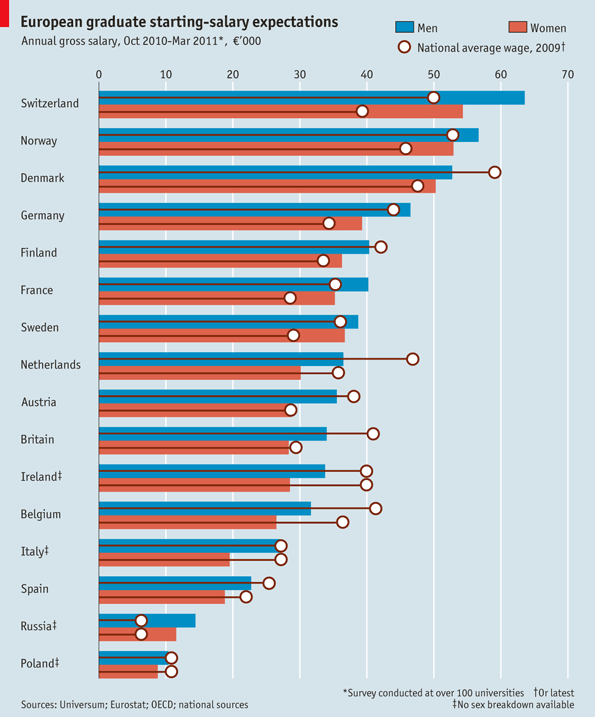
The following chart featured at The Economist illustrates that women in Europe expect to earn significantly less than men after graduating from university. (Of course, women’s expectations are represented in pink, and men’s in blue.) According to the study, European women attending the most prestigious universities expect to earn an average of 21 per cent less than their male counterparts.
Given that women actually do earn an average of 17.5 per cent less than men in the European Union, this difference in salary expectations might not seem shocking. What’s interesting, though, is the accompanying text that attempts to explain these disparities:
Women and men seem to differ in workplace and career aspirations, which may explain why salary expectations differ. Men generally placed more importance on being a leader or manager than women (34% of men versus 22% of women), and want jobs with high levels of responsibility (25% v 17%). Women, however want to work for a company with high corporate social responsibility and ethical standards; men are more interested in prestige (31% v 24%).
By neglecting to address how our social environment can contribute to reported differences in career aspirations, statements like these risk reinforcing gender stereotypes and naturalizing salary inequalities. Can we really assume that gendered salary disparities are due to women’s innately lower inclination to pursue high-paying career paths?
Research says: no, we can’t. As Cordelia Fine writes in her book Delusions of Gender, countless studies have demonstrated that social factors such as prevalent beliefs about gender differences and male-dominated work environments influence women’s responses to questions about their abilities and aspirations. For example, women exposed to media articles claiming that successful careers in entrepreneurship require typically “masculine” qualities were less likely to report an interest in becoming entrepreneurs. Women who knew that the test they were taking was measuring gender differences were more likely to report being highly empathic. Women were less interested in attending an engineers’ conference when it was advertised as male-dominated rather than gender-balanced.
Our perceptions of our abilities, identities, and sense of belonging are influenced by our social environment. If, as this graph shows, women attending the most prestigious universities in Europe aspire to different career paths than men, this fact can’t be taken for granted; addressing this inequality requires an analysis of its own.
Thanks to Dmitriy T.M. for sending in this graph!
Reference: Fine, C. (2010). Delusions of Gender: How Our Minds, Society, and Neurosexism Create Difference. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc.
——————————
Hayley Price has a background in sociology, international development studies, and education. She recently completed her Masters degree in Sociology and Equity Studies in Education at the University of Toronto.
If you would like to write a post for Sociological Images, please see our Guidelines for Guest Bloggers.

Comments 16
Catherine Holloway — September 22, 2011
I really don't think the economist is purposely using pink for women... those bars are actually red, they just look pinker due to the pastel blue background. They're just following their typical graph style, which means making the largest bars on the graph the darkest color.
Anonymous — September 22, 2011
Not to mention that we clearly reward people who contribute measurable collaborative value poorly in comparison to people who network, negotiate and wear suits well. We can not overlook those tasks which are more welcoming to women are also less likely to be well-paid.
Yrro Simyarin — September 22, 2011
It's very important to address the idea that culture causes women to have preference for lower paying fields. However, when addressing the causes of gender wage differences, it is relevant to note that those differences are caused by those preferences, rather than overt discrimination.
There are big steps toward equality in between "women earn less because a woman manager can't get a job", "women earn less because women are discouraged from becoming managers", and "women earn less because they don't want to become managers." Even if the (theoretical) ideal, I guess, would be for women to want to become managers at an equal rate and therefore earn equal pay.
Moreover, I think the post is reading a bit hard into the original article's statement about gender preferences. I saw nothing indicating that the authors assumed an innate preference in job attributes by one gender or another. I saw simply that they found an *expressed* preference difference between genders, the unknown cause of which was left undiscussed.
cee — September 22, 2011
There are some interesting causality issues in the statement
'Women were less interested in attending an engineers’ conference when it
was advertised as male-dominated rather than gender-balanced.'
Is that because they simply weren't interested in the sausage-party atmosphere of an un-balanced crowd, or did they see advertising as male-dominated as a signal that the conference would focus on topics that didn't interest them - like the aforementioned prestige and management instead of ethics and social responsibility?
In the first interpretation, gender is the direct cause of their lack of interest. In the second, gender is simply a visible side effect of the direct cause.
Etcetera — September 22, 2011
I don't see how neglecting to discuss the causes of gender differences in economic aspirations/expectations is supposed to suggest that the causes must be innate. Surely it suggests exactly nothing about the causes!
Anonymous — September 22, 2011
Ironically, perhaps I just found myself quoting this passage of Virginia Woolf to a student: "They too, the patriarchs, the professors, had endless difficulties, terrible drawbacks to contend with. Their education had been in some ways as faulty as my own. It had bred in them defects as great. True, they had money and power, but only at the cost of harbouring in their breasts an eagle, a vulture, forever tearing the liver out and plucking at the lungs - the instinct for possession, the rage for acquisition which drives them to desire other people's fields and good perpetually; to make frontiers and flags; battleships and poison gas; to offer up their own lives and their children's lives. Walk through the Admiralty Arch (I had reached that monument), or any other avenue given up to trophies and cannon, and reflect upon the kind of glory celebrated there. Or watch in the spring sunshine the stockbroker and the great barrister going indoors to make money and more money and more money when it is a fact that five hundred pounds a year will keep one alive in the sunshine."
This is a big crux in feminism: most feminists, most people who care deeply about living well and about family or anything non-monetary, believe--consciously or no--that the whole system, the whole structure is faulty, at best an eternal plucking at the liver and lungs for those who succeed, and a crushing steamroller for those who don't, and many end up feeling the best thing is to stay somewhere in the middle and hope for the best (even if that is never articulated).
So some of this poverty-mentality could come from a deep ambivalence about these foundations that women are just more likely to experience than men. This is not to say that all women are socialists; some socially conservative women look at this system and decide it's all men's work and if they can stay home and raise their family, that is God's plan. And some women, of course, do want to be in empowered positions. But many of us feel torn in two or three or four directions--both practically and philosophically.
Anonymous — September 23, 2011
A very important note: difference in prestige seeking does not account for the full difference. Only today I read an article from a local union, claiming that the salary gap between an industrial worker and a low status nurse (two professiosn of about equal demand for education and stress) is almost 300 euro each month. No matter the level of a job, it's clear that more women = lower pay.
Blabla — September 25, 2011
While doing my master, i saw countless "small" drawbacks for women in Switzerland ! From the "It's normal no girl wants to study informatic" to "Feminism ? Are you one of those ballkickers ????"
I've heard an unexpected professor tell his assistants on how not to frighten girls (Call them "Madam", don't talk to them as little girls, give them confidence !) and higly respected teachers saying about how the society went wrong since women have had rights... (with all the classroom nodding)
Alas, this remarks are everywhere, and all the time !
Another Gender Wage Comparison – Because People Don’t Like Facts. « Dead Wild Roses — September 25, 2011
[...] says: no, we can’t. [Go to Sociological Images for the rest of the story]. LD_AddCustomAttr("AdOpt", "1"); LD_AddCustomAttr("Origin", "other"); [...]
FarMcKon — September 26, 2011
I had to reread the article several times to understand your point. I think the paragraph starting ""By neglecting to address how our social environment can contribute.." is assuming a lot of knowledge, and assumes people read the article from the same view as you did. Expanding that section might make this a lot more readable to a lay-person without your konwledge, or angle.