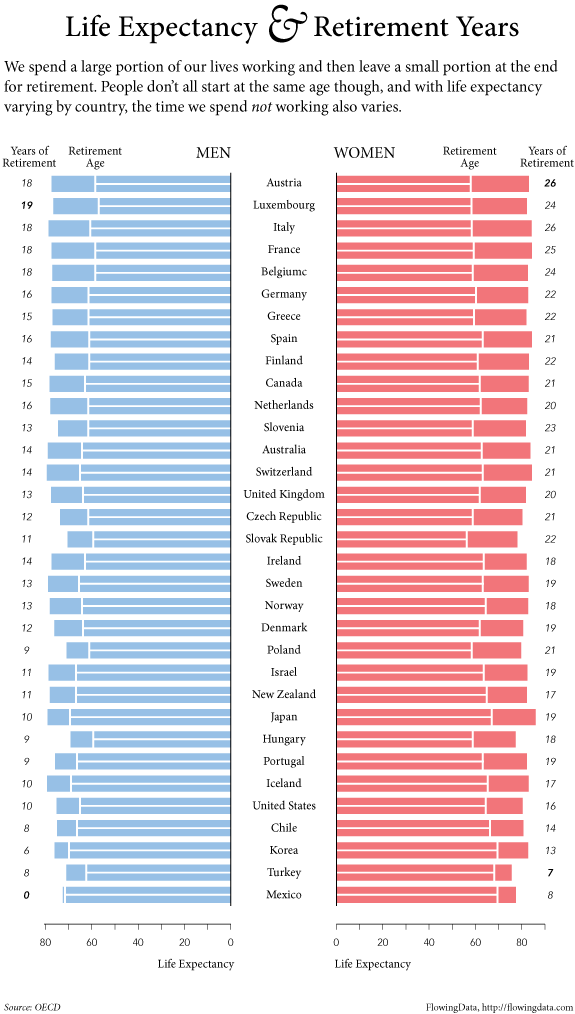
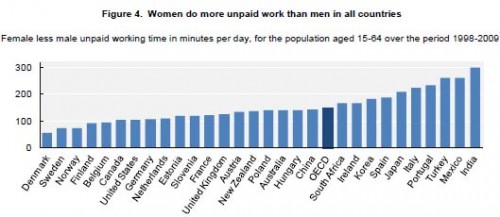
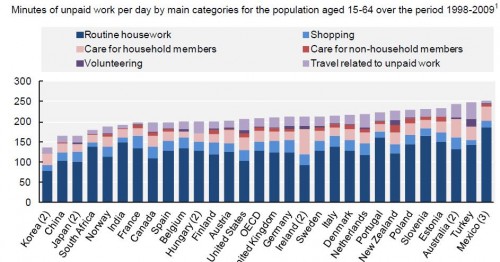
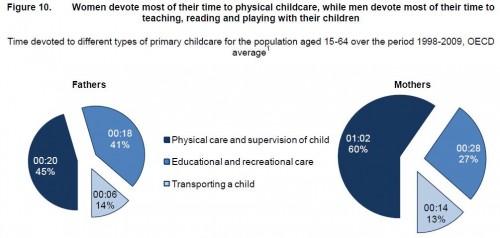
I’ve argued that the visual aids used in computer programs designed to help us learn new languages are ethnocentric, generic, and uninformative. Since then, I have been working on an alternative to these images, compiling a database of culturally organized images called the Culturally Authentic Pictorial Lexicon (CAPL).
What strikes me as both a student and a professor of language and culture is that the visual world differs so greatly across cultures and even minor differences are telling in how we organize and perceive our world. Color is one of the easiest ways to find differences in cultures. I have previously discussed the linguistic and cognitive differences of color, but now I want to show some simple examples of color in culture through analysis of various postal systems.
In China, the postal system uses a deep hunter green:
 (source)
(source)
In Japan, it is a bright red, much like England.
England:
 (source)
(source)
Japan:
 (source)
(source)
In Germany, it is a bright yellow (think DHL):
 (source)
(source)
In Russia, it is a lighter but similar shade of the deep postal blue in the U.S.
Russia:
 (source)
(source)
The U.S.:
 (source)
(source)
This example of postal systems is an easy way to illustrate how color becomes one of the central ways to communicate and, although the same message is shared across cultures, the path to that message varies through color.
Michael Shaughnessy is an Associate Professor of German and Chair of Modern Languages at Washington & Jefferson College. In addition to German language, literature, and culture, he has a professional interest in educational technology, especially the authenticity of multimedia imagery. His book German Pittsburgh (Arcadia Publishing) highlights the contributions of German speaking immigrants to our area.