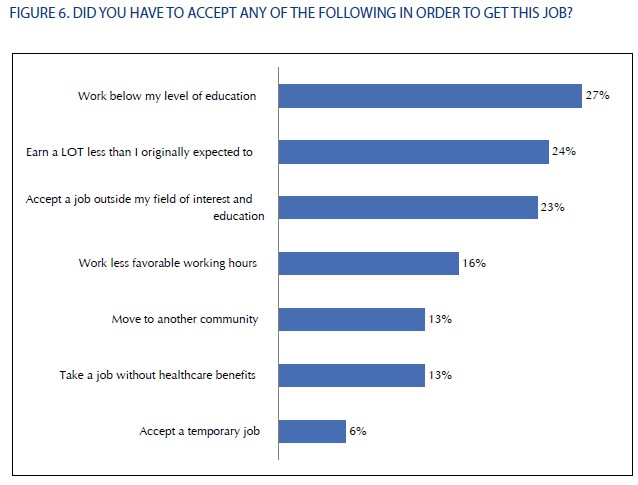
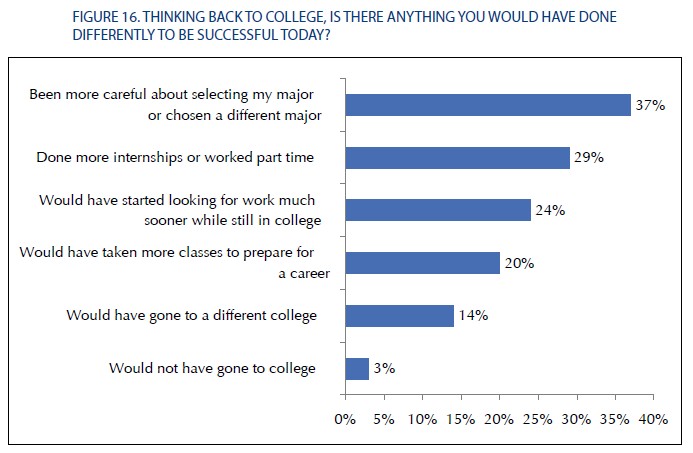
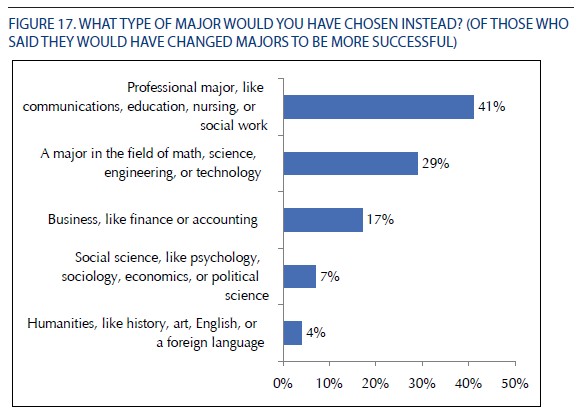
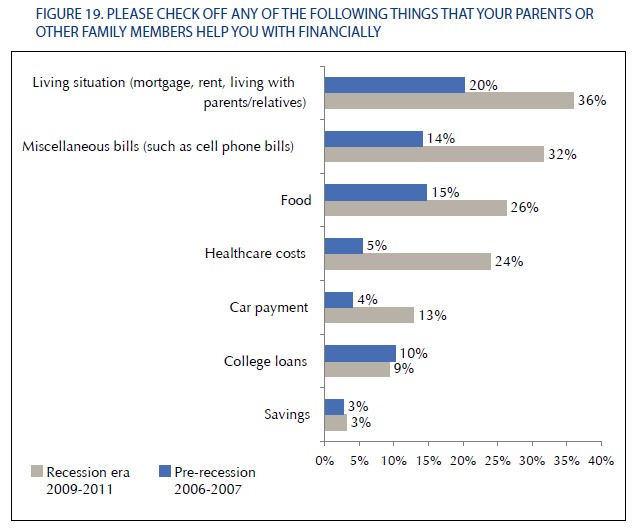
We seem to have a way of regularizing the pain felt by working people—worsening living conditions become little more than background noise to business as usual.
The situation for the unemployed is a case in point. We have a complex, but comparatively miserly, unemployment compensation system.
Workers are generally entitled to 26 weeks of unemployment benefits. However, there are two programs that potentially extend the benefit period for the unemployed. The first is the Emergency Unemployment Compensation (EUC) program, which was enacted in 2008 in response to the economic crisis. As the table below shows, the EUC offers workers in states with high rates of unemployment up to 53 additional weeks of benefits.

Workers who exhaust both their regular unemployment insurance and EUC benefits can receive additional support through the second program, the permanent federal-state Extended Benefits (EB) program. As the table above shows, that program offers a maximum of 20 extra weeks of benefits depending on state unemployment rate levels. However, there is an additional provision to the EB program that is now coming into play with negative consequences.
As Hanna Shaw, of the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, explains:
A state may offer additional weeks of UI benefits through EB if its unemployment rate reaches certain thresholds . . . and if this rate is at least 10 percent higher than it was in any of the three prior years. But unemployment rates have remained so elevated for so long that most states no longer meet this latter criterion (referred to as the “three-year lookback”).
Because of this lookback provision hundreds of thousands of unemployed workers are now losing benefits, not because conditions are improving but because they are not continuing to worsen. The table below highlights the 25 states that have been forced to stop providing EB benefits this year and the number of workers in each state that have been cut adrift as a result. Look at California–more than 95,000 workers have lost their benefits so far this year despite the fact that the state unemployment rate is almost 11 percent.

This is no accidental outcome. In fact, according to Shaw,
Policymakers could have addressed the “lookback” when they extended federal UI at the beginning of the year, but they didn’t. Instead, Congress not only allowed EB payments to fade out, but it also made changes that over the course of the year will reduce the number of weeks of benefits available in the temporary Emergency Unemployment Compensation (EUC) program, which provides up to 53 additional weeks to the long-term unemployed based on the unemployment rate in their state.
How serious is the long term unemployment problem? Check out the chart below. As it shows, the share of the labor force that is unemployed for more than 26 weeks is higher than at any point in the last six decades. Perhaps even more striking is the fact that 41.3 percent of the 12.5 million people who were unemployed in April 2012 had been looking for work for 27 weeks or longer.

In terms of the master narrative, this is just another of the necessary adjustments required to stabilize the “system;” no need for alarm. Makes you wonder about the aims of the system, doesn’t it?
Martin Hart-Landsberg is a professor of economics at Lewis and Clark College. You can follow him at Reports from the Economic Front.