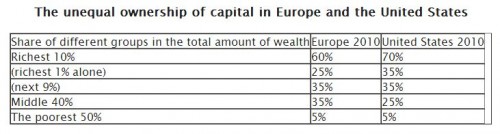
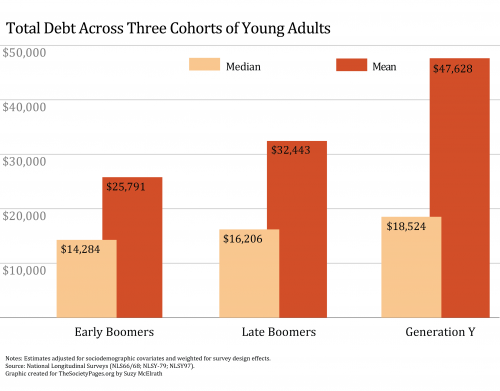
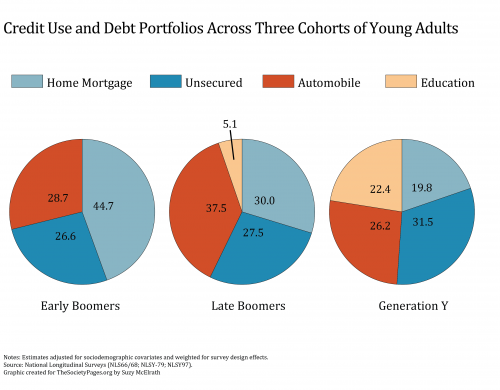
Economic policies often rest on assumptions about human motivation. Here’s Rep. Ryan (Republican of Wisconsin):
The left is making a big mistake here. What they’re offering people is a full stomach and an empty soul. People don’t just want a life of comfort. They want a life of dignity — of self-determination.
Fox News has been hitting the theme of “Entitlement Nation” lately. This Conservative case against things like Food Stamps, Medicare, welfare, unemployment benefits, etc rests on some easily understood principles of motivation and economics.
1. Giving money or things to a person creates dependency and saps the desire to work. That’s bad for the person and bad for the country.
2. A person working for money is good for the person and the country.
3. We want to encourage work.
4. We do not want to encourage dependency.
5. Taxing something discourages it.
Now that you’ve mastered these, here’s the test question:
1. According to Conservatives, which should be taxed more heavily:
a. money a person earns by working.
b. money a person receives without working, for example because someone else died and left it in their will.
If you said “b,” you’d better go back to Conservative class. A good Conservative believes that the money a person gets without working for it should not be taxed at all.
Not all such money, of course. Lottery tickets are bought disproportionately by lower-income people. If a person gets income by winning the PowerBall or some other lottery, the Federal government taxes the money as income. Conservatives do not object. But if a person gets income by winning the rich-parent lottery, Conservatives think he or she should not pay any taxes.
What Conservatives are saying to you is this: working for your money is not as good as instead of inheriting it. This message seems to contradict the principles listed above. But, as Jon Stewart recently pointed out, Conservatives apply those principles of economics and motivational psychology only to the poor, not to wealthy individuals or corporations.
Cross-posted at Montclair SocioBlog and the Huffington Post.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.