
Head football coach Leslie Frazier of the Minnesota Vikings from 2010-2013. Image from Wikimedia Commons.
Racial disparities in hiring practices remain a constant issue in many workplaces. What’s more, these racialized biases are also influencing nonwhite employees’ likelihood of being promoted to leadership positions. This happens even in the National Football League, which has made a point of trying to facilitate the hiring of Black head coaches through the implementation of its famous “Rooney Rule.”
In 2003, the NFL adopted one of the most recognized diversity policies in the U.S., the Rooney Rule. Named after Dan Rooney, former owner of the Pittsburgh Steelers, the Rooney Rule requires that at least one person of color be interviewed for all open head coaching positions in the league. Ironically, Pittsburgh is one of the only places where the rule seems to have worked. Before the 2022 Super Bowl, two of the three Black NFL head coaches were fired, only leaving Mike Tomlin, the head coach of the Steelers since 2007. Although Tomlin is only one season short of being the NFL’s longest-tenured Black head coach, racial disparities in the NFL’s hiring practices still exist.
In their article “Racial Disparity in Leadership: Evidence of Valuative Bias in the Promotions of National Football League Coaches”, Christopher I. Rider and colleagues explore how racial disparities in leadership roles persist despite this policy. They provide an NFL context by using career history data for over 1,300 coaching staff of the NFL between 1985 and 2015 to investigate how, even when employees of color and white employees hold the same lower-ranked position and perform at equal rates, employees of color are less likely to progress toward a leadership role than their white counterparts (also known as valuative bias). They then analyze if the Rooney Rule was effective at reducing valuative bias in promoting lower-level coaches of color to leadership roles.
It remains puzzling that the NFL is made up of primarily Black football players yet white men hold the majority of leadership roles. This reason alone provides the researchers with an informative context for exploring racial disparities in leadership attainment. Additionally, it is easy to measure a coach’s performance by simply looking at the percentage of a team’s wins and the performance of the offense/defense that corresponds with the coach’s primary responsibility. Finally, as demonstrated in the chart below, the NFL coaching staff is great for analyzing promotions to leadership roles because there is a clear ranking among coaching positions.
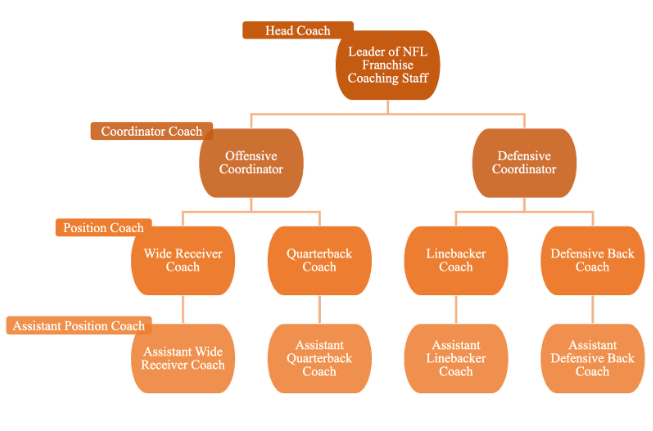
The researchers found that between 1985 and 2015, the Rooney Rule did increase the representation of head coaches of color right after it was implemented. However, when they include all variations of promotions across all coaching positions, they find a significant difference in the average promotion rate for coaches of color (4.5%) and white coaches (7.6%). They also find that when the lowest-level coaches are restricted (assistant position coaches), white coaches are 2.4 times more likely than coaches of color to be promoted. Although they find that white coaches are no more likely to be promoted to head coach than coaches of color in the same position, they find that nearly 80% of promotions to head coach are from coordinator positions. This means that even when a coach of color and a white coach played the same position in college, began their coaching career at the same level, and are currently coaching the same position, white coaches are nearly twice as likely to be promoted to coordinator positions than coaches of color, suggesting that Black coaches who are initially hired into lower-level coaching positions have a much lower chance in career advancement opportunities than their white counterparts.
Although the Rooney Rule increased the representation of coaches of color in all NFL coaching positions, racial disparities in career advancement opportunities across all levels persist in the NFL–especially in lower-level positions, where they are not subject to the Rooney Rule. In other words, valuative bias in promoting coaches of color persists despite the NFL’s high-profile attempt to close the racial gap in leadership positions. By using NFL hiring practices as a case study, the researchers show that organizations must address unequal promoting practices from lower-level positions to close racial disparities in leadership positions.

Comments