Presidential hopeful and U.S. Congressman Ron Paul (R-TX) made the news over the weekend arguing, among other things, that the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is unnecessary or, even worse, creates a kind of moral hazard in populations who come to depend on Federal relief efforts. In remarks reported Friday, Rep. Paul said that Hurricane Irene should be handled “like 1900,” the year that a large storm killed approximately 8,000 individuals in Galveston and a few thousand more onshore, when it struck the low-lying island and nearby small communities on the Texas coast.
It is certainly true that the Federal response to the destruction of Galveston was relatively minor. Systematic Federal management and provision of aid to individuals in disaster crystallized in response to the Mississippi River’s catastrophic flooding in 1927. In 1900, it was limited for the most part to President McKinley sending surplus Army tents to house the newly homeless residents of Galveston, and loaning some ships to transport relief goods.
The nation as a whole, on the other hand, quickly mobilized relief donation efforts through newspapers, state and city governments, and the dense network of fraternal organizations that characterized American civil society in 1900. The nation’s response was along the lines of the civic and political institutions of the time, with all that entailed.
 [Credit: Rosenberg Library’s Galveston and Texas History Center archives]
[Credit: Rosenberg Library’s Galveston and Texas History Center archives]
So, for instance, some of the citizens of Galveston who survived the storm were given liquor for their nerves and pressed into service at gunpoint by local authorities to clear dead and putrefying bodies from the wreckage; some were later partially compensated for their time with a small sum of money. Property owners, however, were exempted from mandatory clearing of debris and corpses.
Voluntary associations – often segregated by gender, race, ethnicity, and class – took care of their own members as best they could, but the broader distribution of relief supplies arriving from other areas was handled by committees of Galveston’s social and economic elites, based on their knowledge of their city’s political districts. Distribution efforts throughout the Texas coast were controversial enough that hearings were held by the Texas State Senate to investigate reports of improper relief distribution, some of which were borne out by testimony but none of which were pursued. Survivors’ letters suggest that in some cases the nicer relief goods – the distribution of which was handled by committees of Galveston’s social and economic elites on the basis of what they knew about their city’s political districts – went to the wealthier victims’ districts, when they weren’t re-routed by less wealthy and somewhat disgruntled Galvestonians tasked with actually lugging the supplies around the city. And Galveston’s African-American community was wholly shut out of the rebuilding process and denied a seat on the Central Relief Committee, despite efforts to secure a place in helping shape the collective destiny of the city. This is hardly surprising: poorer Americans tend to suffer disproportionately in most disasters, and are often left out of planning and rebuilding efforts.
There is much to be said for the response of Galveston’s Central Relief Committee. Under their leadership the city built the seawall that helps protect the city to this day and they initiated a series of successful municipal reforms that became widespread during the Progressive era. But we should not let unexamined nostalgia blind us to the realities of the situation in Galveston in the months after the 1900 storm.
Nor should we forget that the techniques that might have been more or less appropriate in 1900 were attuned to a society that has since changed quite a bit. It would be hard to imagine contemporary Americans pressed into service to clear bodies, barring a truly exceptional event. And despite its shortcomings, American culture is on the whole more egalitarian in 2005 than it was in 1900.
But the dense network of associations through which much assistance flowed to the city simply does not exist in the contemporary U.S. for a variety of reasons, none of which are reducible to the growth of the Federal government. Instead, Americans support each other in crises by way of donations to highly professionalized and technically adept disaster relief organizations like the Red Cross, and by maintaining government organizations charged with preparing for the worst disasters and catastrophes with their tax dollars.
This makes sense in part because contemporary cities and the economic arrangements which undergird them are much more complex beasts than they were in 1900. The following chart property damage and deaths caused by major disasters over the 20th century:
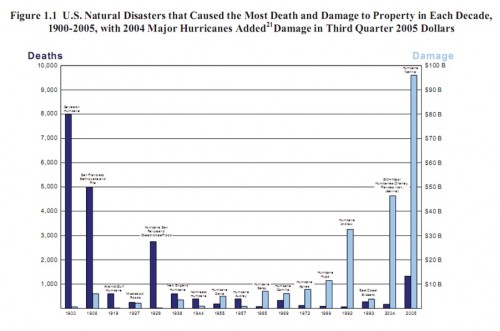 [Source: The Federal Response to Hurricane Katrina: Lessons Learned, p. 6.]
[Source: The Federal Response to Hurricane Katrina: Lessons Learned, p. 6.]
The overall trend is toward less lethal but much costlier disasters, which in turn causes significant disruptions to the ordinary functioning of local businesses and municipal governments that depend on tax revenues from those businesses. This necessitates more Federal involvement, as cities and state governments struggle to get their own houses in order, and to pay for the resources and technical know-how needed to rebuild infrastructure, modern dwellings, and businesses. As Lawrence Powell, a historian at Tulane University in New Orleans, asked of the influx of well-meaning volunteers in response to Katrina, “Can the methods of a nineteenth-century barn raising drag a twenty-first-century disaster area from the mud and the muck?”.
The 20th century history of Federal disaster policy can be described as a cycle of expansion and contraction. Increasingly complex disasters draw forth ad hoc solutions, which are then formalized and later institutionalized until they grow unwieldy and are periodically consolidated in efforts to provide more efficient, systematic, and effective services that are less prone to fraud or waste.
Small and big business, social movement organizations, academics, professionals, voluntary associations and NGOs have all helped shape the trajectory of that cycle, as when civil rights organizations successfully lobbied Congress and the Red Cross after Hurricane Camille in 1969 to provide a baseline of minimum assistance to hurricane victims, rather than the older policy that granted aid on the basis of pre-disaster assets (and which thus tended to favor wealthier victims on the basis that they had lost more than had the poor).
In recent decades, this has tended toward deregulation of coastal development in deference to free market ideals and a Congressional movement in the mid 1990s that sought to pay for disaster relief by, in large part, cutting social service programs that serve the poor. (See Ted Steinberg’s Acts of God for one good historical and political economic critique of U.S. disaster policy.)
How Federal disaster mitigation efforts can be more efficient, just, or effective is certainly a worthy conversation to hold. How best to arrange – and pay for – social relationships around economic, ecological, and technological risk is also an excellent topic for deliberation and debate. But to seriously argue that we should strive to make our disaster response regime more like that enjoyed by Americans in the early half of the twentieth century is, for lack of a better word, silly.
(For that matter, it’s hard to understand what Rep. Paul means by his call for more control by the States; the decision to request the involvement of the Federal government and FEMA already rests with the State governors, as per the Stafford Act.)
Former generations of Americans saw a patchwork of state government solutions as inadequate to managing modern disasters, particularly those that overwhelm municipal or State governments. They built Civil Defense agencies, the Office of Emergency Preparedness, and later FEMA in an effort to combine accountability and economies of scale and expertise, and to ensure that in times of disaster Americans could count on their Federal government to marshal tools and talent when local and State governments are overwhelmed and help is asked.
And as my own research shows, the efforts of these state organizations have long been understood by victims and outside observers alike as expressing and relying on bonds of fellow citizenship and civil solidarity. That in recent decades this legacy has been tarnished with cronyism and mismanagement from above says more about those political actors and the institutions of American electoral politics than it does about the inherent worth of Federal disaster management organizations.
——————————
Brady Potts is a lecturer in the Department of Sociology at the University of Southern California. His current research focuses on the history of public discourse and narratives around risk and hurricane disasters, and the role of civic culture in American disaster response.
If you would like to write a post for Sociological Images, please see our Guidelines for Guest Bloggers.

Comments 21
Umlud — August 29, 2011
There you go, putting facts to rhetoric, ruining a perfectly good campaign-tour "analysis" of the past done through ideologically rose-tinted glasses.
True: some things might have been (and that's a colossally generous dose of "might have been") better in those "good 'ole days" of 1900, but I'd rather not have to live there (and that's what Paul's proposal would mean: I would have to live in that world -- or a facsimile of it). I like my public works infrastructure (i.e., drinking water supply, waste water disposal, electricity) even though it takes time and money to repair them after a natural disaster; my federal disaster response system (i.e., FEMA) even though it draws on money that the federal government may not actually have on hand (because it's an emergency); my federal highways and federally managed air traffic systems bringing supplies in far faster than 1900; my federal agency (i.e., NOAA) that sends up satellites (thank you NASA) to track developing storms and deliver forecasts to state and local governments using government-funded meteorological research so that I have a chance to escape the brute force of an oncoming hurricane; the military reservists and coast guard that help with potential rescue needs; and the financial insurance mechanisms that ensure that I won't be rendered destitute (since private insurance is likely going to be so cost prohibitive as to make it moot, especially in areas that are more prone to hurricanes, such as coastal TX).
Yrro Simyarin — August 29, 2011
You know, it seems like most of your counter-examples are more directly criticisms of the general time period rather than of local civic action. I'm pretty sure most government officials at the time would have administered whiskey for nerves as well. And african americans weren't allowed anywhere near government.
Similarly, after working for so long to replace private charity and civic organization with public ones, it seems somewhat wrong to argue that private organization is not sufficient because it no longer exists...
I don't know that private charity *is* sufficient to handle the scope of problems we see in national disasters today. And obviously we have democratically decided that government is a better way to handle it - that doesn't mean that this decision is inherently right, though. We've democratically made all sorts of bad decisions.
But you can hardly blame the private structure for dealing with these issues for not existing, when a government organization has been created to fill that same void. It's like saying we need social security because people don't have private savings... when they *did* have private savings prior to having their paychecks docked to fund social security.
The comparison to 1900 is not to say "everything should be like 1900", but that if we examine what *did* work in 1900 and combine it with our modern culture and scientific knowledge, we might end up with something better than what we have today. Dismissing it as "silly" accomplishes nothing.
It's all probably a moot argument, though - the invention of radio, television, modern weather monitoring, and widespread transportation in the form of cars and busses probably has much more to do with the trend lines in that graph than do the choice of government or non-government solutions to disaster management.
Anonymous — August 29, 2011
What obstacles are in the way of private relief efforts? There's no reason why voluntary associations (which are still significantly segregated by ethnicity and class), can't arrange for and distribute supplies in whatever manner they want to.
It becomes a different discussion when we talk about how the federal government will pay for an unexpected expense like this: should we go deeper into debt, raise taxes, default, or allow the infrastructure to remain damaged and destroyed?
Larrycharleswilson — August 29, 2011
One thing is generally clear: once media attention shifts to the next "big thing," recovery efforts slow and many of the promised donations never arrive.
Anthony Tantillo — August 29, 2011
Actually, it's not "hard to understand what Rep. Paul means by his call for more control by the States" if you have ever taken a US History or US Political science class.
What Ron Paul has a hard on for is the Articles of Confederation. And before you go "RAH RAH RAH THE SOUTH IS RACIST" that has nothing to do with the Civil War.
Right now their are precedents of how governments. Federal -> State -> Local. Ron Paul would like it to be State -> Local -> Federal, with the Fed being at the bottom of the totem pole. Pretty common thought process for American Libertarians.
But glad that you wasted what I assume an entire hour writing this piece of garbage.
Links: X-treme Edition « Brass Tacks — August 31, 2011
[...] Brady Potts for Sociological Images: Should We Be “Like 1900″? Probably Not. [...]
Legal Firm’s Halloween Party Mocks Foreclosures | Environmental, Health and Safety News — November 1, 2011
[...] of costume themes Ann K., Dolores R., Tessa S., Zeynep A., and occasional guest blogger Brady Potts all sent in an opinion column that ran in the New York Times on Friday about a costume party at [...]
99vs1 — November 1, 2011
[...] of costume themes Ann K., Dolores R., Tessa S., Zeynep A., and occasional guest blogger Brady Potts all sent in an opinion column that ran in the New York Times on Friday about a costume party at [...]