When sports stories wind up in the headlines and network news, something’s usually very wrong. The news biz, whether print or TV, usually keeps athletes confined in the sports section. So now we have the network anchors talking about Adrian Peterson leaving welts on the flesh of his son, age four, or showing us the video of Ray Rice coldcocking his fiancee in the elevator. Other NFL domestic violence stories, previously ignored (no superstar players, no video), are now mentioned since they fit the news theme.
These incidents all suggest that maybe football players are just violent people – men with a streak of violence in their dispositions. This personality trait that allows them to flourish on the field, but too often it gets them in trouble after they leave the stadium.
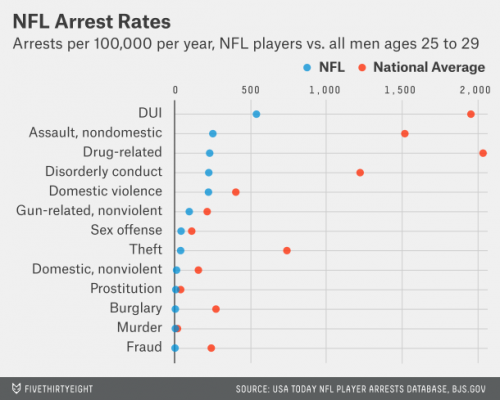
This is the kind of psychological “kinds of people” explanation that I ask students to avoid or at least question, and to question it with data. Conveniently, we have some data. USA Today has the entire NFL rap sheet, and it looks like a long one – more than 700 arrests since 2000. Nearly 100 arrests for assault, another 85 or so for domestic violence. And those are just the arrests. No doubt many battered wives or girlfriends and many bruised bodies in bars didn’t make it into these statistics. Are football players simply violent people – violent off the field as well as on?
Well, no. The largest category of arrests is drunk driving – potentially very harmful, but not what most people would call violent. And besides, NFL players are arrested at a lower rate than are their uncleated counterparts – men in their late twenties.
This suggests that the violence we see in the stadiums on Sunday is situational (perhaps like the piety and moral rectitude we encounter elsewhere on Sunday). The violence resides not in the players but in the game. On every down, players must be willing to use violence against another person. Few off-the-field situations call for violence, so we shouldn’t be surprised that these same men have a relatively low rate of arrest (low relative to other young men).
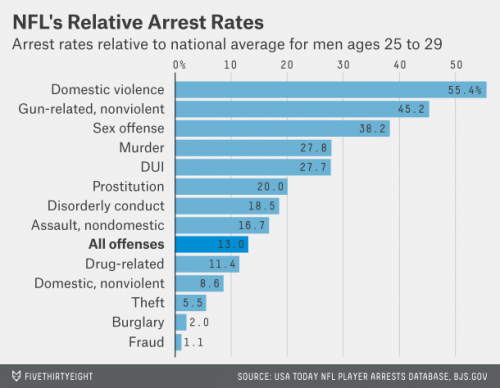
But let’s not discard the personal angle completely. If we look at arrests within the NFL, we see two things that suggest there might be something to this idea that violence, or at least a lack of restraint, might have an individual component as well. First, although NFL arrests are lower for all crimes, they are much, much lower for non-violent offenses like theft. But for domestic violence, the rate is closer that of non-footballers. The NFL rate for domestic violence is still substantially lower than the national average – 55 NFL arrests for every 100 among non-NFL men. But for theft, the ratio is one-tenth of that – 5.5 NFL arrests per 100 non-NFL. Also on the higher side are other offenses against a person (murder, sex offenses) and offenses that might indicate a careless attitude toward danger – DUI, guns.
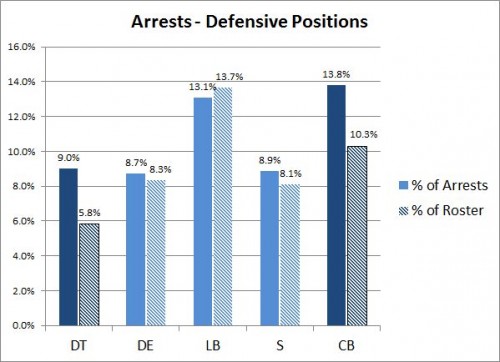
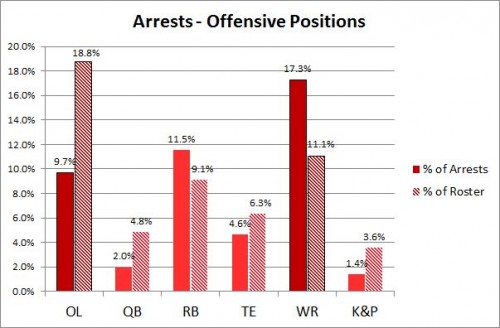
Second, some positions have a disproportionate number of offenders. The graphs below show the percent of all arrests accounted for by each position and also the percent the position represents of the total NFL roster. For example, cornerbacks make up about 10% of all players, but they accounted for about 14% of all arrests. (The difference is not huge, but it’s something; there would be a very slight overlap in the error bars if my version of Excel made it easy to include them.)
The positions disproportionately likely to be arrested are wide receivers and defensive tackles. Those most under-represented in arrests are the offensive linemen.
This fits with my own image of these positions. The wide-outs seem to have more than their share of free-spirits – players who care little for convention or rules. Some are just oddball amusing, like Chad Ochocinco formerly of the Bengals. Others are trouble and get traded from team to team despite their abilities, like Terrell Owens of the 49ers, Eagles, Cowboys, Bills, and Bengals.
As for the linemen, the arrest differential down in the trenches also might be expected. Back in the 1970s, a psychiatrist hired by the San Diego Chargers noted this difference on his first visit to the locker room. It wasn’t the players – the offensive and defensive lineman themselves looked about the same (huge, strong guys) – it was their lockers. They were a metaphor for on-the-field play. Defensive linemen charge, push, pull, slap – whatever they can do to knock over opponents, especially the one holding the ball. Their lockers were messy, clothes and equipment thrown about carelessly. Offensive lineman, by contrast, are more restricted. Even on a run play, their movements are carefully co-ordinated, almost choreographed. Watch a slo-mo of the offensive line on a sweep, and you’ll see legs moving in chorus-line unison. Correspondingly, their lockers were models of organization and restraint.
Maybe these same personal qualities prevail off the field as well. Those offensive lineman get arrested at a rate only half of what we would expect from their numbers in the NFL population. Arrests of defensive linemen and wide receivers are 50% more likely than their proportion on the rosters. That can’t be the entire explanation of course. Running counter to this “kinds of people” approach are the other hard-hitting defensive players – defensive ends and linebackers. According to the principle of violent people in violent positions, they should be over-represented in arrest figures just like the defensive tackles and cornerbacks. But they are not.
If this were a real article, a journal article, this final paragraph would be where the author calls for more data. But the trend in NFL arrests has been downward, and if fewer arrests means less data but also less domestic violence, that’s fine with me.
Cross-posted at Montclair SocioBlog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.
Comments 6
Yrro Simyarin — October 6, 2014
If you're interested in an area for further research, you might also consider the Wonderlic scores for the positions. Offensive line tends to have the highest. Higher intelligence has a correlation with lower criminality.
There's also the question of the degree to which a position is dependent on having statistically unlikely genetics versus a lifetime of preparation. A top end receiver or defensive end is going to be genetically special. Most athletes, no matter how well they train, will never be able to achieve their levels of athleticism. That may cause owners and coaches to overlook character flaws in their evaluations.
robert e — October 6, 2014
While titillating, some gaping holes in the data need to be filled for this analysis to be much more than that. One is the NON-arrest rate--how do NFL players compare to the average mook in being let off the hook for arrestable behavior and in not being cited for lower-level infractions?
Pro athletes enjoy a higher social standing than their non-pro athlete peers, even among police, even among victims of less-than-civil behavior. That status may lead to more tolerance, if not deference in the chain of formalities that lead to arrest records.
Unfortunately, that data is unlikely to exist. But it might be interesting to graph arrest data according to, say, distance from team's home city, or in-season vs off-season.
But there's another obvious path that could reasonably be pursued, and should be if the focus is on violent or unruly personalities vs behavior, and that is comparing NFL athletes with their social peers--professional athletes in different sports, and even other types of professions involving adrenaline and risk, physical or otherwise. How do they compare with NBA or NHL players? Tennis players? Boxers? Casts of prime-time shows? Stock brokers? Soldiers? High steel workers?
Bill R — October 6, 2014
Given the statistics on how football players compare to the general population I think a plausible argument can be made that the real story we are witnessing is the manufacturing of news stories by today's "journalists".
gunnar — October 10, 2014
You should compare these guys to non football players with comparable income. Hardky surprising that burglary is rare. ...
TomBradshaw — October 13, 2014
There is a reason most criminologists don't solely rely on arrest rates in their research. There are two major stats collected for crime arrest rates (i.e. police department official stats) and self-report data (gathered through surveys).
Not surprisingly arrest rates make it look like blacks and Hispanics are ultra criminals while whites law abiding citizens, but the surveys point out that all three races commit crimes at similar rates.
Maybe instead of quoting the NYTimes on sports and violence towards women (or crime in general) we can go ahead and use information from sociology or criminology journals or scholars (and not economists that happen to be writing for the NYTimes).
Jamie Patterson — October 17, 2014
I wonder what those NFL numbers would look like compared to the national average of their financial peers? Compare the NFL players to non professional athletes who are in the same tax bracket. I propose you would see a much larger disparity.