The Americans with Disabilities Act turned 25 years old last month. It was enacted by U.S. Congress with the goal of ensuring that people with disabilities had access to “reasonable accommodations” so that they could participate wholly in public life.
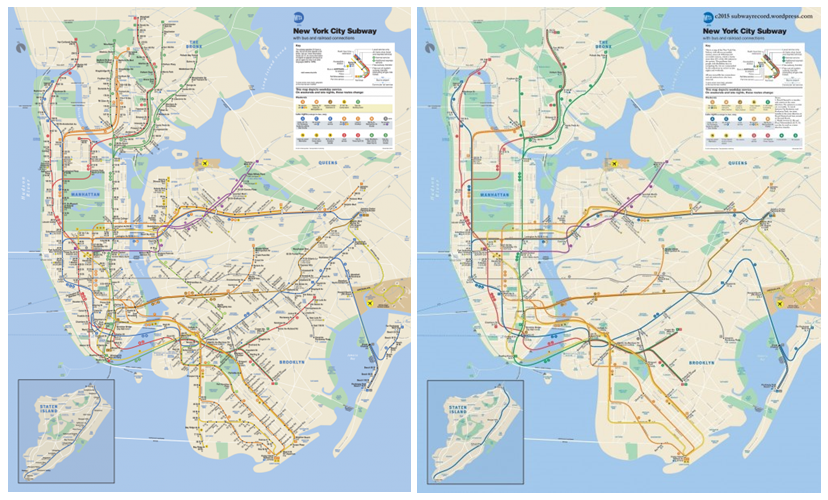
Did it work? Consider the New York City subway. SupraStructure featured these two maps. The one on the left is the NYC subway map of the 490 stations in the system; on the right is the accessible subway map, including only the 100 or so accessible stops:
“Essentially the NYC subway system is useless if you use a wheelchair,” writes Bad Cripple about the map. He continues:
Access to mass transportation for a person such as myself that uses a wheelchair is routinely difficult in the extreme. … Wheelchair lifts on buses are somehow broken or the drivers refuse to use the lift often claiming ignorance. Accessible taxis are as rare as diamonds in many cities. Subways in the vast majority of cities are grossly inaccessible. Rental car companies often do not have the car with hand controls rented weeks or days in advance. Shuttle buses at airports are not always accessible. Hotel shuttle buses are also typically not accessible.
He adds that discount travel is “pure folly” and that newer options like AirBnB and Uber seem to have no interest in accommodating people with disabilities. Not to mention the many places he travels that have broken lifts, elevators, and strangely non-accessible “accessible” accommodations.
As with much civil rights legislation, passing the ADA was just the first step in gaining equality. People have often had to sue piecemeal to get accessibility. A person identifies a restaurant without accessible bathrooms, for example, and begins legal proceedings to force the business to comply. Slowly, little by little — thanks to lawsuits, building codes, and other means — the world is becoming more accessible, though not nearly as quickly as people with disabilities need it to.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.