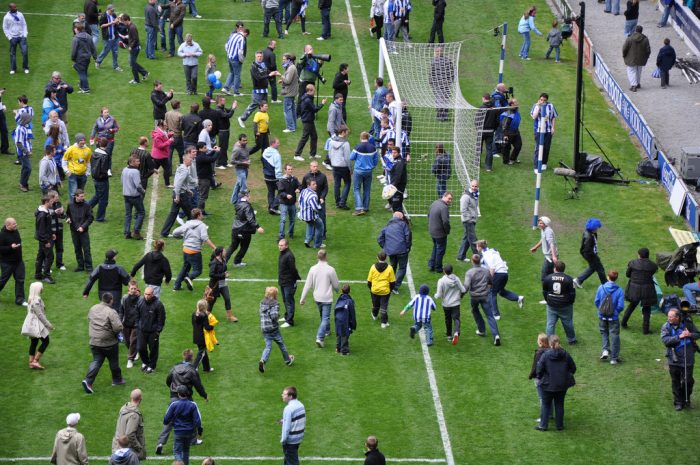
From the Super Bowl to March Madness, sporting celebrations raise questions about rioting every year. After their Super Bowl victory in February, Eagles fans took to the streets, looting and toppling light poles. A recent article in the Washington Post delves into the sociological and psychological explanations for why fans are often violent and destructive after a massive victory.
Sociologist Jerry M. Lewis has studied fan violence for decades, looking at the statistics on sport fan riots since the 1960s . He notes that fan violence in the United States usually consists of people destroying inanimate objects, while in other countries, and especially Europe, violence is directed toward opposing fan bases. Lewis explains that the sports rioting in the US almost always happens after a major victory rather than a loss, as a form of identification with the victorious team.
In the US, sports rioters tend to be young, white males. These passionate fans react excitedly to their favorite teams, reveling in victory and adrenaline which, in this case, results in destruction of city property. Lewis expands,
“They can’t throw a football 60 yards like the quarterback can, but they can throw a rock through the window or pull down a light pole. To them, it becomes their feat of strength and skill.”
Lewis provides an interesting contrast in the public perceptions of sports rioters compared to those who protest or riot because of social upheaval. Media and public understandings of riots seem to depend on who participates, and what is often described as a riot is defined along racial lines. Because of this, sports fans can celebrate while they cause destruction, but protesters often reap the disadvantages.