In survey questions, the result you get might depend on the choices you offer.
An article at The Atlantic explains “Why Americans All Believe They’re Middle Class.” But is that what we all believe? The author, Anat Shenker-Osorio, started with from these figure from a September 2012 Pew report.
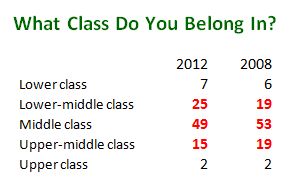
Only 8-9% of Americans put themselves in the lower or upper class. The other 91% say that they are “middle class,” some with a modifier (upper or lower), some without. Shenker-Osorio continues:
Researching how people’s unconscious assumptions affect their perception of economic issues, I explored the linguistic dynamics behind the term “middle class,” especially in comparison to other economic groupings.
That would be fine, except that both she and Pew made one huge omission. The Pew survey didn’t include “working class” as an option. Out of sight, out of unconscious assumptions.
Language and Surveys
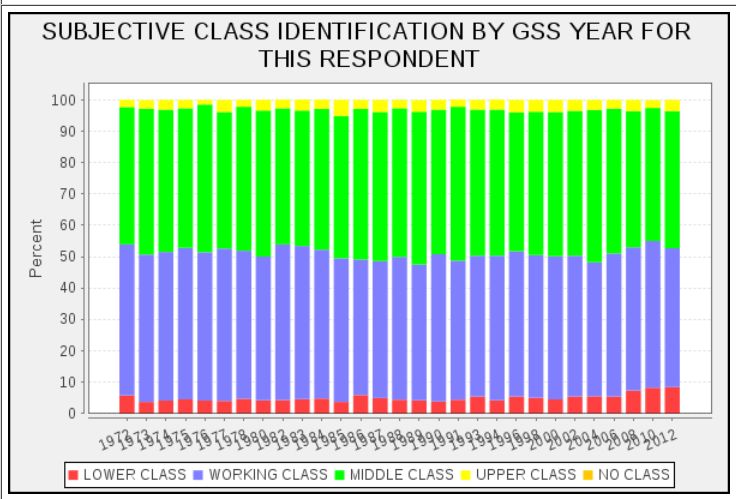
How big an omission is this? Since 1972, the GSS has asked a similar question to tap “subjective social class” (i.e., what class people think they are regardless of their objective circumstances). But the GSS includes “working” along with the upper, middle, and lower.
Like the Pew survey, the GSS finds less than 10% putting themselves in the upper or lower class. But for the past forty years, the remaining nine-tenths of the population have been evenly split between “working” and “middle.”
Shenker-Osorio’s linguistic analysis runs into other data conflicts. It’s not always easy to know what Americans mean by upper, lower, or middle class because:
Americans are relatively skittish about mentioning class. Contrasting databases of text from U.S. and UK sources, we find that Brits use “upper class” and “lower class” more readily; we prefer “wealthy” and “poor.”
But another database, the books in Google nGrams, shows something much different.
Contrasting Data
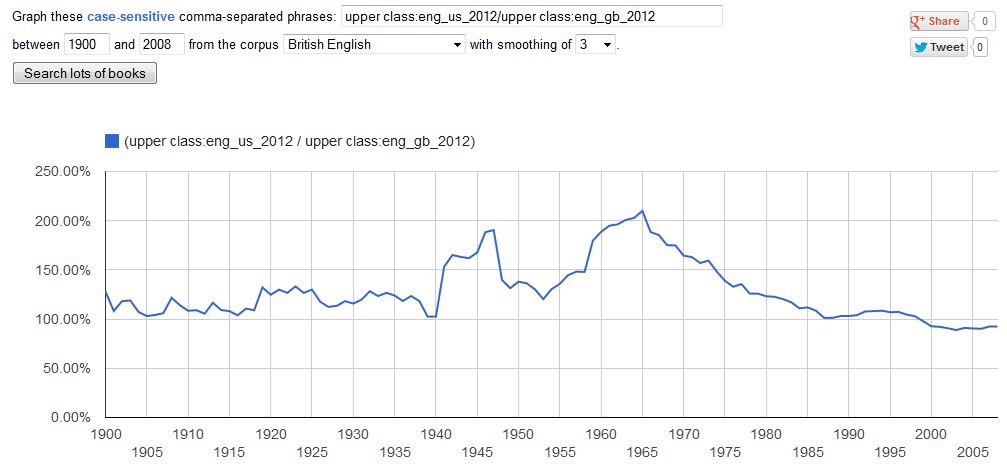
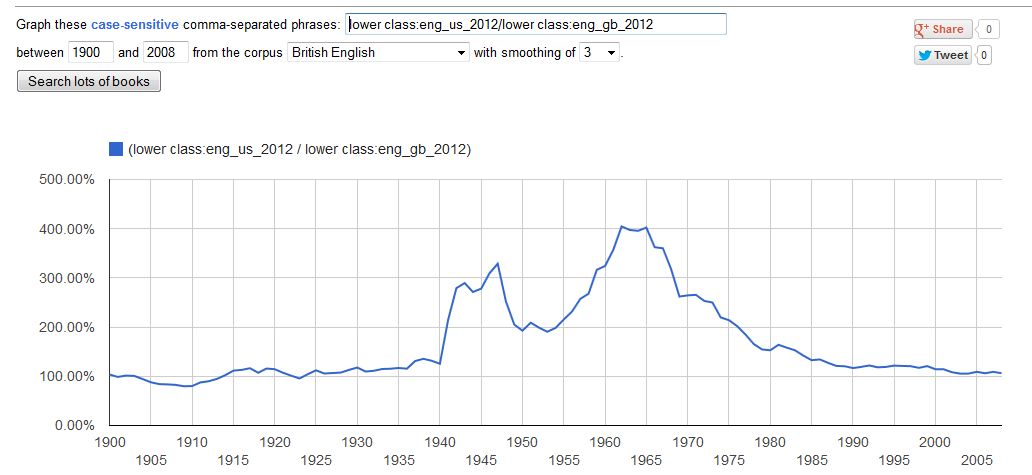
I constructed a ratio of American to British for the terms “upper class” and “lower class.” A ratio of more than 100% means that the term appeared more frequently in American books.
Ratio for “upper class”:
Ratio for “lower class”:
In general, since 1900, US and UK books used these terms at about the same frequency. But from 1955-1965, the US heard a crescendo in class talk. By 1965, US books mentioned the “lower class” four times as often as did UK books. Since then class talk in the US declined as rapidly as it had increased. (For some reason, Shenker-Osorio was unaware of my earlier post on these matters.)
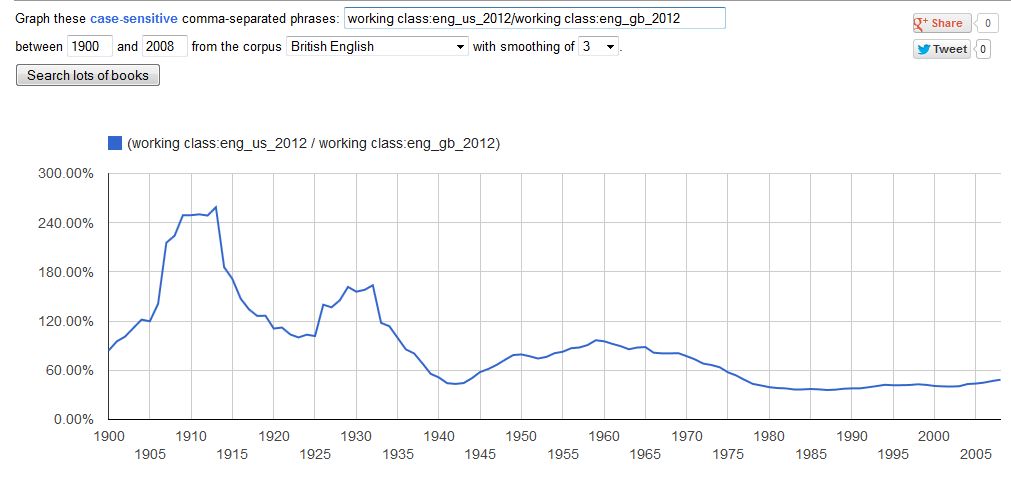
The real US-UK difference is in “working class,” a term that Shenker-Osorio ignores. Since 1935, it has appeared less frequently in US books. For the last 30 years, British books have mentioned the working class twice as often.
Ratio for “working class”:
It may be that the databases Shenker-Osorio used are better than nGrams, and it’s frustrating to find different sources of data pointing in different directions. More important, we still don’t know what people mean when they say they are middle class. Shenker-Osorio sees it as a category of exclusion. The images we have of upper and lower are so extreme as to apply to almost nobody.
Not finding popular depictions of wealth and poverty similar to our own lived experiences, we determine we must be whatever’s left over.
True perhaps, but it tells only what people think middle class is not. I’m not familiar with the research on subjective social class, but it seems that we still don’t know what people think “middle class” actually is. Nor do we know what they have in mind when they say they are working class. I have my own hunches, but I will leave them for a later post.
Cross-posted at Montclair SocioBlog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.
Comments 24
Larry Charles Wilson — August 11, 2013
I someone else tells you when you will work and how much you will be paid for that work you are a member of the working class. The concept of socio-economic classes is a way of allowing workers to think of themselves as something else, which can be important in a "democracy."
JohnFrancisBittrich — August 13, 2013
"What is the working class, fellow workers? The working class is anyone who has a boss and works for wages. Always remember, class is not defined by income level but by your relationship to the means of production. If you don’t own the tools of your production, if you don’t own your workplace, if all you’re doing is selling your labor energy to get a paycheck, it doesn’t matter if you’re a college professor or a ditch digger - you’re in the working class and better be proud of it. Why, the middle class is just a joke made up by the bosses to keep us fighting against each other." -Utah Phillips
Links 2 – 17/8/13 | Alastair's Adversaria — August 17, 2013
[...] The Language of Class – Contrasting Britain and [...]
Guestobsessed.blog — July 1, 2023
Checkers Drive-In Restaurant is one of the best restaurants in the United States. Really their food item and services are amazing. And the great part is that they conducting a guest experience survey to know customers opinion. For the compliment they offering a free sandwich for participating in this survey at GuestObsessed.Com Survey
SpotSurv Feedbacks — September 4, 2024
Great insights! I always appreciate posts like this.
Thank you and good luck.
TellCampero.com Cash Reward Survey