Originally posted at Montclair Socioblog.
Does crime go up when cops, turtle-like, withdraw into their patrol cars, when they abandon “proactive policing” and respond only when called?
In New York we had the opportunity to test this with a natural experiment. Angry at the mayor, the NYPD drastically cut back on proactive policing starting in early December of 2014. The slowdown lasted through early January. This change in policing – less proactive, more reactive – gave researchers Christopher Sullivan and Zachary O’Keeffe an opportunity to look for an effect. (Fair warning: I do not know if their work has been published yet in any peer-reviewed journal.)
First, they confirmed that cops had indeed cut back on enforcing minor offenses. In the graphs below, the yellow shows the rate of enforcement in the previous year (July 2013 to July 2014) when New York cops were not quite so angry at the mayor. The orange line shows the next year. The cutback in enforcement is clear. The orange line dips drastically; the police really did stop making arrests for quality-of-life offenses.
.
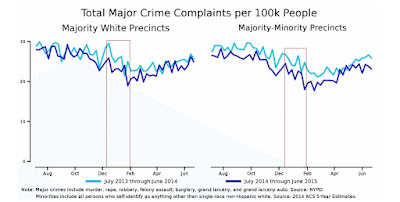
Note also that even after the big dip, enforcement levels for the rest of the year remained below those of the previous year, especially in non-White neighborhoods.Sullivan and O’Keeffe also looked at reported crime to see if the decreased enforcement had emboldened the bad guys. The dark blue line shows rates for the year that included the police cutback; the light blue line shows the previous year.
No effect. The crime rates in those winter weeks of reduced policing and after look very much like the crime rates of the year before.
It may be that a few weeks is not enough time for a change in policing to affect serious crime. Certainly, proponents of proactive policing would argue that what attracts predatory criminals to an area is not a low number of arrests but rather the overall sense that this is a place were bad behavior goes unrestrained. Changing the overall character of a neighborhood – for better or worse – takes more than a few weeks.
I have the impression that many people, when they think about crime, use a sort of cops-and-robbers model: cops prevent crime and catch criminals; the more active the cops, the less active the criminals. There may be some truth in that model but, if nothing else, the New York data shows that the connection between policing and crime is not so immediate or direct.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.


Comments 3
Disqus_eh_um_saco — April 12, 2017
But were all crimes normally reported during those weeks? If they were, would this scenario repeat itself in other places? Would it be the same had it happened in a different month? I'm not sure this experiment can show a definite answer.
From personal experience, living in Brazil, early this year the police in my state went on a total strike for a week and a half. Streets were empty and business were closed, there was looting, over a hundred people were murdered over those days, most of them before federal forces came in to pacify the state. It was mayhem. Just for reference, the IDH on my city is .8, the murder rate of the state is 147 for every 100 thousand.
Danial Sams — May 17, 2021
Cities like New York are considered very secure but I think the crime ration in such cities is very high. Print media and electronic media do not prefer to spread crime news about such major cities which us not a good thing at all. It is easy to visit this https://www.notsalmon.com/2021/04/26/how-meditation-improves-writing-skills-insights-tips/ site from New York to improve writing skills easily.