just a candidate--ask her if she really thought being department Chair was a good idea for a woman with young children), and they end up "choosing" a career that is more compatible with family issues. But that "choosing" is highly socially structured, such that it follows a very predictable pattern in which women end up in lower-paid, less-prestigious positions because we continue to socialize women to often start sacrificing work to family life before they even have a family.
And the evidence is that men DON'T DO THIS. When they choose a career, they focus on how much money it makes, whether they think they'll like it, and so on. The fact that the job might be incompatible with an involved family life rarely enters into the equation for men, because they aren't socialized to worry about those types of concerns the way women are.
So my argument that some women "opt out" wasn't meant in a cavalier "oh, some women just choose to do other things," but rather that they often respond to socialization, social pressure, and their correct belief that many jobs don't yet acknowledge that workers have families and will penalize them for trying to balance the two.
zoelouise — April 5, 2009
Hi Gwen,
I get what you are saying, and agree about the pressured "opting out".
The data presented in your post are not just including women with children, right? And I don't think the bias is only against women with children by any means, nor or they the only ones who give up.
Thanks for this great blog; i find it very interesting.
Analiese’s Reading 4/7 | Quiche Moraine — April 7, 2009
[...] Sociological Images [...]
rajaram — April 8, 2009
Why would white people complain about being killed BY white people in video games? For every negative representation of white …
A Collection of Items on Gender and Science/Tech Topics » Sociological Images — August 13, 2009
[...] fiction, women, and war, Dell markets to women, info on percents of science/engineering Ph.D.s earned by women, PMS Tracker app, gendering robots, highspeed internet gets you your porn faster, better a [...]
Gendering Online Degree Programs » Sociological Images — January 26, 2010
[...] Facebook’s “neutral” icons, a vintage cartoon about what classes women enjoy, and who gets science and engineering degrees?. 47 Comments Tags: education, gender, gender: education, gender: work, work Guest [...]
The Gender Gap in Science, Tech, Engineering, and Math Occupations | Scientopia Guests' Blog — August 4, 2011
[...] (disproportionately women), because of a lack of female role models in STEM fields (including as college professors), or because of gender stereotyping about math or science aptitude (like this, or this if you [...]