 One of the most prominent theorists of the late 20th century, Michel Foucault, spent a career asking his history students to let go of the search for the beginning of an idea. “Origins” become hopelessly confused and muddled with time; they gain accretions that ultimately distort any pure search for the past on the terms of the past. Instead, his alternative was to focus on how these accretions distorted the continuity behind any idea. This method was called “genealogy,” by Nietzsche, and Foucault’s essay expanded on its use. Dawn Shepherd captured the significance of this lesson in a beautiful, single sentence: “Before we had ‘netflix and chill ;)’ we just had ‘netflix and chill.’”
One of the most prominent theorists of the late 20th century, Michel Foucault, spent a career asking his history students to let go of the search for the beginning of an idea. “Origins” become hopelessly confused and muddled with time; they gain accretions that ultimately distort any pure search for the past on the terms of the past. Instead, his alternative was to focus on how these accretions distorted the continuity behind any idea. This method was called “genealogy,” by Nietzsche, and Foucault’s essay expanded on its use. Dawn Shepherd captured the significance of this lesson in a beautiful, single sentence: “Before we had ‘netflix and chill ;)’ we just had ‘netflix and chill.’”
The temptation with something as recent as the web is to emphasize the web’s radical newness. Genealogy asks that we resist this demand and instead carefully think about the web’s continuity with structures far older than the web itself. While genealogy is not about the origins of “chill,” genealogy emphasizes the continuity of “chill.” Genealogy must build from an idea of what “chilling” entailed to say something about what “chill” means now.
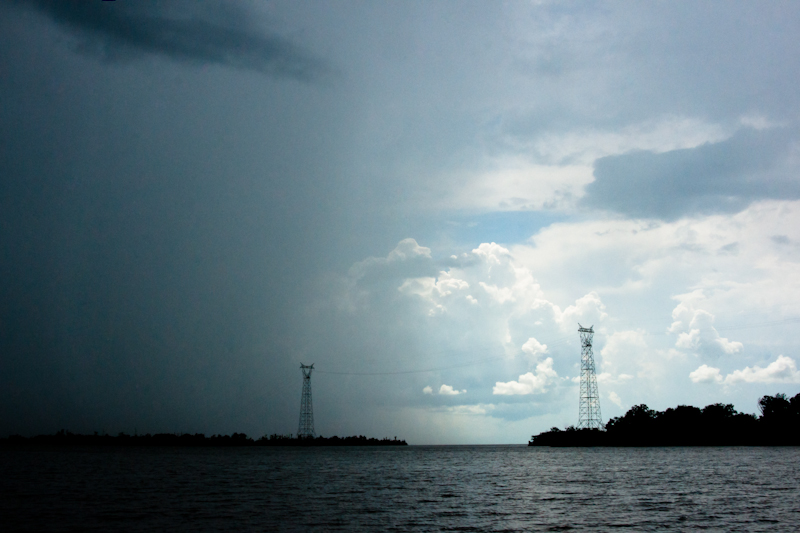
Conversations about these continuities animated many of the conversations at Theorizing the Web 2016. Both the keynote panels and regular sessions asked audiences to imagine the web as part of society, rather than outside of it. In the words of its founders, the original premise of the conference was “to understand the Web as part of this one reality, rather than as a virtual addition to the natural.”
more...